A public company refers to a company that is listed on a recognized stock exchange and its securities are traded publicly. Public enterprises are guided by several socio-economic and political objectives. A private company is one that is not listed on a stock exchange and its securities are held privately by its members. Private enterprises are mainly profit-driven.
Following are the main differences between public company and private company.
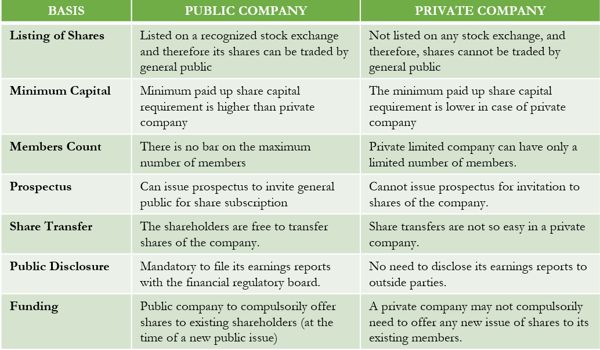
(1) Number of Members
A public company need not include the word “private” in its name. But for a private company, it is mandatory to write the words “private limited” at the end of its name. A public company requires a minimum of seven members and a maximum of unlimited. A private company needs at least one member for its formation but can not exceed fifty.
(2) Issue of Prospectus
Public company issues a prospectus for inviting public to subscribe its shares or debentures. The issue of prospectus/statement instead of the prospectus is mandatory in case of a public company, but this is not the case with the private company. Private company can not issue prospects to invite public for subscription of its shares or debentures.
(3) Restriction on Share Transfer
In a public company, there is no restriction on the transfer of shares. The shareholders of a public company can freely transfer their shares. In a private company, no member is allowed to transfer his/her shares without the consent of the directors of the company. The transferability of shares of a Pvt. Ltd. company is completely restricted.
(4) Commencement of Business
A public company can commence business only after receiving the certificate for the commencement of business. It is compulsory to call a statutory general meeting of members, in the case of a public company, whereas there is no such compulsion in the case of a private company. A private company can commence business after getting a certificate of incorporation from the Company Registrar.
(5) Allotment of Shares
A public company can allot its shares only after receiving the amount of minimum subscription. A public company refers to a company that is listed on a recognized stock exchange and traded publicly. A private company can allot its shares as and when directors desire to do so after the incorporation. A Private Ltd. company is one that is not listed on a stock exchange and is held privately by the members.
(6) Statutory Meeting
A statutory meeting must be held and statutory reports must be sent to the Registrar as well as shareholders of the company in the public company. A public company must hold a statutory meeting and file with the Registrar a statutory report. But a private company has no such obligations. It is neither required to hold statutory meetings nor file and issue a statutory report in a private company.
(7) Invitation to the public
A public company must issue a prospectus or statement in lieu of a prospectus for inviting the public to subscribe to its shares or debentures. A private company on the other hand cannot issue such an invitation to the public.
(8) Legal Formalities
A public company has to fulfill more legal formalities. A private company is required to observe a less number of legal formalities.
Informtion Source: