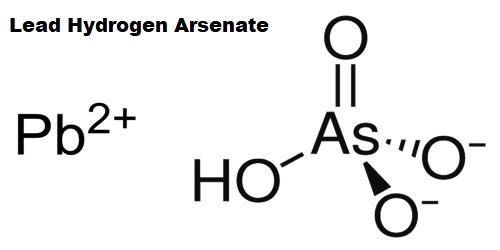
Corkite is a phosphate mineral in the beudantite subgroup of the alunite group. It is a phosphate-sulfate-hydroxide of lead and iron [formula- PbFe[(OH)6:SO4:PO4] that is isomorphous with beudantite. It is A trigonal-ditrigonal pyramidal mineral containing hydrogen, iron, lead, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur.
Corkite is named after County Cork, Ireland; the location where the first notable amount was discovered in 1869. Like many of the other minerals in the beudantite group, corkite is a relatively uncommon, secondary mineral that occurs in oxidation zones near hydrothermal base metal deposits.
General Information
- Category: Phosphate minerals
- Formula: PbFe[(OH)6:SO4:PO4]
- Crystal system: Trigonal
- Crystal class: Ditrigonal pyramidal (3/m) (same H-M symbol)

Properties
It is the phosphate analogue of beudantite and with it, a complete solid solution range exists. Corkite will also form a solid solution with kintoreite.
- Formula mass: 667.82 g/mol
- Color: Brown to light yellowish brown, pale yellow, yellowish green to dark green
- Crystal habit: Crystals pseudocubic rhombohedral with prominent {1011}.
- Mohs scale hardness: 3.5 – 4.5
- Luster: Vitreous, resinous
- Diaphaneity: transparent
- Specific gravity: 4.295 (measured), 4.31 (calculated)
Occurrence: A rare secondary mineral formed at low temperatures or by weathering in oxidized hydrothermal base-metal deposits.
Association: It occurs associated with pyromorphite, malachite, plumbojarosite, limonite and quartz.
Information Source: