Executive Summary
Rupali Bank Ltd Postagola Branch was created and commencement of business started on 1988. As a fully licensed commercial Bank, Rupali Bank Limited is being managed by a highly professional and dedicated team with long experience in banking. The Bank has been graded as a top class Bank in the country through internationally accepted CAMEL rating. Rupali Bank Limited offers all kinds of Commercial, Corporate and Personal Banking services covering all segments of society within the framework of Banking Company Act and rules and regulations laid down by Bangladesh Bank.
The aim of the Bank is to participate actively in the socioeconomic development of the nation by operating a commercially sound banking system. To accept deposit from the customer and to lend the deposit again to customer is the Prime business of Rupali Bank.
The main activities of Rupali Bank are Commercial Banking, Corporate Banking Retail Banking and Islami Banking. Prime Bank’s products can be broadly classified in two groups i.e. Depository product and Loan product.
The Rupali Bank Limited is offering different loan and advances products to the client for financing diverse purposes that fulfill the requirements of the Bank and have good return on the investment as well satisfy clients.
Origin Of the Report:
As the students of Masters of Business Administration (M.B.A) study the subject’s related to business including Accounting, Management, Finance, Marketing, Mathematics, Social and cultural status and little about science and technology. The schools of business at home and abroad try to familiarize each student as they move comfortably in the business environment. But only the theoretical study in the class rooms is not enough rather a practical experience and the only means of practical experience is internship program.
In the business environment at home & abroad there are lots of financial institution, business firms, and industries which provide this facility towards us. If we could not get this facility of internship then a wide gaps will take place between our study and experience. I think this is an extremely valuable asset for us.
As the students of business do this usually for there months. In our country there are many banks particularly the esteemed private sector banks, and elite business firms provide this. In this respect I have done my internship at Rupali Bank Ltd.
Statement of problem:
The main business of a bank is credit. Bank lends individual , Private sector as well as public sector enterprise. Every bank follow its own process for credit management. Commercial bank usually follow committee or sequential process of credit approval. After credit approval and completion documentation bank make disbursement. How long will be disbursed is generally mentioned in the credit negotiation. It is customary that term loans are disburse on installment basis and short term loans are transfer to borrowers account. Borrowers can withdraw from his/ her account when deem it necessary. After disbursing credit, credit officer’s bank is to continuously monitor and review the performance of borrowers. Recovery of credit is the last step of credit management process. It is expected that loan will be repaid after its tenure. But a problem arise when loan becomes a problem loan. Bank are using many alternatives for recovery of problem loan.
Objective of the study:
- Application of theoretical knowledge in the practical field.
- Understand the real management situation and try to suggest for improving existing problems.
- To analyze the financing system of the Bank to find out if the Bank has any field to improve upon and to have greater contribution towards country’s economy.
- To examine the profitability and productivity of the Bank.
- To acquire knowledge about the every day banking operation of Rupali Bank Ltd.
- To know about different types of loan .
- Recovery system of loan.
Scope of the Study:
This report is covered by the structural, functional and overall performance of Rupali Bank Ltd.But it is totally written down depending on a branch activity named Posta gola Branch”.
Methodology:
While conducting the study, sources were explored for primary information and data. But hardly any updated data could be found. In the absence of updated information or data dependence on secondary data has been inevitable. However, whenever possible primary data has been used. Data were also collected by interviewing the responsible officers and from some documents & statement printed by the bank and website of Rupali Bank Ltd.
Sources of Data:
The following sources have been used for the purpose of gathering and collecting data as required.
a).Primary Data:
I) Official records of Rupali Bank Ltd.
II) Face to face Conversation.
III) Data collection by own supervision.
b).Secondary Data:
I) Annual report
II) Working Papers
III) Office Files
IV) Printed Forms
V) Published & Unpublished Documents
VI) Website
Data analysis:
To analysis data , mean level of satisfaction would be calculated to execute the objective the study.
Limitations of the study:
There are certain limitations regarding the studies that are summarized below:
- Deficiencies in data required for the study.
- Field practice varies with the standard practice that also created problem.
- Time provided for conducting the study is another important constraint.
Findings and Recommendation:
Findings and recommendation will be presented through a formal report. In the report findings will be presented in a descriptive as well as in a summarized manner so that the reader can easily understand the findings and use the information of the report further. Necessary recommendation will be made so that authority of Rupali Bank Ltd can develop these sector.
Back ground of Rupali Bank Ltd
Rupali Bank Ltd was constituted with the merger of 3(three) erstwhile commercial banks I.e. Muslim commercial Bank Ltd., Australasia Bank Ltd. And Standard Bank Ltd. Operated in the then Pakistan on March 26,1972 under the Bangladesh Banks (Nationalization) order 1972(P.O No.26 of 1972)Withalltheir assests,benefits,rights,powers,authorities,privileges,liabilities,borrowings,and obligations. Rupali Bank worked as a nationalized commercial bank till December 13 1986.
Rupali Bank Ltd. Emerged as the largest Public Limited Banking company of the country on December 14 1986 under the order No.Avg/Avwe/weK-3/33/86/361 of the govt. of the peoples Republic of Bangladesh
Mission of the Bank :
The bank participates activity in socio – economic development of the country by performing commercially viable and socially desirable banking function.
Vision:
To be in the front of national development by providing all the customers inspirational strength, dependable support and the most comprehensive range of business solution through our team of professional that work passionately to be outstanding in everything we do.
Goal of the Bank:
To share a significant portion of the banking sector’s by utilizing available manpower and also state of the art technology for maximizing the shareholders wealth.
Chief Executive:
The is headed by the Managing Director (chief executive) who is a reputed professional Banker.
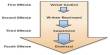
Organogram of Rupali Bank Ltd:
Managing Director
Deputy Managing Director
General Manager
Assistant General Manager
Senior Principal officer
Principal officer
Senior officer
Officer
No. of Branches
Rupali Bank Ltd operates through 492 branches .It is linked to its foreign correspondents all over the world.
Numbers of zones and Corporate Offices:
The Corporate Head office of the Bank is located at Dhaka with one local office (main Branches),four corporate branches at Dhaka, one in Chittagong and twenty- five zonal offices all over the country.
International Banking;
Rupali Bank Ltd. Engages itself in providing best international banking service to its valued clients by serving through 28 Authorized Dealer branch.
It has a good number of correspondent banks world-wide and it handles a big volume of export and import business. It is also engaged in collecting home-based remittances of the people and paying the to the beneficiary promptly.
Products and Services:
A. Deposit Product
- Current Deposit
- Saving Product
- RDPS
- FDR etc
B. Lending Product
1. Lone General
2. Project Loan
3. Transportation Loan
4. HouseBuilding Loan
5. Small Business Loan
6. Personal Loan , etc
C. Money Transmission Product
1. Demand Draft
2. Pay Order
3. Telegraphic transfer
4. Letter of credit , etc
General Banking at Rupali Bank Ltd
During my practical orientation I was placed in Rupali Bank Limited. First I was placed in Federation Branch. I have completed General Banking and some exposure in Advance in this branch. General Banking is the starting point and main function of all the banking operations it is the department which provides day-to-day service to the customers. Everyday it collects deposit from the customers by allowing broking interest rate, meets their demand for cash by honoring Cheques and lend it to the customers against ending interest rate. Lending interest rate in higher than borrowing interest rate, this is the profit for the bank.
Functions of this department
♦This department maintains following functions.
♦Accounts opening section.
♦Cash section Remittance section.
♦Clearing section.
♦Accounts section.
♦Establishment.
Accounts Opening Section
This section opens different types of account for their valued customers. Selection of customer is very important for the bank because bank’s success and failure largely depends on their customers. If customers are bad they creates fraud and forgery by their account with bank and, this destroys the good will of the banks. So, this section takes extreme caution in selecting its valued customer.
Operational Nature of Accounts
♦ Current Deposit Accounts (CD account)
– A current account may be opened by any individual, firm, company, club, associates, etc. Bank: may, however, refuse without assigning any reasons to open current account to any body.
– Minimum balance of Tk. 1000 while open.
– No current account will be opened with Cheques.
– Fund in the current deposit account shall be payable on demand.
– Minimum balance to be maintained of Tk. 1000.
– No interest is payable on the balance of CD.
– In case of closing of current account Tk. 100 is to be realized against incidental charges.
♦ Saving Deposit Accounts (SB account):
– 6.00% interest is provided to depositors.
– The minimum amount of balance to be maintained with this type of account is Tk. 1000.
– A depositor can withdraw two times in a week for more withdrawal depositors are not entitled for any interest.
– To withdraw above Tk. 20,000 the depositors has to notice.
– No savings account will be allowed to be overdrawn.
♦ Short term deposit (STD A/C)
– Generally opened by big business firm.
– Interest depends on the amount deposited.
– Minimum amount of balance has to be maintained with STD account is Tk 1000 or more while open.
– Interest is given at a rate of 3%
– Minimum amount is Tk 1000 must be maintained.
♦ Rupali Bank Savings Scheme (RDS)
– This is a scheme to make the customer introduced to the banking system under this schemes the customers are to pay a certain of money at monthly interval up to a period of 5 to 10 years and after the period they will get the returns along with the full interest earned during the period and the principal amount. Most of the clients under this scheme are middle class and lower middle class people
– Generally opened by small sever.
– Minimum Amount Tk 500 and maximum Tk 5000.
RDS: 5 Years term 10 Years term
Monthly installment
Amount payable after maturity
Monthly
installment
Amount payable after maturityTk. 500Tk. 35773Tk. 500Tk. 85860Tk. 1000Tk. 71547Tk. 1000Tk. 171721Tk. 1500Tk. 107321Tk. 1500Tk. 257582Tk. 2000Tk. 143095Tk. 2000Tk. 343442Tk. 3000Tk.214642Tk.3000Tk.515164TK. 5000Tk.357738Tk.5000Tk.858607
Liquidation of RDS
– In case of premature encashment if the period is below 1 year then no interest will be provide.
– ff above 1 year interest will be given @ Savings.
♦ Fixed Deposit Reserve (FDR)
– FDR is neither transferable nor negotiable.
– It can be opened by all.
– Provided 9.50% – 11.00% interest.
– Interest rate very on period.
– The deposited principal amounts have not fixed by the Bank.
– One can deposit any sum of amount under fixed deposit reserve.
– In case of with drawl before maturity the previous maturity period is considered to pa: interest according to savings interest rate 9.5% it is known as pre matured en-casement.
Interest rate have been rated by the Management of Rupali Bank on FDR have given below
| Maturity period | Rate of interest |
| 3 month | 9.50% |
| 6 month | 10% |
| 1 year | 10.50% |
| 2 year | 11.00% |
Liquidation of FDR:
– Only the account holder himself and the authorized person can liquid the FDR after maturity.
– In case of joint name authentication from both is necessary.
– If demand before maturity the last expired duration is considered to pay interest.
Account opening process:
Step l- Receiving filled up application in bank’s prescribed form mentioning what type of account is desired to be opened.
Stop 2- The form is filled up by the applicant.
Step 3- Two copies of passport sized photographs for individual and in case of firm’s photographs of all partners are necessary.
Step 4- Applicant must submit required document.
Step 5-Applicant must sign specimen signature sheet and give mandate.
Step 6-Introducer’s signature and accounts number verified.
Step 7- Authorized officer accepts the application
Step 8- Minimum balance is deposited only cash is acceptable.
Step 9- Account is opened and deposit slip and a cheque book has given.
Issuing Cheque books to the customers:
The bank issues 10 leaves cheque book for savings account and 20, 50 and 100 leaves cheque books for current account. To complete the issuing of cheque books a customer has to fill up the requisition form for cheque books. Then a new cheque book will be filled up by the account number of the customer. The requisition slips are maintained and recorded in a register as voucher.
Dormant account:
If any account is inoperative for more then one year is called dormant account. To operate this accounts manager’s permission is necessary.
Transfer of Account:
Account holder may transfer his account from one branch to another branch. For this he must apply to the manager of the branch where he is maintaining his account. Then the manager sends a request to the manager of the branch where the account holder wants to transfer his account for opening the account.
Closing of Account
To close an account parties may be request to send an application along with the unused leaves of the cheque book. On receipt of the application the following steps are taken.
i) The signature of the account holder is verified.
ii) The number of the unused cheque leaves shall be noted therefore.
iii) Debiting the incidental charges to the account.
iv) The account holder is advised to draw the remaining balance.
Kinds of Account Holders:
Branch may open accounts of the following categories of depositors:
1) Individuals – Individuals are adult persons of 18 years age or more who are competent to enter into contracts.
2) Joint accounts – More than one adults jointly or adult with minor(s) may constitute joint accounts.
3) Sole Proprietorship concern – A business trading concern owned by a single adult person is sole proprietorship concern.
4) Partnership firms – A business concern owned and managed by more than one persons which may be registered or not registered is a partnership firm.
5) Private limited – A body corporate formed and registered under companies Act 1994, with limited members.
6) Public limited – A body corporate formed & registered under companies Act 1994 with limited liability of the shareholders and with no upper ceiling of shareholding both certificate of incorporation and certificate of commencement has given by registrar.
7) Trusts – Trusts are created by trust deed in accordance with the law.
8) Liquidators – Liquidators are appointed by court of law for companies going into liquidation.
9) Executors – Executors are appointed by a deceased himself before his death by “with” to settle the accounts of the person after his death.
10) Club/Associations/Societies – There are organizations created & registered or not registered under societies registration act.
11) Co-operatives – There are corporate bodies registered under societies registration Act or companies Act or the co-operative societies Act.
12) Non-Govt. Organization – NGOs are voluntary organizations created & registered and society’s registration Act or co-operative societies Act.
13) Non-Trading concern – These are organization registered under societies registration Act or companies Act or co-operative societies Act.
Cash Section:
Cash department is the most vital and sensitive organ of a branch as it deals with all kinds of cash transactions. This department starts the day with cash in vault. Each day some cash i.e. opening cash balance are transferred to the cash officers from the cash vault. Net figure of this cash receipts and payments are added to the opening cash balance. The figure is called closing balance. This closing balance is then added to the vault. And this is the final cash balance figure for the bank at the end of any particular day.
Functions of cash department
-Cash payment
-Cheque cancellation process
-Cash receipt
♦ Cash payment:
Cash payment is made only against cheque.
This is the unique functions of the backing system which is known as “payment on demand” .
It makes payment only against its printed valid cheque.
♦ Cheque cancellation process:
Receiving cheque by the employee in the cash counter and verification of the following by the cash officer in the computer section:
i) Date of the cheque. (it is presented within 6 month from issue date)
ii) Issued from this branch.
iii) An amount in figure and in word does not differ.
iv) Cheque is not torn or mutilated. Then gives pay cash seal and sends to the payment counter and payment office makes payment.
♦ Cash receipt:
Another important function of this department is receipt of cash. Depositors deposit money in the account through this section by deposit slip.
i) It receives deposit from depositors in the form of cash.
ii) So it is the “mobilization unit” of the banking system.
iii) It collects money only its receipts from.
iv) It receives cash for issuing pay order TT, DD.
Books maintained by this section:
i) Vault register: It keeps accounts of cash balance in vault at the bank.
ii) Cash receipt register: Cash receipt in whole of the day is recorded here.
iii) Cash payment register: Cash payments are made in a day are entries here.
iv) Rough vault register: Cash collection for final entry in vault registers done here, as any error and correction is not acceptable.
v) Cash balance book: Balance here is compared with vault register. If no deference is found, indicate no error and omission.
Local Remittance:
Sending money from one place to another place for the customer is another important service of the bank. This service is an important part of transaction system. In this service system, people, especially businessman can transfer funds from one place to another place easily. There are three kinds of technique for remitting money from one place to another these are:
-Demand draft (DD)
-Pay order (PO)
-Telegraphic Transfer (TT)
Demand Draft (DD):
DD is an order of issuing branch on another branch of the same bank to pay specified sum of money to payee on demand. It is generally issued when customer wants to remit money in any place i.e. outside or the clearing house area of issuing branch. Payee can be the purchaser himself or another mentioned in the DD. It is safe technique of transferring money from one place to another.
Payment process of the paying bank:
-Test confirmation if the DD value is more then Tk. 25,000.00
-Confirm that the DD is not forged one.
-Confirm with sent advice.
-Make payment.
Telegraphic Transfer (TT)
Issuing branch requests to another branch to pay specified sum of money to a specific person on demand by telegraph or telex or telephone. Transfer of fund by TT is the rapid and Convenient but expensive method.
Test Arrangement of TT & DD:
Test is the security code by decoding which any branch can be sure that the TT or DD is not forged one. Only the authorized officers know the test code. Each bank maintains secret code for this. That is the test arrangement is the combination of different secret codes.
Clearing Section:
This section receives all kinds of cheque in favor of the valued client for clearing on the part of their banking services. After receiving cheque it is necessary to endorse it and cross it specially. Clearing of cheque is done through the clearing house in Bangladesh Bank.
– 1 st clearing
– 2nd clearing
Types of cheque for clearing:
There are four types of cheque for clearing:
1) Inward clearing cheque.
2) Outward clearing cheque.
3) Inward bills for collection.
4) Outward bills for collection.
♦ Inward clearing cheque
It refers the instruments drawn on Rupali bank received by other banks in the clearing house from the representative of other bank.
♦ Inward bills for collection (lEC):
There are two types of clearing, firstly cheque collects from the other branch of Rupali bank These Cheques are settled by sending mCA i.e. debiting depositors account and crediting sender’s branch account. .
Secondly cheque collects from another bank outside the clearing house. These cheque are settled debiting depositors account and sending DD or TT in favor of senders bank.
♦ Outward Clearing Cheque:
Cheque drawn of another branch of Rupali bank are called Outward Clearing Cheque. These types of cheque are directly sent to the respective branch and request them to send IBCA.
Accounts section:
This is obviously an independent and unique department, which works as the composition of all the departments of the branch. So the conventional large ledger and journal books are kept in the bank. It receives the vouchers from all departments and prepares the subsidiaries and maintains accounts.
Establishment section:
This section deals with employees salary, many types of internal expenses such as purchases of stationary, equipment, machinery, payment of labor cost and convince. In case of leave of absence employee collects prescribed form from this section.
Locker facilities:
Locker facility is available in this branch. Generally people keep their valuable ornaments in the locker. Lockers are three sizes one are small and other are middle and big. Any individual can open a locker.
Product & Service Of Rupali Bank Ltd
Rupali Bank Limited offers various kinds of deposit products and loan schemes. The bank also has highly qualified professional staff members who have the capability to manage and meet all the requirements of the bank. Every account is assigned to an account manager who personally takes care of it and is available for discussion and inquiries, whether one writes, telephones or calls.
Deposit Products:
Rupali Bank Savings Schemes(CSS)
Monthly Benefit Deposit Receipt(MBDR)
Special Deposit Receipt Scheme(SDR)
Education Savings Scheme(ESS)
Fixed Deposit Receipt Scheme(FDR)
Current Account
Savings account
Short Term Deposit
Lending Products:
Bank has its own principle about the credit sanctioned or loan to the customers, but lending product of a bank or of a branch is equal important to verify the outstanding at the end of any fiscal year. Every bank pays special attention about their lending products, because these products are handed over on a regular basis.
Continuous Loan:
a. Secured Overdraft against Financial Obligation {SOD (FO)}
b. Secured Overdraft against Work order/ Real Estate etc [SOD (G)}
c. Cash Credit (Hypothecation)
d. Export Cash Credit (ECC)
Demand Loan:
a. Loan General
Short term, Medium term & Long term loans allowed to individual /firm/industries for a specific purpose but for a definite period and generally repayable by installments fall under this head .this type of lending are mainly allowed to accommodate financing under the category (a) Large & Medium Scale industry and (b) Small & Cottage Industry . Very term financing for (a) Agriculture & (b) Others are also included here .
b. Demand Loan Against Ship breaking
c. Payment against Documents (PAD)
d. Loan Against Imported Merchandise (LIM)
e, Loan Against Trust Receipt (LTR)
g. Packing Credit
Term Loan:
a. Project Loan
b. Transportation Loan
c. HouseBuilding Loan
Loan under SME:
a. Small Business loan
b. Consumer finance scheme
c. Personal loan
Money transmission Product
Carrying cash money is troublesome and risky. That’s why money can be transferred from one place to another through banking channel. This is called remittance. Remittances of funds are one of the most important aspects of the Commercial Banks in rendering services to its customers.
a. Payment order/security deposit receipt (PO/SDR)
b. Demand Draft (DD):.
c. Telegraphic Transfer (TT):
d. Travelers Cheque
e. Out Station bills for collection(OBC)
International Business Products :
In banks when we talk of international business products, we refer to the general mechanism by which a bank converts currency of one country into that of another. Foreign Exchange Department (FED) is the international department by which a bank or an AD branch transects with other international bank or of a branch. Bangladesh Bank issues license to scheduled banks to deal with foreign exchange. These banks are known as Authorized Dealers. If the branch is authorized dealer in foreign exchange market, it can remit foreign exchange from local country to foreign countries by transacting their international business products.
a. Letter of Credit (L/C)
b. Back to back Letter of credit (BTB L/C)
c. Buying and selling of foreign exchange
d. Foreign demand draft (FDD)
e. Foreign telegraphic transfer (FTT)
Social Service Products:
Rupali Bank Considers several service products by looking at the social point of view, At this competitive edge, banking might have reached to preserve its market share and to penetrate new market share through diversification of its product range. Following are the services that are designed to provide for society:
a. Sale of Lottery Tickets for collection of fund for social establishment
b. Collection of Zakat Fund
c. Collection of Haj Deposit
Loan& Advance
This is the survival unit of a bank because until and unless the success of this section is a question to every bank. If this section is not properly working, the bank it self may become bankrupt. This is important because this is the earning unit of the bank. Banks are accepting deposits from the depositors in condition of providing interest to them as well as safe keeping their deposits. Now the question may gradually arise how the bank will provide interest to the clients and the simple answer is advance.
We often use loans and advances as an alternative to one another. But academically this concept is incorrect. Advance is the combination of such items where loan is a part only for this credit section of the bank.
What is meant by loan?
In real life ,individual or business institutions (business /non business or government or non government) face some situation when they feel the necessity of collecting , achieving , or using something for which they may not have adequate required purchasing power. On the other hand there are individual or institution that have surplus fund after fulfilling both of their requiring and investment requirements. By way of deposit bank takes these surplus funds in its own custody. Bank again temporarily transfers these funds for a specific duration in exchange of some interest or profit to those who do not have Required purchasing power but have capacity to utilize borrowed funds for some productive and profitable purposes or projects. Here temporary means that the will return the provided purchasing power as loans after some time as per the terms of the contract.
Bank can provide loan in different ways loan can be in cash or in non cash form. Loan can be defined as the leading of a sum of money by a lender to a borrower to be repaid with a certain amount of interest.
If a bank gives its resources temporarily under certain conditions and for a specific duration , it will be called loan.
Types of Advance:
All loan and advance that are provided by this bank can be categorized into different types according to the nature and characteristics of each product:
Such as :
- Demand Loan
- Term Loan
Nature of Different Types of Advance:
Cash Credit HYPOTHECATION (CC HYPO)
Cash credit is given through the cash credit account. Cash credit is an active and running account where deposit and withdrawals may be made frequently. The debit balance of the account on any day can not exceed the agreed limit.
Instrument HYPOTHECATION DEED.
50% margin requires to open a CC account. (varies)
Operation of cash credit is same as that of overdraft the purpose of cash credit is to meet working capital needs of traders, farmers, and industrialist.
It is granted only the first class parties.
It is charged against a property where neither the ownership nor the possession is passed to the bank.
Cash Credit PLEDGE
The nature, operational work, and characteristics of CC- PLEDGE in as same as C C HYPO.
CC.PLEDGE in different from CC-HYPO only from the securities or business goods against the loan amount.
It is charged against properties where the ownership may remain to the borrower but the possession is passed to the bank. Instrument – Pledge Deed.
Secured Overdraft (SOD)
Overdrafts are those drawings, which are allowed by the banks in excess of the balance in the current account up to a specified amount for definite period as arranged for.
Generally it is given to the businessmen to increase their business activities.
Usually provide against FDR, RDS, i.e. financial obligation or any primary securities. The interest charges from the date of first withdraw.
Interest is calculated and charged only on the actual debit balance on daily product basis.
Balance of OD account are fluctuates
The interest rate of SOD is 3% above of FDR interest rate if the FDR is in our Bank.
If the FDR is in other bank then the interest rate is 11%
Industries Loan
It is a term loan.
It is given for four years at equal installment.
Grass period is allowed of this types of loan.
Grass period is the period that require to earn visible returns.
Others loan
Loan provided for other purpose which is productive and less risk rather industrial sector are treated as others loan.
The terms and conditions of these types of loan are same as industry loan.
House Building Loan
This loan is give for the construction of building house. It is gives for generally four years at equal monthly installment. This loan is not provides frequently. Rate of interest 13%
Staff House Building Loan:
120 times of BASIC salary is provided as SHBL. Bank rate + 1 % interest is charged to the loan amount. Repayment adjusted from their monthly salary. Repayment is made at equal monthly installment.
Consumes Credit Scheme:
Under this scheme credit is given to the customer to purchase necessary and luxury commodities like computer, motor vehicle, television, refrigerator, music system sewing machine, furniture etc.
Other then the employee it is given to the valuable client. Its rate of interest is 14%. It is given for four years at equal monthly installment.
Staff loan against Provident Fund (SLPF):
Bank staff can receive stuff loan against Provident Fund .
Employee Repayment is adjusted from their salary. Maximum sanction from PF.
Loan against RDS:
This loan is provides against RDS fund. 80% are given of the RDS fund.
This is 100% secured for the bank.
Payment Against Document (PAD):
The importers are to open letter of credit through any bank for importing goods. Most of the time they are to extend credit to the importers if not prohibited by Bangladesh bank. This loan creates, on receipt of shipping documents from the negotiating bank, is transferred and lodged to PAD.
PAD is associated with import and import financing. The bank opening letter of credit is bound to honor its commitment to pass for import bills when these are presented for payment provided that it is drawn strictly in terms of the letter of credit, in fact the amount their sends advanced on behalf of the importer.
Loan against imported Merchandise (LIM):
In many cases, a bank has to clear the goods imported under letter of credit at the request of the borrower. When the importer does not come forward to retire the documents inspire of repeated reminders bank has on forced circumstances to clear the imported consignment on arrival of the same to avoid demurrage at the port which adds to the burden of commitment. When the importer fails to retire the documents or request for clearance of goods, the outstanding under PAD is transferred to LIM account.
After clearance, consignments are taken delivery by the importer on full payment of bank’s liability. Normally part delivery is not allowed while on LIM A/C. when the delivery in part is desired by the importer, the LIM is converted into cash credit account retaining proper margin and executing charge documents, the delivery is effected themselves on obtaining pro rate payment.
Trust Receipts (TR):
This is an arrangement under which credit is allowed against trust receipts and imported or exportable goods remain in the custody of the importer or exporter but he is to execute a stamped trust receipt in favor of the bank where a declaration is made that goods imported or bought with the bank’s financial assistance are held by him in trust for the bank. .
Export Cash Credit (ECC):
ECC are extended to an export to facilitate the export of goods & commodities for which there is export letter of credit or contract on hand. It is a pre-shipment & short term credit to be liquidated out of the proceeds of export documents which include negotiation or purchase of export documents.
Securities against Advances
The following securities are to be obtained by the branches depending on the nature of advances while allowing secured advances to the parties.
– Pratirakshya Sanchay Patra, Bangladesh Sanchay Patra, ICB unit certificates,
Wage Earner Development Bond
– Fixed Deposit Receipt issued by Rupali Bank Limited.
– Shares quoted in the Dhaka Stock Exchange Limited
– Pledge of goods and produce
– Hypothecation of goods, produce and machinery
– Immovable property
– Fixed assets of a manufacturing unit
Cheques, Drafts, Pay Order, Railway Receipts, Steamer Receipts, Burge Receipts of the Govt. or Corporations
Process of Loan Sanction:
Step-1 : Sanctioning by the competent authority
A secured advance may be grant to a party only after getting a limit sectioned from the competent authority.
Step-2 : Loan/Advance Proposal
For obtaining a loan/advance the party must make an application in standard form in writing to the branch where he maintains his operative account. After receiving the application from the party, the branch manager will take immediate steps to compile report regarding the party based on the following sources of information:
- Personal investigation
- Confidential supports from
- Other banks,
- Chamber of commerce
- CIB from Bangladesh bank as the earnable.
- Treading account P/C, B/S. M/A if’ any and other documents submitted by the party.
- The average balance and the present maintained in the account.
- The nature of operations during the last six months and the date of opening account.
Step-3 : Preparation of limit proposals
The branch, may prepare a limit proposal after being fully satisfied with the following points:
The financial position of the party.
Purpose for which advance is required.
Nature of securities offered.
The payment arrangement.
Step-4 : Renewal Proposal : Sometimes Bank renew the proposal by considering customers goodwill, capacity, capital, character,etc for providing loan &advance.
Step-5 : Approval by Head Office and Branch responsible.
Limit proposal sent to HO.
Sanction/reject
Receive the limit section advice.
Step-6 : Disbursement of loan.
After completion of documentation bank makes disbursement . How loan will be disbursed is generally mentioned in the negogation . It is customary that term loans are disburse on installment basis and short term loans are transfer to borrowers account. Borrowers can withdraw from his /her account when deem it necessary. It is necessary to audit the credit to verify whether credit has been made by following all the guidelines of credit set in the credit policy.
Step-7 : Loan monitoring and administration.
The loans are repaid in installment .This installment is according to bank directives some loans are repaid all at time. If any loan is not repaid then notices are served to the customer. Sometimes legal action are also for recover the loan.
Loan Classification:
Loan classification is a process by which the risk or loss potential associated with the lone accounts of a bank on a particular date is identified and quantified to measure accurately the level of reserves to be maintained by the bank to provide for the probable loss on account those risky loan.
Like other banks all types of loans of RPBL fall into following four scales:–
Unclassified: Repayment is regular.
Substandard: Repayment is stopped or irregular but has reasonable prospect of improvement.
Doubtful debt: Unlikely to be repaid but special collection efforts may result in partial recovery.
Bad/loss: Very little chance of recovery
5.8 Table of Loan classification:
| 1st phase | 2nd phase | 3rd phase | 4th phase | 5th phase | |
| Classification status | Length of overdue | Length of overdue | Length of overdue | Length of overdue | Length of overdue |
| Unclassified | Less than 12 months | Less than 9 months | Less than 9 months | Less than 6 months | Less than 3 months |
| Substandard | 12 months or more but less than 36 months | 9 months or more but less than 24 months | 9 months or more but less than 24 months | 6 months or more but less than 12 months | 3 months or more but less than 6 months |
| Doubtful | 36 months or more but less than 48 months | 24 months or more but less than 36 months | 24 months or more but less than 36 months | 12 months or more but less than 24 months | 6 months or more but less than 12 months |
| Bad/Loss | 48 months or more | 36 months or more | 36 months or more | 24 months or more | 12 months or more |
Source; CIB
Unclassified Loan: the repayment of advance which have regularity are called unc1assifiec advance. This is a clean loan that is these is no overdue installment or not the expire due date.
Classified: The repayments of advance which have no regularity are classified. That means which are irregular in nature, overdue installment of payment, and expire the due date. There are three standards of classification:
– Sub Standard
– Doubtful
– Bad /Loss
Table of Provision requirements:
| Classification status | 1st phase | 2nd phase | 3rd phase | 4th phase | 5th phase |
| Unclassified | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% |
| Substandard | 10% | 10% | 15% | 15% | 20% |
| Doubtful | 50% | 50% | 50% | 50% | 50% |
| Bad/Loss | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Frequency of classification | Annual | Half yearly | Half yearly | Quarterly | Quarterly |
Source; CIB
Classification Procedure:
The classification procedure is done as per the Central Bank’s instructions in B C D circular No. 34 of 1989, B C D circular NO 20 of 1994. The loans are classified based on following criteria.
Overdue criteria :Term loans become overdue wherever an installment is not received within 3 months of the normal date of repayment for private sector loans and 6 months in case of public sector loans. Continuous type of loans, if not renewed, becomes overdue on the date of expiration of the loan. Classification status of a loan account is determined based on the length of overdue period as under.
Qualitative criteria: In addition to the above mentioned objective criteria loans can also be classified on the basis of qualitative judgment taking into consideration the factors such as borrowers performance, available securities etc.
Special conditions. There are certain special conditions set out in this circular which requires classification even though a loan my not be overdue
Inspecting department instruction: Regardless of the above Bangladesh bank’s inspection department may change the bank’s classification of any loan.
Credit Information Bureau (CIB):
Bangladesh Bank has established within itself a Credit information bureau (CIB) which collects credit information from the banks. Banks are required to furnish such information in respect of credit limit of TK.5000/- and over. They mention the name of facility, security and charge along with outstanding balance. After consolidation such information in respect of each customer, the central bank supplies to the total limits sanctioned to and the number of banks dealing with a party. Thus the banks can find out if any of their customers is having excessive borrowings from the banking system at any particular time.
Recovery system of loan :
After disbursement credit ,credit officer ‘s task is to continuously monitor and review the performance of borrowers. By regular monitoring and reviewing the performance of borrowers ,a credit officer can able to detent the sign of problem loans and can take right action to minimize loan loss. In the RPBL recovery system of loans are:
1.Banks own steps and
2.Taking legal action through the court
1.Banks own steps are given below:
a. Advice for inventory control : In most of the case , inventory is either kept in raw materials form or finished goods form. If inventory level is higher , huge amount of money is tied in that inventory. Bank may advice the borrower to control the inventory level in such a way that huge amount of money is not kept idle.
b .Collect and preserve of all the document related to the loans: Before sanctioning loans all the document related to the loans must be collected and preserved.
c .Limit based loan: According to the loan policy ,bank have specific limits for specific type of loans. The loan officer should not cross the limit.
d. Correction of loans diversion: If bank find that the reason of problem loan is utilization of loan in unproductive sector by the borrower ,then to the cure the loan problem ,bank correct the loan diversion.
e. Renationalization of clients over head expenses : Bank may advice the client to reduce their over head expense .Bank also guide to reduce unproductive and unnecessary expenses. As a result productivity of loan client will increase , and he will be able to repay the debt.
2.Taking legal action through the court :
When bank recovery fail , bank file case against borrowers as the weapon. At present bank can take legal action under the following laws :
a. Artha Rin adalat :After falling the loans from borrowers, banks file cases money suit / title suit under the case in the Artha Rin Adalat.
b. Public demands recovery Act,1913 : Bank file cases under the public demands Recovery Act,1913.
c. Bankruptcy Act ,1997 : Bank file cases under the Bankruptcy Act ,1997 .
SWOT analysis that involves the strength , weakness , Opportunities, & Threats that may be Strategic factors for a specific company of Organization.
Strengths:
- Rupali Bank has many branches throughout the country. Thus it can efficiently serve people of different areas of the country.
- Rupali Bank experienced huge ups and downs in the banking arena so that they are confident enough to be proactive rather than reactive.
- Rupali Bank has its own training institute through which their employees get trained and gather knowledge. This is to train their employees throughout the year.
- Rupali Bank Ltd has good relation with their customers. They give service to their regular customers after 3 PM, though the bank is closed after 3 PM.
- All the levels of the management of Rupali Bank aresolely directed to maintain a culture of the betterment of the quality of the service and development of a corporate brand image in the market through organization wide term approach and open communication system
Weaknesses:
- Human resources of RPBL is not adequate to serve its huge customers efficiently.
- RPBL is avoiding the marketing campaign for their new services. This is why the customers do not know about them fully what they are offering.
- RPBL does not concentrate enough to other promotional tools and the workforce for personal selling activities is also very limited.
- RPBL is in the backward position in case of technology adaptation. Yet it has not been able to introduce mobile banking and online banking in full pledge. Still they are doing many of their work manually such vouchers writing, bill writing etc. which are computerized in most of the banks.
- Many areas in the country are still out of their network.
Opportunities:
- RPBL has large scope of banking operation throughout the country and it is widening day by day. RPBL is still to cover huge business area including SME sector.
- Extension of E-banking will open more scope for RPBL to reach the clients not only in Bangladesh but also in global banking arena. Introducing any branch banking through online is great opportunity to them.
- The Bank can introduce more innovative and modern customer services to better survive in the competition.
- They can also offer micro credit business for individual and small business.
- The bank can diversify its portfolio by introducing new sector.
- Many branches can be opened to reach the Bank’s services in remote locations.
- The Bank can recruit experienced, efficient and knowledgeable workforce as it offers attractive compensation package and good working environment.
Threats:
- The country faces lot of unrests and turmoil in the recent times, so the banking operation is in the trouble position.
- Due to high customer demand, more and more financial institutions are being introduced in the country. Many banks are entering the market with new and lucrative products. The market for banking industries is now a buyer dominated market. Unless RPBL can come up with attractive financial products in the market .it will have to face steep competition in the days to come.
- As previously mentioned world is advancing e-technology very rapidly. Through RPBL has taken effort to join the stream of information technology, it is not possible to complete the mission due to poor technology and infrastructure of our country.
- The worldwide trend of merging & acquisition in financial institution is causing concentration. The industry and competitors are increasing in power their respective areas.
- The common attitude of Bangladeshi clients to default.
- New technologies are emerging in the banking sector with a rapid rate. So keeping pace with them is a major threat.
- Multinational banks with various attractive means of providing commercial banking services can take the Bank’s lucrative clients away.
Findings:
According to CCS policy of Rupali Bank Limited that loan processing time is long .So the authority should care about it for their reputation.
Management system of RPBL is fully democratic.
RPBL always maintains the rules declared by Bangladesh Bank.
Paper-based works are still existed in branch.
Recommendation:
In order to get competitive advantage and to deliver quality service, top management should try to modify the services.
Rupali Bank Ltd should train up their branch personnel about all sort of information regarding SWIFT and its service.
Rupali Bank should always monitor the performance of its competitors in the field of loan and advance.
Rupali Bank should continuously strive and try .to introduce new products and services as access card. ATM booth with future improved quality services.
For customer’s convenience in Rupali Bank Ltd. should provide more personnel to deliver faster services to their honorable customer.
They should also focus on the marketing aspects to let customers know about their products and offerings and more promotion should be given to attract new customer.
Rupali Bank Ltd. must develop electronic banking system to moderate the service.
Evaluate customer’s needs from their perspective and explain locally the shortcomings.
Customer’s convenience should receive priority over other.
Improve office atmosphere to give customers better feeling.
Time consumed at service level should be minimized at optimum level.
Use of effective management information systems.
Use appropriate techniques in evaluating customer need professionally.
To deliver quality service top management should try to mitigate the gap between customer’s expectation and employee’s perception.
The bank can offer to its customer better service if all of its departments are computerized and incorporated under Local Area Network (LAN)
Bank is providing both internal and external training for the officers but bank should be scrupulous about the training facilities so that official can implicate this in their job.
People are very choosy about environment now a day_ so bank premises should be well decorated and Rupali Bank Ltd. should look into the matter very seriously.
Bank should provide advances towards the true entrepreneur with reconsidering conventional system of security and collateral, moreover, the whole process should be completed within an acceptable time.
Conclusion:
Form the learning and experience point of view I can say that I really enjoyed my internship period in Rupali Bank Ltd. at postagola Br. I am confident that this 3 (three) months internship program will definitely help me to realize my carrier in the job market.
Performance analysis of a bank is not so sufficient to measure and express perfectly within this short time of my internship period. But it is a great opportunity for me to get used to with the operational environment of commercial banking of
Rupali Bank ltd. I have tried by soul to incorporate the necessary relevant information in my report.
During the course of my practical orientation I have tried to learn the practical banking to relate it with my theoretical knowledge, what I have gathered and going to acquire from various courses.