Earthquakes are well known for the damage and destruction they leave behind. But what is an earthquake? In this video lesson you will learn about what causes earthquakes and the various components involved in these powerful natural disasters.
Causes of Earthquakes
Earthquakes are usually caused when rock underground suddenly breaks along a fault. This sudden release of energy causes the seismic waves that make the ground shake. When two blocks of rock or two plates are rubbing against each other, they stick a little. They don’t just slide smoothly; the rocks catch on each other. The rocks are still pushing against each other, but not moving. After a while, the rocks break because of all the pressure that’s built up. When the rocks break, the earthquake occurs.
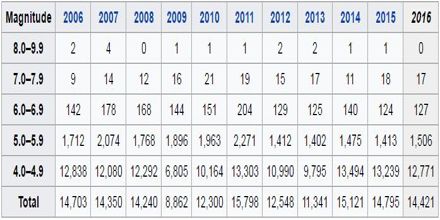
Number of earthquakes worldwide for last ten years,
More than 200,000 earthquakes are recorded each year, though it is estimated that several million occur globally. Many of these go undetected because their magnitude is small or they occur in areas which are not closely monitored. Most seismic events (earthquakes) are very minor, and do not cause any damage – they may not even be felt by the local population. Others cause devastation, much of it due to collapsing buildings.
Number of earthquakes worldwide for last ten years,
How do you predict an earthquake?
However, there are still some ways of monitoring the chances of an earthquake:
- Laser beams can be used to detect plate movement.
- A seismometer is used to pick up the vibrations in the Earth’s crust. An increase in vibrations may indicate a possible earthquake.
- Radon gas escapes from cracks in the Earth’s crust.
Scientists have tried lots of different ways of predicting earthquakes, but none have been successful. They have a pretty good idea of where an earthquake is most likely to hit, but they still can’t tell exactly when it will happen. Most earthquakes result from the sudden release of stress in the earth’s crust, which has built up gradually due to tectonic movement, usually along an existing geological fault.
Some have suggested that other factors such as increased levels of radon, changes in the water table, variation in the electrical properties of rock or the behavior of animals may be diagnostic precursors. These have been the subject of research over several decades, and none has been found to be a good indicator, as they can all occur without being followed by an earthquake.
Some worst Earthquake
Nepal Earthquake (between Kathmandu and the city of Pokhara)
A 7.8 magnitude earthquake struck Nepal in an area between the capital, Kathmandu, and the city of Pokhara on Saturday April 25, 2015 with what has been described as a force equaling that of 20 thermonuclear weapons. The devastation claimed the lives of at least 5,000 people while injuring 10,000 more with authorities warning that casualty numbers could rise. The devastating quake also destroyed major monuments such as the Dharahara tower, temples and world heritage sites near Kathmandu.

Izmit, Turkey
This was a 7.9-magnitude earthquake that struck northern Turkey on August 17, 1990, which lasted for only 3.7 seconds. The city of Izmit was very badly damaged and had a death toll of 17,127 and 43, 959 injured though other sources suggested that the actual figure for fatalities may be closer to 45,000 with a similar number of injured. Another report from September 1999 showed that the earthquake had destroyed 120,000 poorly-engineered houses, heavily damaged 50,000 houses; caused 2,000 buildings to collapse while 4,000 other buildings left severely damaged, and made more than 300,000 people homeless.

Rudbar, Iran
This disastrous event happened on June 21, 1990 and caused widespread damage within 100 kilometers of the epicenter’s radius near the city of Rashi, and about 200 kilometer northwest of Tehran. It destroyed 700 villages across the cities of Rudbar, Manjiil, and Lushan and cost $200,000,000 in damages, including 40,000 fatalities, 60,000 injured and 500,000 people homeless.

Kashmir, Pakistan
The October 8, 2005 Kashmir, Pakistan was visited by an earthquake with a moment magnitude of 7.6.The disaster had a death toll of 85,000 and more than 69,000 were injured. Considered to be smaller in size than the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, it affected countries in surrounding regions with 14,000 deaths in Jammu and tremors felt in Taijikistan and western China. It also cost a staggering $5.4 billion in aids from all around the world.

Sichuan, China
The Great Sichuan Earthquake occurred on May 8, 2008 with a magnitude that measured 8.0 and 7.9. It was so great that it was felt in nearby countries and as far away as Beijing and Shanghai where buildings swayed with tremors. Official figures for the damages include 69,197 deaths with 68,636 in Sichuan province, 374,176 injured and 18,222 missing. This was considered as the deadliest earthquake to hit China after the 1976 Tangshan earthquake, as it left 4.8 million to 15 million people homeless. The Chinese government is appropriating 1 trillion Yuan or $146.5 billion to rebuild areas ravaged by the great quake.

Safety Tips
Earthquakes are a common occurrence, rumbling below Earth’s surface thousands of times every day. But major earthquakes are less common. Here are some things to do to prepare for an earthquake and what to do once the ground starts shaking.
- Have an earthquake readiness plan.
- Consult a professional to learn how to make your home sturdier, such as bolting bookcases to wall studs, installing strong latches on cupboards, and strapping the water heater to wall studs.
- Locate a place in each room of the house that you can go to in case of an earthquake. It should be a spot where nothing is likely to fall on you.
- Keep a supply of canned food, an up-to-date first aid kit, 3 gallons (11.4 liters) of water per person, dust masks and goggles, and a working battery-operated radio and flashlights.