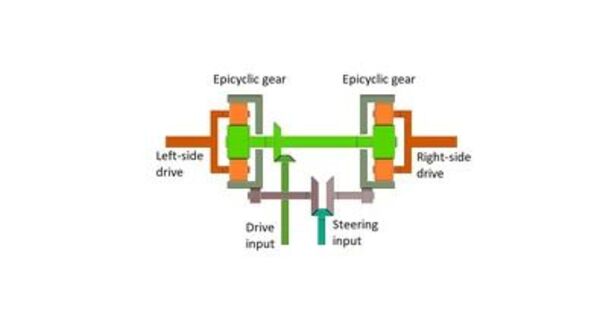
Cross-drive steering transmissions are used in tracked vehicles to provide precise and energy-efficient steering. It usually refers to a system utilized in specific vehicles, especially in heavy-duty or specialized applications where regular steering methods may not be appropriate or efficient. In this configuration, power is transferred from the engine to the wheels via a transmission system that enables both propulsion and steering.
It consists of the following main parts:
- two identical single-stage planetary gearings,
- a differential,
- a hydraulic pump connected to the engine (similar to an oil pump of cars),
- a hydraulic motor powered by the hydraulic pump,
- hydraulic control valves.
A steering transmission combines the two tasks required for a tracked vehicle transmission: a transmission to connect the relatively constant engine speed to varied road speeds, and a steering gearbox to drive the two output shafts (and hence the tracks) at various speeds, thereby steering the vehicle.
A cross-drive steering transmission system transmits power from the engine to all wheels, and steering is accomplished by regulating the distribution of power to individual wheels or sets of wheels. This can be accomplished using a variety of technologies, including differential steering, hydraulic systems, and electronically controlled systems.
Applications
Cross-drive steering transmissions are commonly used in off-road vehicles, agricultural machinery, and military vehicles that require high mobility and traction. These vehicles are more capable of navigating difficult terrain since they can independently adjust the speed and direction of each wheel.
Overall, cross-drive steering transmission systems improve agility and control in specialist vehicles, allowing them to function effectively in a variety of conditions.