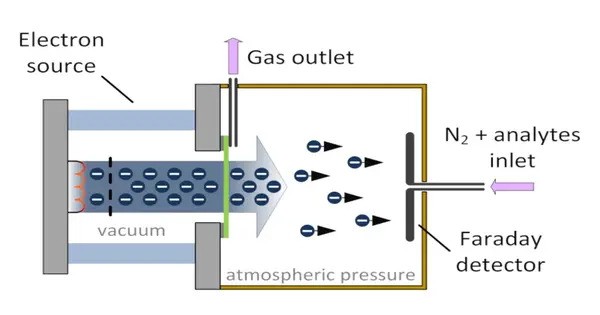
An electron capture detector (ECD) is a device that detects atoms and molecules in gas by attaching electrons using electron capture ionization. It is a very sensitive analytical equipment used in gas chromatography (GC) to detect trace levels of electron-absorbing substances, notably those containing halogens, nitro groups, or certain other electronegative functional groups.
It works on the electron capture concept, which involves capturing electrons from sample molecules in a radioactive source, often a nickel-63 or tritium foil. James Lovelock designed the gadget in 1957, and it is used in gas chromatography to detect small levels of chemical substances in samples.
Here’s a brief overview of how an Electron Capture Detector works:
- Sample Injection: The sample is fed into the gas chromatograph, where it is vaporized and transported by an inert gas (the mobile phase) across a chromatographic column.
- Column Separation: Inside the column, different sample components interact differently with the stationary phase, causing them to segregate according to their chemical properties. The separation enables the identification and quantification of specific chemicals in the sample.
- Detection: The separated components exit the column and enter the detector. An ECD detector contains a radioactive source (often nickel-63 or tritium) that emits beta particles (high-energy electrons).
- Electron Capture: Electronegative compounds in the sample, such as halogenated compounds or nitro compounds, can capture electrons from the beta particles emitted by the radioactive source. This process reduces the current flowing through the detector.
- Signal Generation: The amount of electrons captured is proportional to the concentration of analyte in the sample. As the caught electrons reduce current flow, a signal is produced. This signal is amplified and recorded, often resulting in a chromatogram with peaks representing distinct substances in the sample.
The Electron Capture Detector is especially effective for testing environmental samples, such as air and water, for the presence of contaminants like pesticides, PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls), and other halogenated chemicals. Its great sensitivity allows it to detect these substances at extremely low quantities, making it an essential tool for environmental monitoring and regulatory compliance. However, due to the radioactive source, sufficient precautions must be taken when handling and disposing of ECD detectors.