Introduction:
In recent years Drug Addiction has significantly increased in Bangladesh. This agent of human devastation has spread its tentacles worldwide and also in our country. Every intelligent and humane person in the world, society and international organizations such as the UN and WHO are alarmed by the present rate of addiction. In our country the regular seizures of stocks of heroin and other hard drugs by the police and narcotics department gives us an indication of the extent of addiction in our country. Nowadays nearly ten per cent of outpatients in our hospitals are cases of drug addiction involving heroin, ganja and phensidyl. These are generally youths and young men between 15-30 years of age and come from all strata of the society. But there are adolescents below 15 years of age and men and women over 30. Hospital surveys show that average age of drug addicts is 22. The addicts are students, professionals, businessmen, laborers, rickshaw pullers and from other professions. Students are most affected and drugs have caused deterioration in standards of education and students have also given up going to schools and colleges. These addicts are turning to various criminal activities, in order to procure drugs.
Generally speaking drugs are substances that affect the physical and mental condition of persons significantly and adversely. Any substance that can lead to addiction, misuse and dependence is a drug. Addiction level of drugs increase with each day of use. If drugs are not available, the patient shows critical withdrawal symptoms when immediate medical care is needed to prevent physical and mental deterioration, even death.
Drug addiction beings on rapid erosion of educational and cultural, moral and family values. The addicts lose their professional and educational capabilities, self-dignity, and get involved in serious or petty criminal activities. The sole aim in life of an addict becomes the procurement and use of drugs. Other aims and objectives in life are thrown by the roadside. Besides, dread diseases such as Hepatitis, HIV/AIDS can easily attack drug addicts through use of injectable drugs.
In our country, heroin is mostly smoked within aluminum foil or cigarette paper, but in other countries this is injected. Intravenous injection of pathedine/ morphine and now tadigesic brand of riknomar penic. These are extremely dangerous drugs and increases addiction manifold. Injections through infected needles can cause diseases of the liver, brain, heart, lungs and spinal cord. Normal medication also interacts with heroin and cause many complications, which many addicts do now know about. Such interactions may also cause e death.

Heroin addiction lowers mental enthusiasm and efforts and physical ability The addict loses contact with normal society and becomes self and drug-centered. He engages in all types of activities to obtain money to buy drugs. A Heroin addict may need about Taka 500 worth of the drug a day. He neglects the needs of the family, and those are non-earning may sell off family assets. They also go out on the streets for mugging and robbery.
Justification of the study:
Nurses could be the important and experienced key informants about drug addiction because they have been dealing a lot of drug addicted patients while working in the hospitals. Most of the time the drug addicted patients are admitting for a long time for getting cure based on the nature of addiction. During the admitting time the nurses have the opportunity to talk with the patients even beyond the medical boundary and become a good interpersonal relation between the patients and nurses. Due to this fare interpersonal relation the addicted patients most often discuss their life history with the staff nurses especially how they have been felt into this addiction. Sometimes the nurses could get enthusiastic to know about the personal life of the patients that is relevant with their addiction. The nurses have the scope to go through the personal history form of the patients which is the another information source for them to know about drug addiction. During counseling of the addicted patients the staff nurses accompany the counseling process and during leaving hospitals staff nurses theirselves counsel the patients. The counseling process depends on the personal history of the patients, their life style, economic status, nature and type of addiction. So, the nurses should be the sources of information depot about drug addiction. If the experiences of the nurses are gather through a scientific process it could get new window to serve for the sector of drug addiction. So, this study could be conducted by following the scientific process.
Literature Review:
Copyright 1992 Blackwell Science Ltd
Caring for patients in pain is a pivotal function of nursing practice In particular, pain control is a primary concern of hospice nurses in order to ensure comfort in the terminal phase of the person’s life, and also for nurses in intensive therapy units caring for patients who may have substantial pain related either to pathologic conditions or treatment interventions and who have difficulty communicating their pain This paper reports on a study which aimed to identify and compare the knowledge and the perceived adequacy and acquisition of knowledge of intensive therapy and hospice nurses pertaining to the theoretical, pharmacological and non-pharmacological aspects of pain and its management using multiple-choice, short-answer and open-ended questions The sample consisted of 52 intensive therapy and 48 hospice nurses who were further divided into beginners and experts The findings indicated that although the hospice nurses received higher knowledge scores than the intensive therapy nurses, both groups demonstrated lack of knowledge in specific content areas In addition, the findings demonstrated few differences between the beginners and experts
The subjects, in general, were not confident about their knowledge of analgesics, nor did they believe that their basic nursing education had prepared them adequately to care for patients in pain The working environment and clinical work in hospital since qualification were perceived by the subjects to be the most influential experiences in learning about pain and its management.
To determine the extent to which nurses are able to correctly identify drugs as narcotics and to ascertain their perception of the addiction potential of opiates when used for pain management. Methods: A questionnaire was administered to 86 nurses who attended palliative care workshops in India. Findings: Only morphine (95%), heroin (71%) and codeine (75%) were correctly identified as narcotics by the majority of participants. Imipramine (34%), diazepam (20%) and phenobarbitone (39%) were wrongly classified as narcotics by many nurses. Dextropropoxyphene (11%), pentazocine (21%), buprenorphine (15%) were correctly classified as narcotics by fewer than half the participants. Only 14% knew that that the frequency of psychological dependence due to use of morphine for cancer pain was less than 1%.
A lack of knowledge about common pharmacological agents used in pain control, and exaggerated fears about the likelihood of psychological dependence lead to poor pain management in clinical practice. Studies have demonstrated that many health professionals have a poor understanding about pain assessment and treatment.
Cohen’s (1980) questionnaire survey of 121 nurses also revealed that nurses had inadequate knowledge about use of opioid analgesic drugs and were overly concerned about the possibility of opioid addiction. When asked to estimate the number of persons with pain who become addicted as a result of being treated with narcotic drugs in the hospital, only 31.5% of the nurses correctly thought it was 1% or less. 13% of this sample estimated the chance of addiction at 26% or greater.
A survey was carried out by Weis et al (1983) among house staff and nurses involved with postoperative care to assess their knowledge of analgesics and their attitudes toward postoperative analgesic care. Only one-fifth of the respondents prescribed adequate analgesics for complete pain relief. There were some misconceptions about adding other drugs to narcotic analgesics, as well as fear of the addictive properties of these narcotics. The incidence of addiction after use of opioid drugs for pain relief was correctly identified as <1% by only 15.8% of physicians and 11.4% of nurses.
McCaffrey et al (1990) analyzed data obtained from workshops on pain to determine the nursing knowledge of pharmacological management of pain. Results indicated that nurses lack knowledge in classification of opioids with correct responses ranging from 23 to 98% across seven analgesic drugs. Less than 25% of nurses correctly identified the frequency of psychological dependence.
These above studies indicate that nurses and other health professionals have inaccurate knowledge about common pharmacological agents used in pain control, and they have exaggerated fears about the likelihood of psychological dependence on opioids as a result of the use of narcotics for pain control. This study was conducted to understand the perception and knowledge of nurses about narcotics in Indian setting.
The data was collected from pretest surveys during two workshops conducted by the author (SKC). The participants had varying years of experience in nursing, and oncology. These workshops were conducted in the year 1999 and 2000. These were conducted at two large cancer centers in South India.
The procedure used by the workshop leader was to distribute the questionnaire at the beginning of the session and to tabulate the results during the day to share the results with the attendees. Consent for using the findings for further teaching and reporting in a journal was obtained from the participants. The tool, included two sections. The first section assessed knowledge of drug classification by asking the subjects to identify ten drugs as narcotic or nonnarcotic. Subjects were given choices of “narcotic”, “nonnarcotic”, and “don’t know”. The drugs listed were cocaine, codeine, heroin, morphine, Fortwin (pentazocine), Proxyvon (dextropropoxyphere), Tidigesic (buprenorphine), imipramine, calmpose (diazepam), and luminol (phenobarbitone).
The second section was a single item assessing knowledge of narcotic addiction. Subjects were asked to identify the frequency (by percent) of addiction in patients treated with narcotic drugs for pain. Ten possible choices were given ranging from <1% to 100%. A definition of the term “narcotic addiction” was included on the tool. It was defined as the behavioral pattern of drug use, characterized by overwhelming involvement with the use of drug, the securing of its supply, and a high tendency to relapse after withdrawal. It is not used interchangeably with physical dependence (Jaffe 1985). Data was analyzed using the statistical package SPSS tenth version.
There were a total of eighty-six respondents. (N=86). All participants were female. The median age was 31. The median number of years of experience in nursing was 9 years. The median duration of experience with cancer patients was 2 years.
The results of the narcotic classification questionnaire are presented in. Correct answers for individual drugs ranged from 95% for morphine to 17% for cocaine. The majority of participants correctly identified only morphine, heroin and codeine as narcotics. Imipramine, phenobarbitone and diazepam were wrongly judged as narcotic by 40%, 45% and 23% of nurses respectively. Fewer than half the participants correctly classified dextropropoxyphene, pentazocine, and buprenorphine as narcotics.
None of the participants could give all correct responses. Seven nurses gave 8 or 9 correct answers and 52 gave four to six correct responses. 19 had fewer than four correct answers. An attempt was made to examine the association between the correct scorers and years of experience in nursing. It was found that nurses who had fewer years of experience had better knowledge about narcotic substances, as compared to those who had more than ten years of experience. This difference was found to be statistically significant (p < 0.05).
Knowledge about the frequency of drug addiction is presented in. Only 14% of nurses correctly identified the frequency of addiction among cancer patients on opiates as <1%. 32% of the nurses thought the frequency of addiction was more than 50%.
Nurses are integral to palliative care delivery and it is important that they have a clear understanding of the nature of the drugs prescribed. In our study nurses had a poor knowledge about the classification of narcotic drugs and about the low potential of addiction in patients using opiates for pain relief. Similarly, McCaffrey et al (1990) found in pain management workshops that many nurses had inadequate knowledge about the pharmacological management of pain. When asked to classify analgesics, the percentage of correct responses for seven drugs ranged from 17% for cocaine 95% for morphine.
On examining the association between the knowledge about narcotics and years of experience in nursing, it was found that nurses who had fewer years of experience had better knowledge, as compared to those who had more than ten years of experience. This implies that those trained recently have a better knowledge about narcotic drugs rather than those trained more than ten years back. This trend is positive, and it is hoped that present nursing training would give more attention to cancer pain and use of morphine for pain relief.
Confusion regarding opioid analgesics probably results from multiple factors. The term narcotic has been used to refer to morphine related strong analgesics. The media often refer to all substances of abuse as ‘narcotic’ drugs and some health professionals also use the term loosely.
Less than a quarter of the nurses in McCaffery’s study correctly identified the frequency of psychological dependence. Marks and Sachar (1973) reported that only 60% of physicians correctly identified the chance of addiction from use of narcotic drugs for pain relief as <1%. 16% thought that addiction occurred in between 1 and 5% of patients; and 22% thought the incidence of addiction was greater than 6%. Chart review of 37 patients in their hospital showed that physicians underprescribed analgesics and nurses compounded the problem by administering less opioid medication than was prescribed. Concern about iatrogenic addiction was probably a significant factor in the under use of analgesics.
In India, legal and administrative obstacles to the use of opioids drugs for pain control can easily convey the message that such drugs are better avoided. The present study indicates that many nurses have fears about patients developing psychological dependence on opioid drugs. Consequently nurses may fail to play an active role in titrating opioids and in administering analgesics for breakthrough pain. If this is to improve, it is imperative that staff and student nurses in India have adequate opportunities to learn about the properties of commonly used analgesics, and the scientific use of opioids for pain management.
Study design
- Research question
- Broad objective
- Specific objectives
Methods and Materials
- Study population
- Inclusion criteria
- Exclusion criteria
- Data Collection, Management & Analysis
- Ethical consideration
- Informed Consent
- Variables
- Operational definition
Research Question:
The problem of the research was concerned with understanding about the Knowledge level of nurses about drug addiction arisen from handling the drug addicted patients working in Barisal Medical College Hospital.
Research Objective
General Objective
To assess the knowledge level of nurses about drug addiction working in the Barisal Medical College Hospital.
Specific Objectives
- To assess the level of knowledge of the nurses working in the Barisal Medical College Hospital about drug addiction.
- To know the socio demographic background of the drug addicted patients, source of abusive drug and nature of addiction from the respondents.
- To explore the consequence of drug addicted patients through the respondents.
Operational definition:
Drug addiction: In this study drug addiction included all types of chronic addiction in any drug except smoking.
Knowledge on drug addiction: In this study knowledge of the respondents include
- Emergency management of drug addicted patient
- Counseling of drug addicted patient
- Supporting the admitted drug addicted patient
- Behaviour with the drug addicted patient
- Common syringe using and its consequences
- Consequences of f drug addiction
Consequences of drug addiction: This study includes the knowledge of the respondents about the fate of drug addicted persons so far their knowledge.
Key variables
The study constitutes 2 types of variables, whereby knowledge of the staff nurses was dependent upon several variables.
Independent Variable
Knowledge of the staff nurses on drug addiction.
Dependent variables
- Age
- Sex
- Training received
- Duration of service
- Knowledge of handling drug addicted patients
- Source of addicted drug
- Nature of addiction
- Nature of treatment provided
- Nature of counseling
Materials and methods
Type of study
This study was a cross sectional study conducted among the nurses to assess the level of knowledge about drug addiction, at Barisal Medical College Hospital.
Study Place
This study was basically carried out in Barisal Medical College Hospital, Barisal.
Study Period
The study was conducted over the period of June 2011 to December 2011
Study Population
Staff nurses of Barisal Medical College Hospital, who are working across different wards.
Inclusion criteria:
- Nurses working in the Barisal Medical College Hospital
- Nurses willingness to participate in the study.
Exclusion Criteria:
- Nurses, who decline to participate in the study
Sample Size
The sample size for the study was 100 nurses who were selected purposively.
Sampling Technique
Purposive sampling technique was followed in the study, so that, multiple respondent and responses could be ensured.
Data Collection Tools
For smooth conduction of the study, a structured questionnaire was developed. The questionnaire was divided into several parts. The first part focused on nurses socio demographic information’s, second part on their knowledge on drug addiction, third part on attitude towards drug addicted patients and fourth part focused on recommendations for the drug addicted patients.
Data Collection Procedure
After explaining the purpose of the study data was collected through face to face interview using /English structure questionnaire.
Conduction of the study, quality control and monitoring
Data was collected from selected hospital by the investigator. The collected data was checked and verified at the end of the work every day. Any inaccuracy and inconsistency was corrected in the next working day. However, cross checking of the collected data was done randomly.
Data Processing and data analysis
The data entry process just started immediately after the completion of data collection. The collected data was checked, verified and then entered into the computer in analyzable format. Only fully completed datasheet was entered into the computer for the final analysis and incomplete or inconsistent sheets were revisited. The data analysis process was carried out with the help of SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Science) Windows software program.
Ethical consideration
Prior to the commencement of this study, the research protocol was approved by the research committee (Local Ethical committee). The aims and objectives of the study along with its procedure, risks and benefits of this study was explained to the respondents in easily understandable local language and then informed consent was taken from each patient. Then it was assured that all information and records will be kept confidential and the procedure will be used only for research purpose and the findings will be helpful for developing policy to increase the knowledge on managing drug addicted patients by the nurses.
Informed Consent
A well and clearly understood inform consent form was filled in up by the respondents and interviewer in case of each interview. However, translations and clarifications were carried out the according to the need of the respondents. This ensures that each of participants got the information they need to make an informed decision and provide their opinion freely.
Findings and Results
Background Characteristics
Table 1: Age of the Respondent
Descriptive Statistics
| N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| Age of the respondent | 100 | 32 | 56 | 39.61 | 5.278 |
| Valid N (listwise) | 100 |
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | 32 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| 33 | 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | |
| 34 | 7 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 10.0 | |
| 35 | 9 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 19.0 | |
| 36 | 8 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 27.0 | |
| 37 | 12 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 39.0 | |
| 38 | 11 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 50.0 | |
| 39 | 10 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 60.0 | |
| 40 | 11 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 71.0 | |
| 41 | 7 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 78.0 | |
| 42 | 5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 83.0 | |
| 43 | 3 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 86.0 | |
| 44 | 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 87.0 | |
| 45 | 3 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 90.0 | |
| 47 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 92.0 | |
| 52 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 94.0 | |
| 53 | 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 95.0 | |
| 54 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 97.0 | |
| 55 | 1 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 98.0 | |
| 56 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
It was observed from the study that, the study was conducted among the respondent nurses, whose age was in between 32 to 56 years, with an average age of 39.61 years. It was also observed from the study that, most of the respondents were from the age group of 36 to 40 years. 52% of the respondents were from this age group. It was notable from the frequency distribution that, only 8 respondents were aged more than 50 years. It was found that 19 respondents were below the age of 36 years.
Table 2: Marital status of the respondents
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | married | 97 | 97.0 | 97.0 | 97.0 |
| Separated or unmarried | 3 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
To know about the marital status of the respondents, it was found that, almost 97% of the respondents were married, whereas only 3% of the respondents mentioned that they were either separated or unmarried.
Table 3: Academic background
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Diploma nurse | 89 | 89.0 | 89.0 | 89.0 | |
| BSC nurse | 11 | 11.0 | 11.0 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 100 | 98.0 | 100.0 | ||
To assess the academic background of the respondents, it was found that, 89 of the respondents have Diploma in Nursing qualification, and 11 respondent were reported to have BSC in Nursing degree.
Table 4: Position of the respondents
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Nursing superintendent | 4 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Senior staff nurse | 91 | 91.0 | 91.0 | 95.0 | |
| Staff nurse | 2 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 97.0 | |
| Assistant nurse | 3 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 | |
| Total | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
To have an overview on the respondents working position, it was observed from the study that, 91% of the respondents were senior staff nurses, while only 4% of the respondents were nursing superintendents. At the junior level, only 2% of the respondents were staff nurses and 3% of the respondents were assistant nurse.
Table 5: Descriptive Statistics of Duration working in hospital
| N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation | |
| Duration working in hospital | 100 | 5 | 31 | 16.00 | 5.773 |
| Valid N (listwise) | 100 |
It was observed from the descriptive status that, all of the respondents have experience in working at hospitals. The minimum duration of working at the hospital was 5 years, whereas, maximum experience or duration of working was found 31 years.
Table 6: Where the respondents works
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Indoor | 96 | 96.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Outdoor | 4 | 4.0 | |||
| Total | 100 | 100.0 | |||
To know about the place of working about the respondents, it was found from the study that 96 respondents works at the indoor units whereby only 4 of the respondents were engaged in outdoor services.
Table 7: Have roster duty
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Yes | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
In order to know whether respondents have to perform roster duty, all respondents urged that, they have to work according to the roster duty.
Table 8: How long work in a day
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | 8 | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
All of the respondents mentioned that, they have to work 8 hours in a day. Some respondents mentioned that, they may have to work for more working hours when required.
Table 9: Have heard about drug addition
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Yes | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
In response to the query of respondent’s knowledge and familiarity with drug addiction, the study find that, all of the respondents have heard about drug addiction and they know about drug addiction.
Figure 1: Type of drug available in Bangladesh
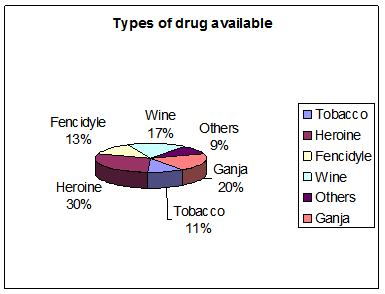
While mentioning about the types of drugs available in Bangladesh, 30% of the respondents identified availability of Heroine as a significant observation. Besides, 20% of the respondents also mentioned about the availability of Ganja/Marijuana. In line with these, 13% of the respondents also mentioned about the availability of Fencidyle and 17% respondents mentioned about the Wine. It was noteworthy that, only 11% of the respondents mentioned about the availability of Tobacco, whereas, Globat Adult Tobacco Survey in Bangladesh notified more than 37% of the Bangladesh in using tobacco products. 9% of the respondents demonstrated about the availability of other drugs in Bangladesh.
Figure 2: Who are usually involved in drug addiction
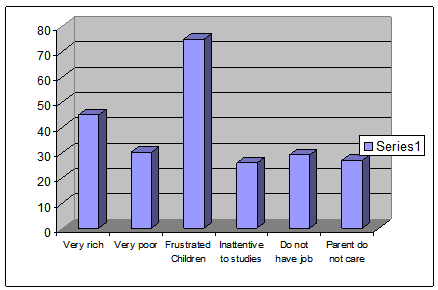
For identifying the major population groups, who are usually involved in drug addiction, it was alarming one to find that, more than 75% of the respondents identified the Frustrated children to be the drug addicted. Hereby, the polarity in income status also significantly contributes toward drug addiction, which is due to societal problems. 45% of the respondents urged that members of very rich families are usually involved in drug addiction, whereas, 30% respondents mentioned drug addiction is prevalent in very poor families. Nonetheless, respondents also demonstrated about a present problem like inattentiveness to studies as a basic reason for drug addiction and 26% respondents were in favor of this opinion. 29% respondents also agreed that, those who have no job also used to take drugs. 27% Respondents also demonstrated about the children who did not receive any care from their parents, are often addicted to the drugs.
Table 10: Know about physical consequence of drug addition
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Yes | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
While assessing the knowledge of the respondents about the physical consequences, all of the respondents noted that they are familiar to physical consequence of drug addiction.
Figure 3: Physical consequences of drug addiction
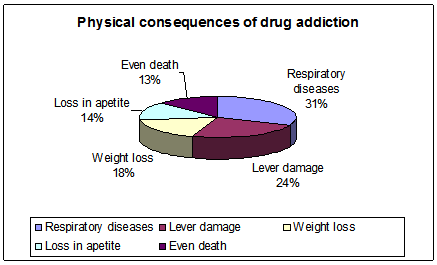
In order to know about the physical consequences about the drug addiction, most of the respondents (31%) mentioned that drug addiction can even result in respiratory diseases. Besides, 24% of the respondents believe that as a measure of damaging the lever.18% of the respondent’s claims drug addiction to be the basic reason for losing weight while 14% mentioned the drug addiction to be a cause of loss of appetite. Moreover 13% of the respondents believe that drug addiction can even lead toward death.
Table 11: Know how a person can involve in drug addiction
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
| Valid | Yes | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
In response to the question, whether respondents know that how a person can be involved in drug addiction, all respondents unanimously informed that, they knows about the ways of involvement toward drug addiction.
Figure 4: how a person can be involved in drug addiction
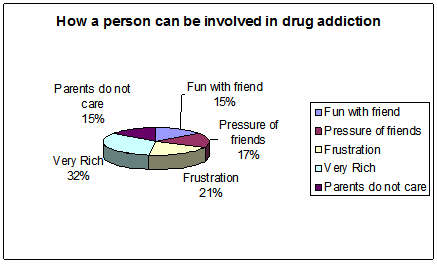
While examining the reasons of drug addiction, and how a person can be involved in drug addiction, the study finds that, it starts with mostly Fun with friend (15%). Sometimes pressure from the friends (17%) can also lead them to drug addiction. 21% of the respondents have notified that, frustration remains the reason for involvement in drug addiction. Being very rich constitutes topmost risk for drug addiction with a percentage of 32. 15% of the respondents also noted that, lack of parental care lies at the core of drug addiction for the young.
Table 12: Know about social consequences of drug addiction
Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
Valid | Yes | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
In response to the query of respondent’s knowledge and familiarity social consequences of drug addiction, the study find that, all of the respondents know about social consequences of drug addiction.
Figure 5: Social consequences of drug addiction
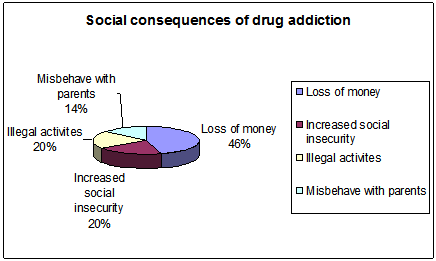
In order to know about the social consequences of drug addiction, most of the respondents (46%) argue that, it results in loss of money, which includes wastage and treatment for the addicted. 20% the respondent’s increased social insecurity of respondents as the social consequences. 20% respondents believed that this series of consequences can promote Illegal activities in the society. 14% of the respondents also identified that, drug addiction even consequences on misbehaving with the parents.
Table13: The roles of parents to overcome the situation
Frequency | Valid Percent | ||
Valid | Behave friendly with children | 31 | 30.8 |
Taking proper care of their mental health | 43 | 42.9 | |
Regular care of child and counseling them | 26 | 26.3 | |
Total | 91 | 100.0 | |
Respondents were asked about the role of the parents to overcome from the drug addiction, whereby respondents mentioned that, behaving friendly with the children (31%) can help the addicted to overcome. Most of the respondents also noted that, taking proper care of the mental health (43%) of the addicted children can help healing the situation. 26% of the respondents believes that Regular care of child and counseling them can help in recovery of the children from the consequence of drug addiction
Table 14: Service providers have the responsibilities to overcome the situation
Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
Valid | Yes | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Whether service providers have the responsibilities to overcome the situation or not, it was received from the respondents end that, all of the service providers have their own responsibility for overcoming from the situation.
Figure 6: Respondents of service providers for ensuring services
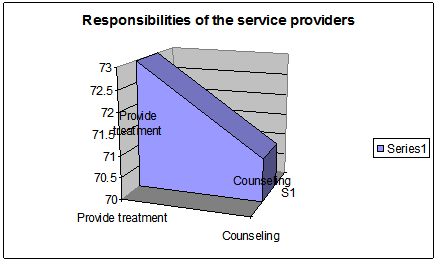
The respondents have identified two type of responsibilities required to be provided by the service providers. 73% of the respondents have identified providing treatment to the drug addicted can be the foremost responsibility of the service providers, whereas, 71% uses to believe that, counseling is the primary responsibility of the service providers.
Table 15: Country has the responsibilities
Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
Valid | Yes | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Respondents were unified about the question states responsibility for drug addicted. All respondents urged that, country has its own responsibility and have the responsibility for the special vulnerable group like drug addicted.
Figure 7: Role of the state for drug prevention
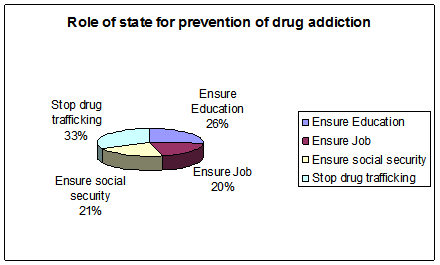
While mentioning about the role of the state in preventing drug addiction, it was found that, 26% of the respondents claimed for ensuring proper education and 20% respondents claimed for job for preventing drug addiction. 21% of the respondents demonstrated about the necessity of ensuring social security as a measure for prevention of drug addiction, whereas, most respondents emphasized upon stopping the drug trafficking (33%).
Table 16: Parents has role to reduce drug addiction
Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
Valid | yes | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
While responding to the query of role of parents in reducing drug addiction, all of the respondent urged that, they have a significant role in this.
Figure 8: Role of the parents for reducing drug addiction
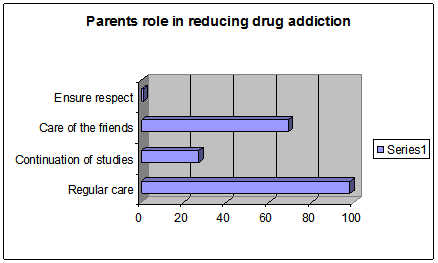
While identifying the role of parents in reducing drug addiction, the respondents mostly emphasized upon the regular care of the children (98%). Besides, supervise continuation of studies (27%) by the parents can play a vivid role. 69 of the respondents also demonstrated to care for the friends, with whom, the children mixes with needs to be taken care of. Respondents also mentioned about respecting the opinions of the children as a negligible but mentionable component.
Figure 9: Service available for drug addicted
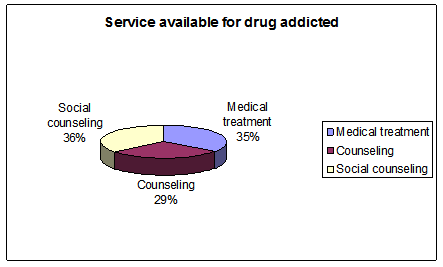
It was found in the study that, respondent mainly mentioned about 3 types of service available for drug addicted. Whereas, 36% of respondents emphasized upon social counseling, 29% of the respondent also mentioned about counseling for drug addicted. Other 35% of he respondents mentioned about the medical treatment for the patients.
Table 17: Service providers support to drug addicted people
Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||
Valid | Yes | 100 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
Whether the service providers provide support to the drug addicted people, 100% of the respondents noted that, service provider’s support is necessary for the prevention of drug addiction.
Figure 10: Why support is necessary for drug addicted
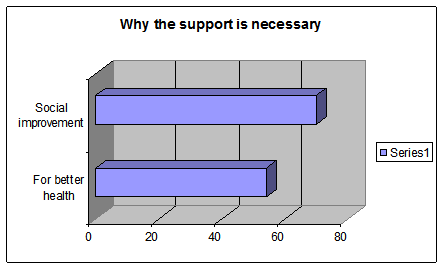
The respondents have identified the various form of support to be an essential part of the patient’s rehabilitation and proper survival. 54% respondents mentioned the necessity of support or better health, whereas 70% respondents noted it necessary for social improvement of the drug addicted and come out of the devastating cycle.
Comments and General findings:
Respondents argued that the target group has to be made aware and fully informed about drugs, its misuse and horrifying consequences. Educational institution, student and youth organizations should be involved in group discussion and meetings, with advocacy and awareness programs through posters, slogans, radio and TV programme and various mass communication agenda, including the print media. Community leaders, politicians, sport and movie personalities can take active part in the campaign against drug addiction. Organizations to resist drug addiction must be built up by the students and youths
Alternative Programmes: The inherent strengths of the youth in society have to be put to constructive work. Monotony, idleness, unemployment cause despair and frustration in the patient, and to seek solace elsewhere the target group look to drugs for comfort and to forget the trouble and tension of everyday life. Monotony and frustration may be eliminated through sports and games, physical training and competitive games, social work which make the youth adjust to the environment. Student life exposes the youth to many social pressures which leads to despair and tensions and the need for drugs to forget the stresses of modern life. Counseling of students on mental and physical health and tackling of various problem at school and college is required. Medical care is extremely and urgently necessary for the addicts. Withdrawal symptoms hinder the giving up of the habit. The first step in treatment is to stop drugs and treat for the withdrawal symptoms. Various physical symptoms of withdrawal have to be treated at this stage. Stopping the taking of heroin has to be under the supervision of a specialist. To get the patient to agree to treatment for addiction is the first step in the treatment. The patient will try to make excuses to avoid treatment. Sometime the patient stops taking requisite medication. The giving up of heroin without specialist advice is a waste of time, energy and money.
Once the addiction is removed from the human body, the patient and his/her family has to cooperate in a courses of long-term treatment prescribed by the specialist which include considerations of the patient’s depression, social environment, recreation and other aspects. The preferred treatment mode is psychotherapy. The patient and his family must be convinced of the fact that giving up drug is not the end of the treatment course, but just the end of the beginning of the treatment. Long-term follow-up treatment is the only cure to this terrifying problem. The patients who cannot or do not undergo follow-up treatment, may again revert to addiction.
Discussion:
It was observed from the study that, the study was conducted among the respondent nurses, whose age was in between 32 to 56 years. The academic background of the respondents was mostly Diploma in Nursing qualification, some have BSC in nursing degree. 95 % of the respondents were found working at senior staff nurses level where 4% respondents were the juniors. The minimum duration of working at the hospital was 5 years, whereas, maximum experience or duration of working was found 31 years. Iit was found from the study that 96 respondents work at the indoor units whereby only 4 of the respondents were engaged in outdoor services. All respondents urged that, they have to work according to the roster duty and they have to work 8 hours in a day.
All of the respondents have heard about drug addiction and they know about drug addiction, while mentioning about the types of drugs available in Bangladesh, respondents identified availability of Heroine, Ganja/Marijuana, Fencidyle, Wine, Tobacco and other drugs to be available in Bangladesh.
For identifying the major population groups, who are usually involved in drug addiction, it was alarming one to find that Frustrated children are to be prone the drug addiction. Hereby, the polarity in income status also significantly contributes toward drug addiction, which is due to societal problems and differences. Members of very rich and very poor families are usually involved in drug addiction; recently, inattentiveness to studies is working as a basic reason for drug addiction. Frustrated people, who have no job also used to take drugs. Respondents also demonstrated about the children who did not receive any care from their parents, are often addicted to the drugs.
The physical consequences about the drug addiction, is so serious. Drug addiction can even result in respiratory diseases, damaging the lever, losing weight, loss of appetite and can even lead toward death.
While examining the reasons of drug addiction, and how a person can be involved in drug addiction, the study finds that, it starts with mostly Fun with friend, sometimes pressure from the friends, frustration remains the reasons for involvement in drug addiction. Being very rich constitutes topmost risk for drug addiction. Respondents also noted that, lack of parental care lies at the core of drug addiction for the young.
In order to know about the social consequences of drug addiction, most of the respondents noted that it results in loss of money, which includes wastage and treatment for the addicted. Increased social insecurity and illegal activities in the society are also the footnotes in the case. Some respondents also identified that, drug addiction even consequences on misbehaving with the parents.
Behaving friendly with the children can help the addicted to overcome. Most of the respondents also noted that, taking proper care of the mental health of the addicted children can help healing the situation and regular care of child and counseling them can help in recovery of the children from the consequence of drug addiction.
Most of the respondents have identified providing treatment to the drug addicted can be the foremost responsibility of the service providers, whereas, others uses to believe that, counseling is the primary responsibility of the service providers. All respondents urged that, country has its own responsibility and have the responsibility for the special vulnerable group like drug addicted.
While mentioning about the role of the state in preventing drug addiction, it was found that, the respondents claimed for ensuring proper education, job, ensuring social security as a measure for prevention of drug addiction, whereas, most respondents emphasized upon stopping the drug trafficking.
While identifying the role of parents in reducing drug addiction, the respondents mostly emphasized upon the regular care of the children. Besides, supervise continuation of studies by the parents can play a vivid role. Respondents also demonstrated to care for the friends, with whom, the children mixes with needs to be taken care of. Respondents also mentioned about respecting the opinions of the children but mentionable component.
It was found in the study that, 3 types of service available for drug addicted whereby respondents emphasized upon social counseling. They also mentioned about counseling for drug addicted and medical treatment for the addicted patients.
Whether the service providers provide support to the drug addicted people, 100% of the respondents noted that, service provider’s support is necessary for the prevention of drug addiction.
The respondents have identified the various form of support to be an essential part of the patient’s rehabilitation and proper survival. The support for the drug addicted is necessary because it can help to ensure better health and social improvement of the drug addicted and come out of the devastating cycle of addiction to drugs.
Limitation of the study:
The study was conducted with the objective of investigate the knowledge of drug addiction among the nurses in AGM Osmai Medical College Hospital in Barisal. It was intended to know the major causes drug addiction, side effect of drug addiction, and practices of nurses to provide services to drug addicted people. It was good if the study compare other hospital in a wide perspective. But due to time and cost constraint the study only conducted in one hospital and only with 100 respondents. The limitation of the study was the sample size. It used 100 respondents only which is not enough to generalize the findings. At the same time it used only quantitative data. If this study uses more qualitative data for in-depth information the report would be more informative and reliable.
Recommendations:
- Nurses knows about drug addiction, drug availability while mentioning about the types of drugs available in Bangladesh, respondents identified availability of Heroine, Ganja/Marijuana, Fencidyle, Wine, Tobacco and other drugs to be available in Bangladesh and even knows about the drug addicted group which consists of basically the very rich or poor families, frustrated, inattentive persons. Thus, more training have to be provided to the nurses for understanding the signs, cares, recovery of drug addicted patients.
- The physical consequences about the drug addiction, is so serious as drug addiction can even result in respiratory diseases, damaging the lever, losing weight, loss of appetite and can even lead toward death. So nurses should carry out the message among the patients who are drug addicted
- Nurses can help in treatment, social counseling process. Thus, more information towards the parents and caregiver’s group of the drug addicted should be informed for recovery and survival of the drug addicted.
- As drug addicted comes from different strata of the society, while examining the reasons of drug addiction and social and other consequences, the core of drug addiction should be understood properly and disseminated through the nurses.
- There is no alternate of counseling with drug addicted. Thus, behaving friendly with them can help the addicted to overcome. Most of the respondents also noted that, taking proper care of the mental health of the addicted can help healing the situation and taking regular care and counseling them can help in recovery of the addicted from the consequence of drug addiction, whereby, nurses play the role of caregiver as a change agent.
Conclusions:
The main elements in combating Drug addiction include measures to control availability and use of drugs, treatment of withdrawal symptoms, and restoration of social moral and religious values. To prevent re-addiction in patients, innovative treatment containing medical, social and religious aspects have to be put in place. The patient should be treated in a hospital or clinic under supervision of doctors and nurses. The patient’s history has to be known and understood in detail by the health professionals and then medication and course of treatment may be prescribed. The patient’s personality and mental make-up has to be understood by the doctor along with the patient’s physical and mental disabilities. Easy availability of treatment will ensure the elimination of this socially and physically dreaded disease. Treatment of addiction in our country is still not in a hopeful stage. Its is time that experienced and qualified health professionals, nurses come to the aid of the addict in our society, and give genuine and prolonged treatment and care.s and nurses medication choices, Pain.