Concept of Job Satisfaction
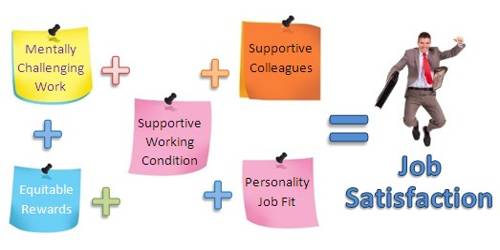
Job satisfaction is one of the most researched variables in the area of workplace psychology and has been associated with numerous ranging from leadership to job design. It can be defined as an employee’s attitude towards the job. It is not same as motivation, rather it is concerned with the attitude and internal state of an individual regarding a particular job. It could, for example, be associated with a personal feeling of achievement, and hence, shaped or determined by pay, supervisory style, and age factors. If the existing job fails to provide psychological or physiological need of an individual, satisfaction from the job might be low.
The concept of job satisfaction, viewed through different lenses by various scholars, is defined differently. Greenberg and Baron (2008), for instance, viewed job satisfaction as a feeling that can produce a positive or negative effect toward one’s roles and responsibilities at work and added that it is important to understand the concept of job satisfaction as there is no single way to satisfy all workers in the workplace.
More specifically, job satisfaction can be explained as an employee’s general attitude towards the job. It is a pleasurable feeling that results from an employee’s perception of achieving the desired level of need or satisfaction. Job satisfaction fulfills an individual’s psychological and physiological needs through the organizational process. It is a multidimensional attitude which is made up of the attitude towards pay, promotions, co-workers, supervision, the work environment and so on. High job satisfaction implies that the employees are liking the job, whereas, low job satisfaction relates to the disliking of the job by individuals. Job satisfaction is an intangible variable which is expressed through emotional feelings.
Therefore, we can conclude that job satisfaction is an employee’s positive response toward the various aspects of a job. It helps to improve job performance and can be determined by the deviation between employee’s expectation about job outcome and what the job actually offers.
Considering that job satisfaction impacts every employee across the globe it is hardly surprising that it has received a lot of attention in the research literature. However, this has lead to a large number of definitions, theories, and measures. At a European level, the focus has been less about these traditional theories of job satisfaction. Instead, job satisfaction is typically examined as a consequence of workplace stress and the job demand-control model.
Information Source: