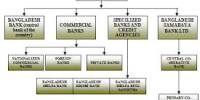
Main objective of this report is to analysis Different Investment Modes of Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited. This report covers the organizational structure, background and objectives, functional, departmentalization and Business performance of IBBL as a whole and the part covers operational scenario of Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited. Finally draw SWOT analysis and find out some problems related on different Investment Modes and suggest recommendation.
Methodology:
The study is performed based on the information extracted from different sources collected by using a specific methodology. This report is analytical in nature. The methodology is mentioned bellow:
Population: All the Branches of IBBL located in everywhere in Bangladesh has been taken into consideration as population.
Sample: Islami Bank Bangladesh Ltd. Zinzira Bazar Branch, Local Office is the vital sample.
Data collection: Sources of data of this report can be divided into two categories.
Primary Sources:
- Face to face conversation with the respective officers and staffs.
- Interviewing officers and staffs.
- Relevant file study on provided by the officers concerned.
- In depth study of selected cases.
Secondary Sources:
- Annual Report of Bangladesh Bank.
- Audit Reports.
- Relevant books, Newspapers and Journals.
- Internet and various study report.
Concept, History &Growth of Islamic Banking Around The World
CONCEPT OF ISLAMIC BANKING:
The concept of Islamic Banking represents a radical departure from traditional banking. Islamic banking has to derive its inspiration from the religious edicts of Islam and has to mould its operations within the framework of the teachings of Islam. The most distinctive feature of Islamic Banking is its total abstinence from interest is observance of Islamic Banking and prohibition of all interest based transactions. The Islamic Banks organize their operations on the basis of profit/loss sharing and other modes which are permitted in Islam.
The General Secretariat of Organization of the Islamic Conference defines an Islamic Bank as “Islamic Bank is a financial institution whose statutes, rules and procedures expressly state its commitment to the principles of Islamic Shariah and to the banning of the receipt and payment of interest on any of its operations.”
All OIC countries including Bangladesh have approved the above definition of Islamic Bank. The Islamic Development Bank and other national and multinational Islamic Banks have also adopted the above definition as their operating guide.
Islamic Banking Act 1983 of Malaysia (Act No 4.276) has given the following definitions:
“Islamic Banking” means any company which carries on Islamic Banking business and holds a valid license, and all the offices and branches in Malaysia of such a bank shall be deemed to be one bank.
The Islamic Republic of Iran has promulgated “The law for usury-free banking” on August 30, 1983 incorporating the detail objectives and duties of the Banking System in Iran.
“Islamic Banking business” means banking business whose aims and operations do not involve any element, which is not approved by the Religion of Islam.
HISTORY & GROWTH OF ISLAMIC BANKING:
The Islamic Banking movement as we know it today is recent phenomenon. The history of modern Islamic Banking dates back the 1950’s when a small private Islamic Bank appeared in Pakistan but subsequently wound up. In the decade of 1950’s the concept of Islamic Banking was a matter of thanking & research and the result was preserved in the papers of different scholars of the Muslim World. The 1960 was the decade for practical experiment and 1970’s 1980’s and 1990’s were the decade for establishment. The current millennium is expected to be the decade of success and expansion at a faster rate.
During 1960’s it was observed that the Muslims of Malaysia used to save primarily for performing Hajj and such savings were mostly kept idle in pillows, under mattresses and floors for avoiding interest which was unproductive & damaging for the growth &development free financial institution known as “pilgrims savings corporation”. Though it was not a full fledged bank, even we can say that it was the beginning of an institution free of interest which is unconditionally prohibited in Islam.
“Mitghamr Bank” is the pioneer of modern Islamic Banking, which was established by Dr. Ahmed-El-Naggar in 1963 by his Personal endeavor at Mitghamr in Egypt with a view to bringing operation successfully in the light of Islamic Shariah for about five years. Now the Islamic Bankers of the world have treated the short life of Mitghamr Bank as the first model of Islamic Banking A survey report by the National Institute for Management Development, Cairo, Egypt, shows that the Mitghamr Bank was tremendously successful in achieving its objectives and the tremendous success of the Bank was the cause of its closure by the vested interest in 1967.
Islamic Development Bank was established in 1975 and during the following three years 7(Seven) Islami Banks & financial institutions namely
i) Dubai Islami Bank
ii) Kuwait Finance House
iii) Faisal Islami Bank, Sudan
iv) Jordan Islami Bank for Finance and Investment
v) Islamic Bank System International Holding S.A. Luxembourg
vi) Faisal Islami Bank of Egypt
vii) Islamic Investment Co. Ltd. was established.
In 1978 Islamic Foreign Ministers Conference in their Dakar (Senegal) meet recommended to the members of OIC to make systematic efforts to establish Islamic Banks gradually and during the next three years of their recommendation 20 Islamic Bank and financial institution came into existence.
The statistical information in a consolidated form about the share capital and growth in the deposits & investment of some of the major Islamic Banks are stated below.
Islamic Development Bank:
The Islamic Development Bank is an international financial institution, which was set up in Jeddah October, 1975 (1396H) by the member states of the Organization of Islamic Conference. Its purpose is to foster economic development and social progress of member countries and Muslim communities throughout the world. It started with 22 member countries but over the years its membership has gone up to 43 countries. The authorized capital of the Bank is 2000 million Islamic Dinars (equivalent to 2 billion Special Drawing Rights of the International Monetary fund). The subscribed capital stands now at 1822.67 million Islamic Dinars.
The bank has assisted in the establishment and growth of Islamic Bank in a number of member countries. It has set up a Research and training Institute to conduct and promote research and impart training in the field of Islamic economics, banking and finance.
The IDB introduced and Investment Deposit Scheme towards the end of 1400H to accept deposits from Islamic banks in order to absorb their surplus liquidity. These deposits were utilized in the foreign trade financing operations by IDB. However, IDB has found it difficult to deploy all these funds and has there for, recently been refusing large deposits from the Islamic Banks.
Dar-al-maal al-Islami
Dar-al-Maal al-Islami (DMI) has played a vital role in the growth and development of the Islamic finance movement.
It is designed as a holding company and established as a legal entity in the form of a authorized capital of $ 1 billion.
The DMI has absorbed in itself the Islamic Investment company and its two affiliates viz, the Shariah Investment Services, Geneva and the Islamic Investment Company, Sharjah, which had already been operating for a number of years.
DMI, which started operations in January, 1982 with a paid up capital of $ 310 million has given utmost attention to setting up of a nit work of Islamic financial institutions which include Islamic Banks, investment companies and Takaful (Islamic insurance).
The Dubai Islamic Bank:
The Dubai Islamic Bank, established in 1975, is one of the pioneers in pioneers in Islamic Banking. The ranges of its investment avenues includes housing, industrial projects and commercial activities. The bank has shown good profit in most of the years and in certain years the retune given to depositors has been we above that given by the conventional banks. Dubai Islamic Bank has invested substantial amounts in Kuwait Finance House, the Bahrain Islamic Bank and the Faisal Islamic Bank of Egypt and Sudan.
The Kuwait Finance House
The Kuwait Finance House was established in 1977 to conduct banking business in accordance with the principles of Shariah “without practicing usury in the form whatsoever”. It has 49 percent participation in its share capital by Government and private individuals have subscribed the rest of the capital. The bank has eight branches in Kuwait and transacts all kinds of banking business within the framework of Islamic Shariah.
Faisal Islamic Bank Sudan
The Faisal Islamic Bank of Sudan was established in 1978. It has succeeded in rapidly expanding its operations.
Faisal Islamic Bank of Egypt
Faisal Islamic Bank of Egypt is the foremost interest-free banking of the country. It started its operations in January, 1978. It has an impressive record of performance.
The Bank Islam Malaysia
The Bank Islam Malaysia, which was established in July 1983, is the second Islamic Bank in South East Asia. Thirty percent of its equity has been taken up by the Federal Government, which has assured strong support to the Bank. Established with a paid up capital of 100 million Ringgit (43 million dollar) the bank is third largest in Malaysia. The bank at present has only one office in the capital of the country but it has an ambitious program of opening branches in all the constituent states.
Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited
Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited was incorporated on 13-03-1983 and received its Banking license on 28-03-1983. The authorized capital of the Bank is Tk. 100.00 crores and paid up capital is Tk. 64.00 crores.
Inspired by the success of Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited 5 other Islamic Banks namely, Al-Baraka Bank, Social Investment Bank, Al-Arafa Islami Bank, Shajalal Bank and Shamil Bank of Bharain have been established in Bangladesh. Prime Bank and Dhaka Bank have established Islamic Branches.
Islamic Bank Bangladesh Ltd.
Introduction:
Bangladesh is one of the largest Muslim countries in the world. The people of this country are deeply committed to Islamic way of life as enshrined in the holy Quran and the Sunnah. Naturally, it remains a deep cru in their hearts to fashion and design their economic lives in accordance with the precepts of Islam. The establishment of Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited on March 13, 1983, is the true reflection of this inner urge of its people, which started functioning with erect from March 30, 1983. This bank is the first of its kind in South-East Asia. It is committed to conduct all banking and investment activities on the basis of interest fee profit-loss sharing system. In doing so, it has unveiled a new horizon and ushered in a new silver lining of hope towards materializing a long cherished dream of the people of Bangladesh for doing their banking transactions in line with what is prescribed by Islam. With the active co-operation and participation of Islamic Development Bank (IDB) and some other Islamic banks, financial institutions, government bodies and eminent personalities of the Middle East and the gulf countries, Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited has by now earned the unique position of a leading private commercial bank in Bangladesh.
Banking plays an important role in the economy of any country. In Bangladesh Muslim constituted more than 80% of its population. These people possess strong faith on Allah and they want to lead their lives as per the constructions given in the holy Quran and the way shown by the prophet Hazrat Muhammad (Sm). But no Islamic banking system was developed here up to 1983. The Traditional banking is fully based on interest or “Riba”. But interest is absolutely prohibited by Islam. As a result the people of Bangladesh have been experiencing such a non-Islamic prohibited banking system against their normal values and faith.
The present world especially the third world is affected by unemployment socio economic injustice inflation, inequitable distribution of income and wealth etc. The main aim of traditional banking is to earn profit by borrowing and lending money in exchange of interest. As a result there is an unfair competition among the bankers and among the customers.
Under conventional framework a bank borrows to lend and it mobilizes savings/deposits by borrowing from savers and loans those deposits to productive interest on deposits and advances respectively. The banks generally maintain a difference is known as interest spread, which is the main income of an interest-based bank. There is no interest received by the Islami Bank. In this case IB receives its entire deposits from the investment of the clients on the basis of profit- sharing place it to the actual entrepreneurs on the basis of the profit sharing. So, it is clear that in case of the traditional banking systems, a fixed percentage of interest, irrespective of income earned is paid to the depositors. The depositors of IB are never deprived of excess income, which the bank may make at the end of year, Not only this traditional bank give fixed interest rate even when they incur operational loss. The critics of Islamic banking system are of the opinion that both are found same in terms of deposits mobilization and advances investment.
Banking functions of IBBL is an important aspect in our economy as it has broken the line of interest based traditional banking system through the introduction Islamic Shariah based banking. Since its commencement in 1983, it has already gained a good reputation in customers as well as the masses of people of Bangladesh. Islamic Banking is especially important in the world countries, which are characterize by unemployment, inequitable distribution of income and wealth, etc. But there are so many constraints in our country in functioning the Islamic Bank Bangladesh Ltd. (IBBL). The paper is an attempted to evaluate the modes of IBBL in terms of productivity and effectiveness. Since it is difficult to measure the productivity of a bank, especially the interest-free IBBL, as it does not any visible product. Some specific indicators have been selected for the purpose of measurement of productivity.
Historical Background of IBBL:
In August 1974, Bangladesh signed the Charter of Islamic Development Bank and committed itself to reorganize its economic and financial system as per Islamic Shariah. In January 1981, Late President Ziaur Rahman while addressing the 3rd Islamic Summit Conference held at Macca and Taif suggested. “The Islamic countries should develop a separate banking system of their own in order to facilitate their trade and commerce”.
This statement of Late President Ziaur Rahman indicated favorable attitude of the Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh towards establishing Islamic banks and financial institutions in the country. Earlier in November 1982, Bangladesh Bank, the country’s Central Bank, sent a representative to study the working of several Islamic Banks abroad.
In November 1982, a delegation of IDB visited Bangladesh and showed keen interest to participate in establishing a joint venture Islamic Bank in the private sector. They found a lot of work had already been done and Islamic banking was in a ready form for immediate introduction. Two professional bodies Islamic Economics Research Bureau (IERB) and Bangladesh Islamic Banker’s Association (BIBA) mode significant contributions towards introduction of Islamic Bank in the country.
They came forward to provide training on Islami Banking to top bankers and economists to fill up the vacuum of leadership for the future Islamic banks in Bangladesh. They also help seminars, symposia and workshops on Islamic economics and banking throughout the country to mobilize public opinion in favor of Islamic banking.
Their professional activities were reinforced by a number of Muslim entrepreneurs working under the aegis to the then Muslim Businessmen society (now reorganized as industrialist & Businessmen Association). The body concentrated mainly in mobilizing equity capital for the emerging Islamic Bank.
At last, the long drawn struggle to establish an Islamic bank in Bangladesh becomes a reality. Islamic Bank Bangladesh Limited was established in March 1983. In which 19 Bangladeshi nationals, 4 Bangladeshi institutions, and 11 banks, financial institutions and government bodies of the Middle East and Europe Including IDB and two eminent personalities of the kingdom of Saudi Arabia Joined hands to make the dream a reality.
Business Philosophy of IBBL:
The philosophy of IBBL is to the principles of Islamic Shariah. The organization of Islamic conference (OIC) defines an Islamic Bank as “a financial institution whose status, rules and procedures expressly state its commitment to the principles of Islamic Shariah and to the banking of the receipt and payment of interest on any of its operations. The sponsor, perception is that IBBL should be quite different from other privately owned and managed commercial bank operating in Bangladesh, IBBL to grow as a leader in the industry rather than a follower. The leadership will be in the area of service, constant effort being made to add new dimensions so that clients can get “Additional” in the matter of services commensurate with the needs and requirement of the country growing society and developing economy.
Mission and objective:
- To conduct interest free banking.
- To establish participatory banking instead of banking on debtor creditor relationship.
- To invest through different modes permitted under Islamic Shariah.
- To accept deposits on profit-loss sharing basis.
- To establish a welfare-oriented banking system.
- To extend co-operation to the poor, the helpless and the low-income group for economic uplift.
- To pay a vital role in human development and employment generation.
- To contribute towards balanced growth and development of the country through investment operations particularly in the less developed area.
- To contribute in achieving the ultimate goal of Islamic economic system.
Objectives of Islami Bank
It is a golden desire of every Muslim that his social and political lives should be in accordance with the divine guides prescribed in the holy Quran and the Sunnah. In the same tune of aspiration as above, he desires to follow a unified life in financial and business life. So, the objectives of the Islamic Banking may be derived from the broader objectives of the Islamic economy. Two quotations may help us understand our objectives.
Ibn al- Qayyim says. The basis of the Shariah is the wisdom and welfare of the people in this world as well as the hereafter. This welfare lies in complete justice, mercy, well-being and wisdom. Anything that departs from justice to oppression, from mercy to harshness, from welfare to misery and from wisdom to folly, has nothing to do with the Shariah Al-Ghazali says, “The very objective of the shariah is to promote the welfare of the people which lies in safeguarding their faith, their life, their intellect, their posterity and their property. Whatever ensures the safeguard of these five serves public interest and is desirable.”
However M. Umer Chapra, in his book “Towards a just Monetary System discussed some of the most fundamental characteristics of Islamic money and banking system. Those are as follows:
- Broad-based economic well-being with full employment and optimum rate for economic ground;
- Socio-economic justice and equitable distribution of income and wealth;
- Stability in the value of money to enable the medium of exchange to be a reliable unit of account, a just standard of deferred payments, and a stable store or value.
- Mobilization and investment of savings for economic development in an equitable manner such that a just return is ensured to all parties concerned, and
- Effective rendering of all services normally expected from the banking system.
Islamic economy including Islamic banking is now entering a new phase, which calls fore more integrative as well as a more critical approach to meet the present day complex financial needs. Now, the economists are faced with the challenging task of reviewing the whole situation emerging at least in three areas.
Firstly, to bring together the works done by different economists into a comprehensive view of the monetary system of Islam in its fullness, as against concentrating on specific, sometimes even disjointed, elements of money and banking.
Secondly, to review critically the different models of Islamic banking presented over the years in the context of the practice of Islamic banking with a view to refining the theory as well as improving the practice.
Thirdly, it is essential to put the whole theory and practice of Islamic banking in the perspective of an Islamic economy and the Islamic moral and social order. Any element of the Islamic system, however important, cannot produce the desired results, if it is allowed to operate in isolation. It must lead to other complementary changes to complete the process.
Role of contribution of IBBL to Bangladesh Economy:
Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited has many success stories of achievements.
It has 263 brances across the country.By providing Banking services among clients.
These are summarized below:
- IBBL is the pioneer institution of Islamic Banking in Bangladesh.
- The success of IBBL has imbibed other sponsors at home and abroad to establish Islamic Banking in Bangladesh. Four national, one international Islamic Banks have since been established in the country. A private sector traditional bank has also established two full-fledged Islamic Banking branches. Several other existing and proposed traditional banks have also expressed their intention to introduce Islamic Banking.
- IBBL has successfully mobilized deposits from a section of people who hither-to-before did not make any deposit with interest based banks.
- The Islamic Banking products which are offered by IBBL through its 118 branches located at important centers all over the country and spontaneous acceptance of those products by the people proves the superiority of Islamic by the people proves the superiority of Islamic banking.
- IBBL’s market share of deposit investment and ancillary business is steadily increasing
- IBBL, through still a tiny bank, handless more than 10% of country’s export and import trade.
- Among the contemporary commercial Banks IBBL’s position is first in respect of mobilization of deposit, deployment of found and earning profit.
- Investment in industrial sector occupies nearly 33% of IBBL’s investment portfolio. This is a unique example of industrial finance by a commercial Bank.
- More than 1.15,000 workers are employed in the industrial projects financed by IBBL. IBBL has thus made significant contribution to solving unemployment problem of the country.
- Dhaka-the capital of Bangladesh being a Mega city has acute transport problem. IBBL has joined hands with an enterprising group to introduce afleet of Premium Bus service, which has attracted the attention of all section of the people and mitigated transportation problem of the city to some extent.
- IBBL invested tk.263225million in 2010
Depositors and entrepreneurs under their fold and coverage. These depositors and entrepreneurs so long avoided interest-based banking on grounds of religious injunctions.
The gradual and successful globalization of Islamic banking coupled with growing awareness of the people about its financial and social benefits makes it clear that the next century is going to be the century of Islamic banking.
Special features of the IBBL:
Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited (IBBL) was incorporated on13.03.1983 as a public company with limited liability under the companies act, 1913. The bank started functioning with effect from 30.03.1983 as the first Shariah based interest-free bank in South-East Asia.
The bank is committed to run all its activities as per Islamic Shariah. IBBL through its steady progress and continuous success has, by now, earned the reputation of being one of the leading private sector banks of the country. The distinguishing features of IBBL are as under:
All it’s activities are conducted on interest-free system according to Islamic Shariah.
- Investment is made through different modes permitted under Islamic Shariah.
- Investment income of the bank is shared with the Mudaraba depositors according to a ratio to ensure a reasonably fair rate of return on their deposits.
- Its aims are to introduce a welfare-oriented banking system and also to establish equity and justice in the field of all economic activities.
- It extends Socio-economic and financial services to the poor, helpless and low-income group of the people for their economic upliftment particularly in the rural areas.
- It plays a vital role in human resource development and employment generation particularly for the unemployed youths.
- Its aim is to achieve balance growth & equitable development of the country through diversified investment operations particularly in the priority sectors and in the less developed areas.
Different Investment Modes of IBBL
Investment:
The special feature of the investment policy of the Bank is to invest on the basis of profit-loss sharing system in accordance with the tenets and principles of Islamic Shariah. Earning of profit is not the only motive and objective of the Bank’s investment policy rather emphasis is given in attaining social good and in creating employment opportunities.
Pursuant to the Investment policy adopted by the Bank a 7-year perspective Investment plan has been drawn up and put into implementation. The plan aims at diversification of the investment port-folio by size sector geographical area, economic purpose and securities to bring in phases all sectors of the economy and all types of economic groups of the society within the fold of Bank’s investment operations.
Accordingly the plan envisages composition of the investment port-folio with 2.50% for agriculture and rural investment, 18% for industrial term investment, 13%for industrial working capital, 10% for housing and real estate, 4% for transport and communication, 0.50% for electricity, gas water and sanitation services, 2% for storage, 43% for import, export and local trade and trade related activities, 1% for poultry and dairy, 2% for Rural Development Scheme, 2.50% for other special Schemes, 0.50% for micro-industry and 1.00% for other productive purposes by the end of the plan period i.e. the year 2002.
Growth of Investment
The investment of the Bank demonstrated steady growth over the years. The total investment of the Bank stood at Taka 187437.32 million in 2008. It was Taka 214615.8 million in 2009. Total investment stood at Taka 263225.1 million as on 30.06.2010. By December 31, 2010 number of investment clients stood at 1,39,738.
Table: Growth of Investment
| Year | Investment( million) |
| 2004 | 35,539.35 |
| 2005 | 67,095.31 |
| 2006 | 100,455.74 |
| 2007 | 120,584.68 |
| 2008 | 187,437.32 |
| 2009 | 214615.8 |
| 2010 | 263225.1 |
Objectives and principles
The objectives and principles of investment operations of the Bank are:
- To invest fund strictly in accordance with the principles of Islamic Shariah.
- To diversify its investment portfolio by size of investment, by sectors (Public & Private), by economic purpose, by securities and by geographical area including industrial, commercial & agricultural.
- To ensure mutual benefit both for the Bank and the investment client by professional appraisal of investment proposals, judicious sanction of investment, close and constant supervision and monitoring there of
- To make investment keeping the socio economic requirement of the country in view.
- To increase the number of potential investors by making participatory and productive investment.
- To finance various development schemes for poverty alleviation, income and employment generation with a view to accelerate sustainable socio-economic growth and upliftment of the society.
- To invest in the form of goods and commodities rather than give out cash money to the investment clients.
- To encourage social upliftment enterprises.
- To shun even highly profitable investment in fields for bidden under Islamic Shariah and are harmful for the society.
- The bank extends investments under the principles of Bai-Murabaha, Bai-Muazzal, Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk and Musharaka. The Bank is making sincere efforts to go for investment under Mudaraba principle in near future.
Investment policy & Strategy:
Investment Policy :
- Strict observance of Islamic Shariah principles.
- Investment to national priority sectors.
- Diversified investment portfolio : Diversification by Size, Sector, Geographical Area, Economic Purpose, Securities and Mode of Investments.
- Preference to short-term investments.
- Preference to investment of Small Size.
- To ensure safety & security of investments.
- To look to profitability of investments.
- To give support to denationalization industrial program of the Government.
- Investment to Trade and Commerce Sector (wholesale, retail and service).
- Investment to Foreign Trade (import & export).
- Investment to Industrial Sectors.
- Exploration of the possibility of investment in the existing Money & capital Market and help organization of Islamic Money & Capital Market.
Investment Strategy:
- To check exodus of investment clients.
- To induct new investment clients.
- To induct good investment clients of other Banks.
- To enhance existing limits of good investment clients, where found necessary and justified.
- Extension of investment to transport sector.
- Extension of investment to backward as well as forward linkage industries.
- Extension of investment to Real Estate Sector.
- Extension of investment to Jute Sector; particularly for trading and export purposes.
- Strengthening supervision, control and monitoring mechanism.
- Training and motivation of manpower to handle increased and diverse volume of investments.
- To give due consideration to high risk, high return and low risk, low return investment proposals.
- Adaptation of modern technology.
1) Bai Mechanism (Trading mode):
a) Bai-Murabaha: Bai-Murabaha may be defined as a contract between a buyer and a seller under which the seller sells certain specific goods (permissible under Islamic shariah and the Law of the land) to the buyer at a cost plus agreed profit payable in cash or on any fixed future date in lump sum or by installments. The profit marked up may be fixed in lump sum or in percentage of the cost price of the goods.
Important Features:
- It is permissible for the Client to offer an order to purchase by the Bank particular goods deciding its specification and committing himself to buy same from the Bank on Murabaha, i.e. cost plus agreed upon profit.
- It is permissible to make the promise binding upon the Client to purchase from the Bank, that is, he is to either satisfy the promise or to indemnify the damages caused by breaking the promise without excuse.
- It is permissible to take cash/collateral security to guarantee the implementation of the promise or to indemnify the damages.
- It is also permissible to document the debt resulting from Bai-Murabaha by a Guarantor, or a mortgage, or both like any other debt, Mortgage/Guarantee/Cash Security may be obtained prior to the signing of the Agreement or at the time of signing the Agreement.
- Stock and availability of goods is a basic condition for signing a Bai-Murabaha Agreement. Therefore, the Bank must purchase the goods as per specification of the Client to acquire ownership of the same before signing the Bai-Murabaha agreement with the Client.
- After purchase of goods the Bank must bear the risk of goods until those are actually sold and delivered to the Client, i.,e., after purchase of the goods by the Bank and before selling of those on Bai-Murabaha to the Client buyer, the Bank shall bear the consequences of any damages or defects, unless there is an agreement with the Client releasing the Bank of the defects, that means, if the goods are damaged, Bank is liable, if the goods are defective,(a defect that is not included in the release) the Bank bears the responsibility.
- The Bank must deliver the specified Goods to the Client on specified date and at specified place of delivery as per Contract.
- The Bank shall sell the goods at a higher price (Cost +Profit) to earn profit. The cost of goods sold and profit mark-up therewith shall separately and clearly be mentioned in the Bai-Murabaha Agreement. The profit Mark-up may be mentioned in lump sum or in percentage of the purchase/cost price of the goods. But, under no circumstances, the percentage of the profit shall have any relation with time or expressed in relation with time, such as per month, per annum etc.
- The price once fixed as per agreement and deferred cannot be further increased.
- It is permissible for the Bank to authorize any third party to buy and receive the goods on Bank’s behalf. The authorization must be in a separate contract.
b)Bai-Muajjal : Bui-Muajjal may be defined as a contract between a buyer and seller under which the seller sells certain specific goods permissible under Islamic Shariah and the Law of the country to the buyer at an agreed fixed price payable at a certain fixed future date in lump sum or within a fixed period by fixed instalments. The seller may also sell the goods purchased by him as per order and specification of the buyer.
Important features:
i) Bank is not bound to declare cost of goods and profit mark-up separately to the client.
ii) Spot delivery of the item and payment is deferred.
iii) Ownership and possession of the goods is transferred by the Bank to the client before receipt of sale price.
iv) Client may offer an order to purchase by the Bank any specified goods and committing himself to buy the same from the Bank on Bai-Muajjal Mode.
v) It is permissible to make the promise binding upon the client to purchase from the Bank. That is, he is to either satisfy the promise or to indemnify the damages caused by breaking the promise.
vi) Cash/Collateral Security should be obtained to guarantee the implementation of the promise or to indemnify the damages.
vii) Mortgage /Guarantee/ Cash Security may be obtained before /at the time of signing the agreement.
viii) Stock and availability of goods is a pre-condition for Bai-Muajjal agreement. The responsibility of the bank is to purchase the desired goods at the disposal of the client to acquire ownership of the same before singing the Bai-Muajjal Agreement with the client.
ix) The Bank after purchase of goods must bear the risk of goods until those are actually delivered to the client.
x) The Bank must deliver the specified goods to the client on specified date and at specified place of delivery as per contract.
xi) The Bank may sell the goods at one agreed price, which will include both the cost price and the profit.
xii) The price once fixed as per agreement and deferred cannot be further increased.
C) Bai-Salam: Bai Salam maybe defined as a contract between a Buyer and a Seller under which the Seller sells in advance in the certain commodity (ies)/ products (s) permissible under Islamic Shariah and the law of the land to the Buyer at an agreed price payable on execution of the said contract and the commodity (ies)/product(s) to the buyer at a future time in exchange of an advanced price fully paid on the spot.
Important features:
- Bai-Salam is mode of investment allowed by Islamic Shariah in which commodity (ies)/ Products(s) can be sold without having the said commodity (ies)/products(s) either in existence or physical/ constructive possession of the seller. If the commodity (ies)/product(s) are ready for sale, Bai-Salam is not allowed in Shariah. Then the sale may be done either in Bai-Murabaha or Bai-Muajjal mode of investment.
- Generally, Industrial and Agricultural products are purchased/sold in advance under Bai-Salam mode of investment to infuse finance so that product is not hindered due to shortage of fund/cash.
- It is permissible to obtain collateral security from the seller client to secure the investment from any hazards viz. non-supply/partial supply of commodity (ies)/product(s), supply of low quality commodity (ies)/product(s) etc.
- It is also permissible to obtain Mortgage and /or personal Guarantee from a third party as security before the signing of the Agreement or at the time of signing the Agreement.
- Bai-Salam on a particular commodity (ies)/product(s) or on a product of a particular field or farm cannot be effected [for Agricultural product(s) only].
- The seller (manufacturer)Client may be made agent of the Bank to sell the goods delivered to the Bank by him provided a separate agency agreement is executed between the Bank and the Client (Agent).
d) Istishna’a : Istishna’a is a contract between a manufacturer/seller and a buyer under which the Manufacturer/seller sells specific product(s) after having manufactured, permissible under Islamic Shariah and Law of the Country after having manufactured at an agreed price payable in advance or by installments within a fixed period or on/within a fixed future date on the basis of the order placed by the buyer.
Important feature:
- Istisna’a is an exceptional mode of investment allowed by Islamic Shariah in which product(s) can be sold without having the same in existence. If the product(s) are ready for sale. Istishna’a is not allowed in Shariah. Then the sale may be done either in Bai-Murabaha or Bai-Muajjal mode of investment. In this mode, deliveries of goods are deferred and payment of price may also be deferred.
- It facilitates the manufacturer sometimes to get the price of the goods in advance, which he may use as capital for producing the goods.
- It gives the buyer opportunity to pay the price in some future dates or by installments.
- It is a binding contract and no party is allowed to cancel the Istishna’a contract the price is paid and received in full or in part or the manufacturer starts the work.
- Istishna’a is specially practiced in Manufacturing and industrial sectors. However, it can be practiced in agricultural and constructions sectors also.
Share Mechanism :
Mudaraba : It is a from partnership where one party provides the funds while the other provides the expertise, labour and necessary business activities. The first party is called the Sahib-al Mall and the letter referred to at the Mudarib. Any profits accrued are shared between the two parties on a pre-agreed basis, while capital loss in exclusively born by the partner providing the capital.
Important features:
- Bank supplies capital as Sahib-Al-Mall and the client invest if in the business with his experience.
- Administration and management is maintained by the client.
- Profit is divided as per agreement.
- Bank bears the actual loss alone.
- Client can not take another investment for that specific business without the permission of the Bank.
Musharakah : The terma “Shirkat” and Musharaka” have been derived from Arabic worids “Shairkah” and “Sharika” The word shirkah means a partnership between more than one partner. Thus the word “Musharaka” and “Shirkat” means a partnership established between two or more partners for purpose of a commercial venture participated both in the capital and management where the profit may be shared between the partners as per agreed upon ratio and the loss. If any incurred, is to be borne by the partners at per capital/equity ratio.
In this case of Investment, “Musharaka” meaning a partnership between the Bank and the Client for a particular business in which both the Bank and the Client provide capital at an agreed upon ratio and manage the business jointly. Share the rent as per agreed upon ratio and bear the loss, if any in proportion to their respective equity.
Bank may move itself with the selected Client for conducting any Shariah permissible business under Musharaka mode.
Important features:
- The investment client will normally run and manage the business.
- The Bank shall take part in the policy and decision making as well as overseeing (supervision and monitoring) the operations of the business of the Client. The Bank may appoint suitable personal(s) to run the manage the business and to maintain books of accounts of the business property.
- As the investment client shall manage the enterprise, the Bank may pay more share of profit to him than that of his proportionate capital contribution.
- Loss, if any, shall be shared on the basis of capital ratio.
Leasing Mode (Ijara Mechanism):
A) Hire purchase/ Ijarah : The term Ijarah has been derived from the Arabic works Ajr and Ujrat which means consideration, return, wages or rent. This is really the exchange value or consideration, return, wages, rent of service of an Asset. Ijarah has been defined as a contract between two parties, the Hiree and Hirer where the Hirer enjoys or reaps a specific service or benefit against a specified consideration or rent from the asset owned by the Hiree. It is a hire agreement under which a certain asset is hired out by the Hiree to a Hirer against fixed rent or rentals for a specified period.
B) Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk:
Meaning and Definition:
Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk is a Special type of contract, which has been developed through practice. Actually, it is a synthesis of three contacts:
- Shirkat
- Ijarah and
- Sale
These may be defined as follows:
i) Shirkatul Melk
Shirkat means partnership. Shirkatul Melk means share in ownership. When two or more persons supply equity, purchase an asset, own the same jointly, and share the benefit as per agreement and bear the loss in proportion to their respective equity, the contract is called Sharkatul Melk contract.
ii) Ijarah
The term Iiarah has been derived from the Arabic works (Air) and (Uirat) which means consideration, return, wages or rent. This is really the exchange value or consideration, return, wages, rent of service of an asset. Ijarah has been defined as a contract between two parties, the Hiree and Hirer where the Hirer enjoys or reaps a specific service or benefit against a specified consideration or rent from the asset owned by the Hiree. It is a hire agreement under which a certain asset is hired out by the Hiree to a Hirer against fixed rent or rentals for a specified period.
iii) Sale
This is a sale contract between a buyer and a seller under which the ownership of certain goods or asset is transferred by seller to the buyer against agreed upon price paid / to be paid by the buyer.
Thus, in Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk mode both the Bank and the Client supply equity in equal or unequal proportion for purchase of an asset like land, building, machinery, transports etc. Purchase the asset with that quit money, own the same jointly, share the benefit as per agreement and bear the loss in proportion the their respective equity. The share, part of portion of the asset owned by the Bank is hired out to the Client partner for a fixed rent per unit of time for a fixed period. Lastly the Bank sells and transfers the ownership of it’s share/part/portion to the client against payment of price fixed for the part either gradually part by part or in lump sum within the hire period or after the expiry of the hire agreement.
Important Features:
- In case of Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk transaction the asset/ property involved is jointly purchased by the Hiree (Bank) and the Hirer (Client) with specified equity participation under a Shirkatul Melk Contract in which the amount of equity and share in ownership of the asset of each partner (Hiree Bank & Hirer Client) are clearly mentioned. Under this agreement, the Hiree and the Hirer become co-owner of the asset under transaction in proportion of their respective equity participation.
- In Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk Agreement, the exact ownership of both the Hiree (Bank) and Hirer (Client) must be recognised. However, if the partners agree and wish that the asset purchased may be registered in the name of any one of them or in the name of any third party, clearly mentioning the same in the Hire Purchase Shirkatul Melk Agreement. However, in IBBL, no third party registration shall be allowed.
- The share/ part of the purchased asset owned by the Hiree (Bank) is put at the disposal/ possession of the Hirer (Client) keeping the ownership with him (Bank) for a fixed period under a hire agreement in which the amount of rent per unit of time and the benefit for which rent to be paid along with all other agreed upon stipulation are also to be clearly stated. Under this agreement, the Hirer (Client) becomes the owner of the benefit of the asset but not of the asset itself, in accordance with the specific provisions of the contract which entitles the Hiree (Bank) is entitled for the rentals.
- As the ownership of hired portion of the asset lies with the Hiree (Bank) and rent is paid by the Hirer (Client) against the specific benefit, the rent is not considered as price or part of price of the asset.
- In the Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk Agreement the Hiree (Bank) does not sell or the Hirer (Client) does not purchase the asset but the Hiree (Bank) premise to sell the asset to the Hirer (Client) part by part only, if the Hirer (Client) pays the cost price/equity/agreed price as fixed for the asset as per stipulation within agreed upon period on which the Hirer also gives undertakings.
- The promise to transfer legal title by the Hiree and undertakings given by the Hirer to purchase ownership of the hired asset upon payment part by part as per stipulations are effected only when it is actually done by a separate sale contract.
- As soon as any part of Hiree’s (Bank’s) ownership of the asset is transferred to the Hirer (Client) that becomes the property of the Hirer and hire contract for that share/part and entitlement for rent thereof lapses.
- In Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk Agreement, the Shirkatul Melk contract is effected from the day the equity of both parties deposited and the asset is purchased and continues up to the day on which the full title of Hiree (Bank) is transferred to the Hirer (Client).
- Hire Purchased under Shirkatul Melk transaction facilitates the Client (Hirer) to get benefit from the hired asset in exchange of rental and also to become full owner of the asset by purchasing it part by part.
- If, for any reason, the hire contract is revoked prior to the transfer for full title of the asset to the Hirer, then the title of the asset will be shared by both Hiree and Hirer – the Hirer will share that part of title which has been transferred to him against payment and the Hiree will share the remaining part.
- The Hirer to secure the Bank (the Hiree) will pledge/ hypothecate / mortgage his portion / part / share in the asset (acquired / to be acquired) and or any other asset/ property of his own / third party guarantor to the Bank to fulfill his all liabilities/ commitments including the accrued rental, if any.
Rules for Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk
- It is a condition that the subject (benefit/service) of the contract and the asset (object) should be known comprehensively.
- It is a condition that the asset(s) to be hired must not be a fungible one (Perishable or consumable) with can not be used more than once or in other words, the asset(s) must be a non-fungible one which can be utilized more than once or the use/benefit/service of which can be separated from the asset(s) itself.
- It is a condition that the subject (benefit/service) of the contract must actually and legally be attainable/derivable. It is not permissible to hire something, the handing-over of the possession of which is impossible. If the asset is a jointly owned property, any partner, according to the majority of the jurists, may let his portion of the asset(s) to co-owner(s) or the persons(s) other than the co-owner(s). However, it is also permissible for a partner to hire his share to the other partner(s).
- It is a condition that the Hirer shall ensure that he will make use of the asset(s) as per provisions of the Agreement or as per customs/norms/practice, if there is no expressed provision.
- The hire contract is permissible only when the asset(s) and he benefit/service derived from it is within the category of ‘Hala’ or at least ‘Mobah’ as per Islamic Shariah.
- The Hiree is under obligation to enable the Hirer to the benefit from the asset(s) by putting the possession of the asset(s) at his disposal in useable condition at the commencement of the hire period.
- In a hire contract, the period of hire and the rental to be paid per unit of time be clearly stated.
- Everything that is suitable to be considered a price, in a sale, can be suitable to considered as rental in a hire contract.
- It is a condition that the rental falls due from the date of handing-over of the asset to Hirer and not from the date of contract or use of the asset.
- It is permissible to advance, defer or install the rental in accordance with the Agreement.
- It is permissible to review the hire period or the rental or the both, if the Hiree and the Hirer mutually agree to do so.
- The hired asset is a trust in the hands of the Hirer. He will maintain the asset(s) with due produce and shall not be held responsible for the damage or destruction of the asset without transgression, default or negligence, otherwise he must be responsible for the same.
- The Hiree/owner bears all the costs of legally binding basic repairs & maintenance including the cost of replacement of durable parts on which the permanence and suitability of the hired asset(s) depend or as per Contract.
- It is permissible to make the Hirer to bear the cost of ordinary routine maintenance, because this cost is normally known and can be considered as part of the rental.
- It is permissible for the Hirer to let the asset to a third party during the hire period whether for the same rental or more or less as long as the asset is not affected by the change of user and not barred/restricted by the hire agreement/customs to do so.
- It is permissible to purchase an asset bearing a hire contract. The hire contract may continue since the purchaser agrees to its continuity up to the end of the hire term. All rights and liabilities emanating from the hire contract will transfer to the new owner. But if the sale-contract is drawn and the purchaser is oblivious of the hire contract, he has the right to rescind the purchase contract and the hire continues.
- As soon as the hire period terminates, the Hirer is under obligation to return the asset to the owner or if the Hiree agree he may enter a fresh hire contract or purchase it from the Hiree on payment of agreed upon price as per market rate.
- The hire contract is binding and no one party shall unilaterally rescind except reasons that abrogate binding contract such as damage or destruction.
- If the hired asset is damaged or destructed by the act of Allah and if the Hiree offers a substitute with the same specifications agreed upon in the hire contract the contract does not terminate.
- It is also permissible to sell the hired asset by the Hiree to the Hirer during the tenure of the hire period either part by part or in full at a time. As soon as any part or in full the asset is sold during the tenure of the hire agreement the hire contract for that part of for the full asset as the case may be, be lapsed and the rental ceased to apply accordingly.
- It is permissible for the Hirer to promise or to give undertaking to purchase the hired asset during the tenure of the hire period, either part by part or in full or at the end of the hire period in full. It is also permissible for the Hiree to give similar promise to sell the asset.
- The hire with promise to purchase and sale is different from the memorandum of sale. The rent paid by the Hirer cannot, in any way, be considered as part of the price of the asset, rather it is the price of the service of that asset.
- In a Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk contract, it is permissible to divide the sale/cost price of the asset or ownership of the Hiree to the asset into several part of the price of the asset; rather it is price of the service of the asset.
- In a Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk contract, it is permissible to divide the sale/cost price of the asset or ownership of the Hiree to the asset into several parts and to sell each part of ownership on payment of proportionate sale/cost price of the Hiree.
- Under Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk Agreement, both the Hiree and the Hirer must pay their respective equity as agreed upon to purchase the demised asset under joint ownership.
- Ownership of the asset of both the Hiree and the Hirer should be recognized as per law of the land.
Operational Procedure in IBBL:
Modus Operandi: The Modus Operandi of Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk will be as follows:
Induction of client:
- Hole preliminary discussion with the prospective Client regarding his Investment needs, business experience, viability of the project and Shariah permissibility of the asset, the business and the uses of the asset.
- Brief him on the salient features of Hire Purchase under Shirkatul Melk mode of Investment. Apprise, in particular, the usual terms and conditions under which the Bank makes such investment. Discuss about Clients’ equity participation and its immediate availability.
- Look to the past performance of the Client, Check-up Head Office Current Investment Policy and Branch’s track record of Hire purchase under Shirkatul Melk Investment of the item(s).
- If the Proposal is found permissible under Islamic principles and suitable, advise the Client to submit formal Application. If not found suitable, regret politely.
- Request potential Client to open an Al-Wadia Current Account. Let him maintain the Current Account. Let him maintain the Current Account satisfactorily for a reasonable period. (This will generally mean six month).
Application
- Obtain application in triplicate from the Client of F-167A and record the same in the Investment Proposal Received and Disposal Register (B-53).
- Obtain and affix attested photograph(s) of the Proprietor / Partner/ Directors / Trustee / Administrator on the top right hand corner of the application.
Scrutinize the application of the Client to see that –
- All columns are properly filled in;
- Particulars and information given therein are complete and correct in all respects;
- All required Documents/Papers as listed in the footnote for the applications are submitted.
- It is signed by the Client as per specimen signature with the Bank and duly verified by the authorized official of the Bank.
Some general instruction
- Rates stamp duty on various types of documents will be supplied by the concerned department of Head office, (Law department), from time to time.
- Signature of the Client on Documents should be verified by the Incumbent-in-charge/ authorized official in pencil.
- Before preserving the documents in strong Room, the investment committee of the branch should certify that all the formalities of documentation have been properly done and completed strictly as per terms of the sanction advice (A format to be developed for the certificate as per Performa).
- After completion of documentation, enter the documents in documents execution register; put into an envelope/file cover duly inscribing the name of the client deal-wise and preserve in the strong room in fire proof safe/Almirh under Joint custody of the incumbent-in-charge of the branch and the officer-in-charge of the investment department 2nd officer of the Branch.
Special Investment Schemes:
The Bank, since its inception, has been working for the upliftment and emancipation of the underprivileged, downtrodden and neglected sections of the populace and has taken up various schemes for their well being. The objectives of these schemes are to raise the standard of living of low-income group, development of human resources and creation of avenues for self-employment. There are shown different types of investment under different investment scheme. They are shown by a graph:
(TK. Million)
| Serial No | Name of Scheme | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | Household Durable Scheme | 961.64 | 686.49 | 638.4 |
| 2 | Housing Investment Scheme | 418.92 | 452.67 | 429.24 |
| 3 | Real Estate Investment Program | 10154.95 | 7933.20 | 7183.26 |
| 4 | Trasport Investment Scheme
| 4732.15 | 3630.48 | 3087.55 |
| 5 | Car Investment Scheme | 138.79 | 53.81 | 41.16 |
| 6 | Investment Scheme For Doctor | 15.27 | 17.06 | 15.34 |
| 7 | Small Business Investment Scheme | 1703.44 | 1159.63 | 1104.65 |
| 8 | Agiculture Implements Investment Scheme | 127.15 | 76.64 | 27.21 |
| 9 | Micro Industries Investment Scheme | 47.44 | 50.39 | 31.50 |
| 10 | Rural Development Scheme | 5110.00 | 3752.20 | 3011.72 |
| Sub Total | 23410.00 | 17812.57 | 15570.03 | |
| Total | 263225.00 | 214616.00 | 18054.00 | |
| % of Total Investment | 8.89% | 8.30% | 8.65% |
Household Durables Scheme
The objective of the scheme is to increase standard of filing and qualify of life of the fixed income group by extending them investment facilities to purchase household articles such as furniture like Almirah, sofa set, wardrobe; electric and electronic equipment like television, refrigerator, gas cooker; air conditioner, PC, washing machine; electric generator-IPS, UPS; motor cycle; corrugated iron sheet, cement, rod, wood etc, for construction of dwelling house; gold ornaments, tube-well, mobile telephone set etc; medical/ engineering instruments/equipment, computer, books etc for students.IBBL invest this sector in 2010.
Housing Investment Scheme
The Bank has introduced this scheme recently to ease the serious housing problem in the urban areas and to make arrangement for comfortable accommodation of the fixed income group.
Officials of the Defense Forces: Permanent Officials of Government, Semi-Government and Autonomous Organizations; Teachers of the established Universities, University Colleges & Medical College: Graduate Engineers, Doctors and Established professionals; Bangladeshi Officials of reputed Multinational Companies, International Financial Organizations, Donor Agencies, Foreign Embassies etc. Officials of local established & reputed public Limited Companies; Wage Earner professionals like Doctors, Engineers, Accountants, Teachers and other profession doing good job abroad with hand-some pay-package shall be eligible to apply for availing investment facilities under the Scheme.
Real Estate Investment Program
Professionals, Service-holders, Businessmen, Real Estate Developer and other categories of people who are not entitled for availing investment facilities under Housing investment Scheme, shall be eligible under this program. Investment is to be extension/ completion of the house already constructed, commercial building. Shopping complex, flat/ apartment etc.
Transport Investment Scheme
To ease the existing transportation problem and ensure speedy economic growth and development of the country particularly the expansion of trade, commerce and industry, the Bank has taken up this Scheme. Under this Scheme investment is being allowed to the existing successful businessmen and potential entrepreneurs in this sector for all types of road and water transport like bus, mini-bus, truck, launch, cargo-vessel, transport for rent-a-car service; and baby taxi, tempo, pick-up van for self-employment; and ambulance for clinic & hospital. The Bank is also extending investment facilities to multinational companies, established business houses and well to do officials and professionals for acquisition of private cars, microbus and jeeps.
Car Investment Scheme
Car is considered as an essential mode of transport in the modern society, particularly by a section of the officials, business houses and business executives and established professionals for movement in discharging their duties and responsibilities punctually and efficiently. To meet this need, Islami Bank has introduced the “Car investment Scheme” for the mid and high ranking officials of government and semi-government organizations, corporations, executives and directors of big business houses and companies and also for persons of different professional groups on easy payment terms and conditions.
Investment Scheme for Doctors
The Bank has taken up this Scheme to help unemployed qualified doctors to go for self- employment and to provide latest medical equipments to specialist doctors to extend modern Medicare facilities throughout the country.
Small Business Investment Scheme
This Scheme has been taken up for self-employment of educated unemployed youths of rural and urban areas and to provide investment to small businessmen and entrepreneurs. Investment is extended for about 200 economic activities in sectors as live-stock, fishery, agro-trading/shop-keeping, transportation, agricultural implements, forestry and service viz. laundry, signboard painting etc.
Agriculture Implements Investment Scheme
In keeping with view of the people-oriented and welfare objectives of the Bank, this scheme has been introduced to provide power tillers, power pumps, shallow tube wells, thresher machines etc. on easy terms to unemployed rural youths for self-employment and to the farmers to help augment production in agricultural sector.
Micro-Industries Investment Scheme
To create wider base for industries as well as to encourage establishment of micro-industries in different areas of the country by the potential entrepreneurs and for diversification of the Bank’s investment portfolio, the Bank introduced ‘Micro industries Investment Scheme’. Different sectors including food and agriculture based industries, plastic & rubber industries, forestry and forestry and furniture industries, engineering industries, leather industries, chemical industries, textile industries, recycling industries, service industries, electrical accessories industries, computer technology industries, paper products industries, handicrafts industries, fishery & live stock farming, hollow bricks, roof tiles and any other viable micro-industries have been identified for financing under the Scheme.
Rural Development Scheme
Bangladesh is predominantly an agricultural country with vast majority living in rural areas. Near than 60% of the people live below the poverty line. Seasonal unemployment and under idle and without job in most of the time of the year. As a result people in large number are migrating to urban areas, particularly in metro polish in search of employment thereby creating social and environment hazards. Islami Bank has, therefore, taken up a Scheme to reactive the rural economy and develops model villages through integrated rural development approach. The objective of the Scheme is to create income generating and productive self-employment opportunities through extension of investment for the development of rural areas and thereby contribute in alleviating rural poverty. Investment will be allowed for the purpose of, amongst others, production of 21 types of main crops viz. food, cereals and cash crops, off-farm activities like dairy, beef fattening, goat rearing, poultry, shop keeping, peddling etc, rural transport like rickshaw, rickshaw-van, cart etc; irrigation equipment, hand tube-well, housing materials. in all covering about 343 types of economic activities, Islami Bank Foundation, a subsidiary of the Bank, engaged in social welfare activities shall, side by side, take care of the requirement of sanitation, Medicare and education of the villages through integrated area development approach under Islamic model.
Kaligonj Garments Weavers Investment Scheme
The Scheme has been taken up to assist the Garments weavers of Kaligonj area particularly in respect of requirement of working capital, BMRE of existing unit by adding further machineries, to develop new entrepreneurs and to assist the workers for getting further training for producing products of various modern design and for modernization of the Garments Sector.
SME Investment:
Alike developing country of Bangladesh SME Lone is very important for developing economy. IBBL invest this types of loan in small and middle enterprise. The investment of SME are increasing day by day. Three years investment in SME are shown below:
(Tk. Million)
| Year | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| SME invest | 78456 | 57159 | 37154 |
| Increasing | 21297 | 200005 | 14540 |
| Rate of Increasing | 37% | 54% | 64% |
Opportunity & Threats of IBBL in Bangladesh.
Despite tremendous popular support spectacular success in terms of mobilization of deposit and distribution of profit Islamic banking in Bangladesh yet to achieve the desired level of success due to the absence of appropriate legal framework for carrying out Islamic Banking operations in the country. All the government- approved securities in Bangladesh are interest bearing, Besides, Islamic Money Market in Bangladesh is yet to develop. As a result the Islamic banks, which are committed to avoid interest, cannot invest the permissible part of their Statutory Liquidity Reserve and short Term Liquidity in those securities.
Inspire of the present limitations, Islamic -banking system has tremendous potentiality and prospect in Bangladesh, Firstly, the successful launching and needs to an Islamic Money Market in the country. Secondly Islamic banks have brought together man.
Conclusion
Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited has made an evaluation in the conventional banking system. This bank is committed to run all it’s activities as per Islami Shriah of IBBL through its continued success and steady progress has, by how, earned the reputation of being one of the leading probate sectors banks of the country. It has made revaluation specially in the field of bank investment IBBL became successful in proving that bank investment can be made properly, Profitably following profit and loss sharing concept with abolishing interest, and which is also beneficial to human being and society. And these all characteristics of bank investment are absolutely absent in case of conventional bank. Islami money market in Bangladesh is yet to develop. As a result the Islamic Banks which are committed to avoid interest can not invest the permissible part of their strategy liquidity reserve and short term liquidity surplus in those securities.
In spite of the present limitation, Islami banking system has tremendous potentiality and prospect in Bangladesh. Firstly, the successful launching and operation of Islami bank in Bangladesh has established the fact that banking without interest is feasible. Secondly, the launching of Islami Bank has shown the needs of an Islamic money market in the country. Thirdly, Islami Bank has brought together many depositors and entrepreneurs under their fold and coverage. These depositors and entrepreneurs so long avoided interest-based banking on ground of religious injunctions.
Recommendations
During the period of preparing my Master Paperabout different modes of investment of Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited, Zinzira Brance, our recommendations about operation of IBBL are as follows:
- Islami Bank Bangladesh Limited should establish new/updated financial products to attract to potential depositors.
- Customer’s credit scheme should ameliorate by various modern banking systems.
- IBBL ought to also precede incorporate “On Line Banking” or “Electronic Banking” keeping in mind up coming competition of the challenging age.
- Current portfolio should be exaggerated. Not to give weight only in working capital financing.
- Information technology of IBBL should be updated more over there is no Internet connection available in the IBBL. So, IBBL should develop IT to ensure better service to the customers and support communication with outside.
- Regarding the investment modes, Shariah law should be expanded among the potential investors.
- Salary has been recently increased by IBBL, which is very significant decision to motivate among the employees, and this decision should be continued.
When contact is made between the IBBL and client then IBBL always maintains the Shariah law but most of the client puts the signature without witting the Shariah law, which creates problem between the IBBL and client in letter.