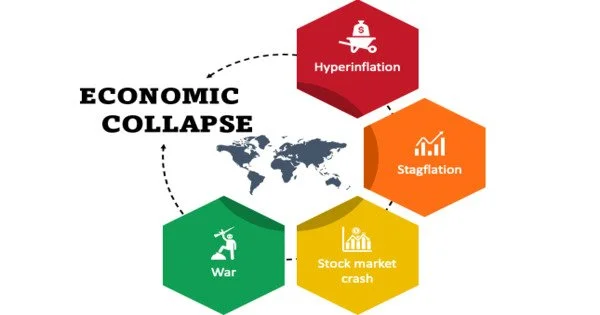
An economic collapse is a severe and sudden decline in economic activity, which can result in high unemployment, a sharp drop in the value of assets, and widespread financial hardship. It refers to a sudden and severe decline in the economic activity of a country or region.
The causes of an economic collapse can be complex and multifaceted, but some of the common factors that contribute to economic collapse include:
(1) Hyperinflation
Hyperinflation occurs when the government allows inflationary pressure to build up in the economy by printing too much money, resulting in a gradual rise in commodity and service prices. Governments resort to printing money and issuing credit in order to manage an economic slowdown. When the government loses control of price increases and raises interest rates to slow the accelerating inflation, hyperinflation occurs.
(2) Stagflation
Stagflation describes a situation in which the economy is growing slowly while experiencing high rates of inflation. Such an economic situation creates a quandary for policymakers because the measures implemented to reduce inflation may raise unemployment levels to abnormally high levels. Stagflation and its economic consequences can last for years or decades.
For example, from the 1960s to the 1970s, the United States experienced stagflation. During that time, economic growth was stagnant, and inflation peaked at 13% per year, while inflation in the United Kingdom was 20% per year. Stagflation is usually difficult to manage, and governments must incur enormous costs to bring the economy back into balance.
(3) Stock market crash
A stock market crash occurs when there is a loss of investor confidence in the market, and there is a dramatic decline in stock prices across different stocks trading in the stock market. When a stock market crash occurs, it creates a bear market (when prices drop 20% or more from their highs to hit new lows), and it drains capital out of businesses.
(4) War and political instability
War and political instability can cause economic collapse by disrupting trade, damaging infrastructure, and causing widespread economic disruption.
(5) Global pandemics
Pandemics such as the COVID-19 pandemic can also cause economic collapse. The pandemic led to widespread shutdowns of businesses, travel restrictions, and disruptions to supply chains, which had a significant impact on the global economy.
Crashes occur when there is a prolonged period of rising stock prices, price-earning ratios exceed long-term averages, and there is excessive use of margin debt by market participants.
It’s important to note that economic collapses are often the result of a combination of these factors rather than a single cause. Understanding these causes can help policymakers and economists take steps to prevent economic collapse and mitigate the impact of any economic shocks.