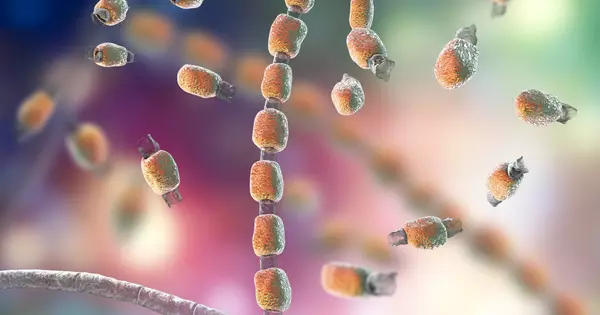
Fungal infections are a type of infections caused by fungi, which are a diverse group of microorganisms that can grow on various surfaces, including the skin, hair, and nails. Some common fungal infections include Athlete’s foot, Ringworm, Yeast infections, and Aspergillosis. Symptoms can vary but may include itching, redness, scaling, and discharge.
Fungal infections are caused by fungi, which are microorganisms that can cause various diseases. It is a fungi-caused disease. They can affect different parts of the body such as the skin, nails, hair, mouth, throat, lungs, and genital area. Some common fungal infections include Athlete’s foot, Candidiasis, Ringworm, Jock itch, Tinea versicolor, and Aspergillosis. Symptoms may include itching, redness, scaling, rashes, and thickened nails. Traditional classifications are based on the part of the body affected: superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet, and beard, and yeast infections, such as pityriasis versicolor, are examples of superficial fungal infections.
Treatment of fungal infections usually involves antifungal medications, which can be applied topically or taken orally, depending on the severity and location of the infection. Treatment usually involves antifungal medications applied topically or taken orally, depending on the severity and type of infection. Good hygiene practices and maintaining a healthy immune system can help prevent fungal infections.
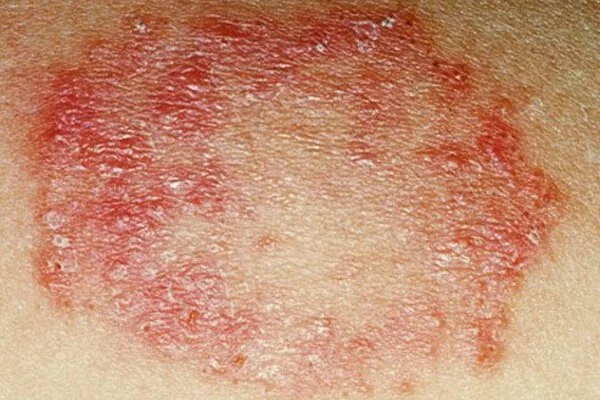
Signs and symptoms, microscopy, culture, and sometimes a biopsy and the use of medical imaging are used to make a diagnosis. Some superficial fungal infections of the skin can resemble other skin conditions such as eczema and lichen planus. Depending on the specific infection and its extent, antifungal medications are typically used in the form of a cream, or by mouth or injection. Some cases necessitate surgical removal of infected tissue.
Fungal infections are widespread and common, affecting over one billion people each year. In 2020, an estimated 1.7 million people died as a result of fungal disease. Several are overlooked, such as sporotrichosis, chromoblastomycosis, and mycetoma.
Fungal infections are more common in people who have weakened immune systems. This includes people suffering from illnesses such as HIV/AIDS, as well as those taking medications such as steroids or cancer treatments. Diabetes patients are also prone to fungal infections. Groups at risk include the very young and the very old. Individuals taking antibiotics are more likely to develop fungal infections. Children with weakened immune systems (such as cancer patients) are vulnerable to invasive fungal infections.