Airtel Bangladesh Limited is a GSM-based cellular operator in Bangladesh. Airtel is the sixth mobile phone carrier to enter the Bangladesh market, and originally launched commercial operations under the brand name “Warid Telecom” on May 10, 2007. As an emerging company Airtel is doing extremely well. After the launch of Airtel in Bangladesh, the competition has become more strengthen among the telecom operators. Each of them is fighting to boost up its market share by offering new promotion and benefits to the customers. Since, all of the operators are offering almost same categories of products it has become a big challenge to retain the existing subscribers and acquisition of new customers. At this moment Airtel is trying to reach the customers with various promotional activities and is attempting to make their brand presence felt. Through their significant advances in Bangladesh, Airtel is moving ahead on the track to achieve their goals.
The purpose of making this report was to know about the changes that took place when Airtel took over Warid in 2010. There were lots of rumors of this change from 2008 and it was more like an open secret within the organization that Airtel will merge with Warid. There were lots of tensions that people will lose their job, but Airtel’s business model is such that nobody lost their job, instead the IT officials got the chance to work in IBM, Ericsson and Siemens. So the change was good and employees adapted pretty nicely.
However the HR practice of Warid were very firm so employee dissatisfaction were pretty high, but Airtel put a lot of emphasis on employee engagement, so turnover rate in Airtel is almost zero.
Introduction
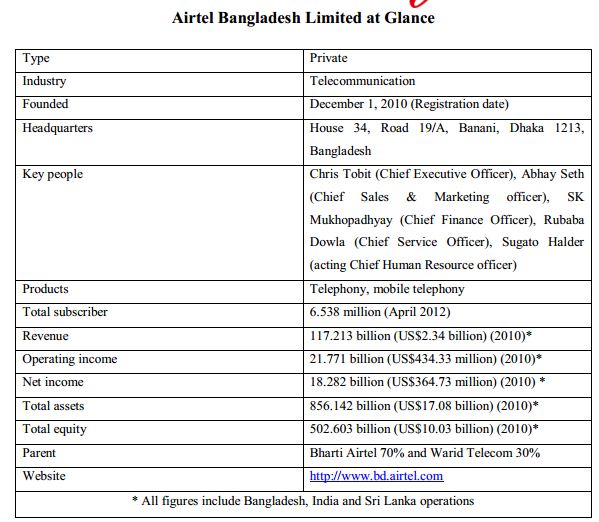
Airtel Bangladesh Limited is a GSM-based cellular operator in Bangladesh. Airtel is the sixth mobile phone carrier to enter the Bangladesh market, and originally launched commercial operations under the brand name “Warid Telecom” on May 10, 2007. Warid Telecom International LLC, an Abu Dhabi based consortium, sold a majority 70% stake in the company to India’s Bharti Airtel Limited for US$300 million. Bharti Airtel Limited took management control of the company and its board, and rebranded the company’s services under its own Airtel brand from December 20, 2010. The Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission approved the deal on Jan 4, 2010.
Bharti Airtel made a fresh investment of USD 300 million to rapidly expand the operations of Warid Telecom and have management and board control of the company. This is the largest investment in Bangladesh by an Indian company. Dhabi Group continues as a strategic partner retaining 30% shareholding and has its nominees on the Board of the Company.
The new funding is being utilized for expansion of the network, both for coverage, capacity, and introduction of innovative products and services. As a result of this additional investment, the overall investment in the company will be in the region of USD 1 billion.
This is Bharti Airtel’s second operation outside of India. The company launched its mobile services in Sri Lanka in January 2009 on a state-of-the-art 3.5G network. On July 19, 2007, the company crossed the 1 million customers mark in the first 70 days of operation. Airtel Bangladesh had 6.345 million subscribers as of March 2012.
Bharti Airtel Limited operates in 20 countries across South Asia, Africa and the Channel Islands. It operates a GSM network in all countries, providing 2G, 3G and 4G services depending upon the country of operation. Airtel is the third largest telecom operator in the world with over 243.336 million customers across 20 countries as of March 2012. It is the largest cellular service provider in India, with over 181 million subscribers at the end of March 2012.
Current Market Situation
According Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission (BTRC) the total number of mobile phone subscribers has reached 90.636 million at the end of April 2012. It was just 45.21 million by the end of February 2009. The total number of mobile phone subscribers has been doubled within 3 years and it is still increasing significantly. Presently, the cell phone is an integral part of our daily life. Mobile phone operators are continuously offering more value added services to enrich the lives of the customers.
At the same time the competition among the telecom companies has reached to the peak level. This situation is compelling the one telecom operator providing the better quality services and keeping the call charge lower than the other operators. Currently, the telecom industry is dominating by GrameenPhone with its 41.65% market share. Egyptian Orascom Telecom’s Banglalink retained the second spot. The number of Banglalink users reached 25.008 million and holding 27.59% of total market share. Robi, formerly known as AKTEL, owned by Axiata (Bangladesh) Ltd, remained in the third position with 20.13% market share. The market’s late entrant Airtel Bangladesh Ltd is obtaining the fourth position and its current market share is 7.21%. Citycell, the country’s first and only CDMA operator remains in the fifth spot with 1.801 million customers. The state-run Teletalk now remained at bottom place with 1.295 million customers.
PROJECT
Summary:
I have selected to work on the change of HR Practice in Airtel that took place after it took over Warid Telecom. So basically this report is about comparison of HR practice between Warid Telecom and Airtel Bangladesh Limited (ABL).
The HR practice in Warid were Recruitment and Selection, Compensation, Training, Performance Management System, Employee Separation.
The HR practice of ABL are Talent Acquisition, Talent Management, Compensation, Performance Management System, Employee Engagement and Employee Separation. The change in the HR practice took place because of the unique business model that Airtel uses. This model focuses only and solely on two things-customer acquisition and servicing (retention) and business development/expansion. All other functions like hard work, network management, backend applications, VAS, telecom infrastructure are all outsourced. As a result the current number of employees is about 500. The ones who were supposed to be laid off were hired by the outsourced companies instead.
Objective of the report:
The report is prepared on the “Change of HR practice between Warid Telecom and Airtel Bangladesh Limited after merger and acquisition” with the attempt of getting an in depth knowledge on the HR practice between these two and understand its importance.
Methodology:
The nature of the report is exploratory and descriptive. The required information is collected from the following sources:
Primary data: Primary data is collected through interview and questionnaires.
Secondary data:
Internal Sources: Published documents of Airtel’s Website
External Sources: Books, Articles, Journals, Newspaper, Web browsing.
Questionnaire Design
Questionnaire was prepared with both open and close ended questions. The target population was the HUMAN RESOURCE officials of Airtel Bangladesh Limited. The population size is 10, and the sample size is 5.
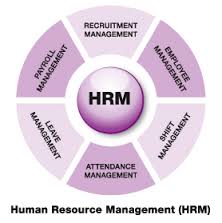
Human Resource, in theoretical review
Human Resource management (HRM) is the management of an organization’s workforce, or Human Resources. It is responsible for the attraction, selection, training, assessment, and rewarding of employees, while also overseeing organizational leadership and culture, and ensuring compliance with employment and labor laws. In circumstances where employees desire and are legally authorized to hold a collective bargaining agreement, Human Resource will typically also serve as the company’s primary liaison with the employees’ representatives (usually a labor union). Human Resources planning, structure and organization are all important to managing human capital — or, Human Resources — the most valuable asset in an organization. Aligning Human Resource and business goals, managing talent, improving employee engagement and working together with executive leadership are several key components to Human Resource management.
Human Resource is a product of the human relations movement of the early 20th century, when researchers began documenting ways of creating business value through the strategic management of the workforce. The function was initially dominated by transactional work such as payroll and benefits administration, but due to globalization, company consolidation, technological advancement, and further research, Human Resource now focuses on strategic initiatives like mergers and acquisitions, talent management, succession planning, industrial and labor relations, and diversity and inclusion.
In startup companies, Human Resource’s duties may be performed by a handful of trained professionals or even by non-Human Resource personnel. In larger companies, an entire functional group is typically dedicated to the discipline, with staff specializing in various Human Resource tasks and functional leadership engaging in strategic decision making across the business. To train practitioners for the profession, institutions of higher education, professional associations, and companies themselves have created programs of study dedicated explicitly to the duties of the function. Academic and practitioner organizations likewise seek to engage and further the field of Human Resource, as evidenced by several field-specific publications.
Human Resource Management: Defined
Human Resource Management has come to be recognized as an inherent part of management, which is concerned with the human resources of an organization. Its objective is the maintenance of better human relations in the organization by the development, application and evaluation of policies, procedures and programmes relating to human resources to optimize their contribution towards the realization of organizational objectives.
In other words, HRM is concerned with getting better results with the collaboration of people. It is an integral but distinctive part of management, concerned with people at work and their relationships within the enterprise. HRM helps in attaining maximum individual development, desirable working relationship between employees and employers, employees and employees, and effective modeling of human resources as contrasted with physical resources. It is the recruitment, selection, development, utilization, compensation and motivation of human resources by the organization.
Human Resource Management: Evolution
The early part of the century saw a concern for improved efficiency through careful design of work. During the middle part of the century emphasis shifted to the employee’s productivity. Recent decades have focused on increased concern for the quality of working life, total quality management and worker’s participation in management. These three phases may be termed as welfare, development and empowerment.
Human Resource Management: Nature
Human Resource Management is a process of bringing people and organizations together so that the goals of each are met. The various features of HRM include:
• It is pervasive in nature as it is present in all enterprises.
• Its focus is on results rather than on rules.
• It tries to help employees develop their potential fully.
• It encourages employees to give their best to the organization.
• It is all about people at work, both as individuals and groups.
• It tries to put people on assigned jobs in order to produce good results.
• It helps an organization meet its goals in the future by providing for competent and well-motivated employees.
• It tries to build and maintain cordial relations between people working at various levels in the organization.
• It is a multidisciplinary activity, utilizing knowledge and inputs drawn from psychology, economics, etc.
For these feature Human resource management has been changed from Warid to Airtel.
Human Resource Management: Scope
After merger and acquisition the practice of Human Resource has been changed from Warid to Airtel. The scope of Human resource management is very wide.
1. Personnel aspect-This is concerned with manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, transfer, promotion, training and development, layoff and retrenchment, remuneration, incentives, productivity etc.
2. Welfare aspect-It deals with working conditions and amenities such as canteens, creches, rest and lunch rooms, housing, transport, medical assistance, education, health and safety, recreation facilities, etc. Industrial relations aspect-This covers union-management relations, joint consultation, collective bargaining, grievance and disciplinary procedures, settlement of disputes, etc.
Human Resource Management: Beliefs
The Human Resource Management philosophy is based on the following beliefs:
• Human resource is the most important asset in the organization and can be developed and increased to an unlimited extent.
• A healthy climate with values of openness, enthusiasm, trust, mutuality and collaboration is essential for developing human resource.
• HRM can be planned and monitored in ways that are beneficial both to the individuals and the organization.
• Employees feel committed to their work and the organization, if the organization perpetuates a feeling of belongingness.
• Employees feel highly motivated if the organization provides for satisfaction of their basic and higher level needs.
• Employee commitment is increased with the opportunity to dis¬cover and use one’s capabilities and potential in one’s work.
• It is every manager’s responsibility to ensure the development and utilization of the capabilities of subordinates.
Human Resource Management: Objectives
• To help the organization reach its goals.
• To ensure effective utilization and maximum development of human resources.
• To ensure respect for human beings. To identify and satisfy the needs of individuals.
• To ensure reconciliation of individual goals with those of the organization.
• To achieve and maintain high morale among employees.
• To provide the organization with well-trained and well-motivated employees.
• To increase to the fullest the employee’s job satisfaction and self-actualization.
• To develop and maintain a quality of work life.
• To be ethically and socially responsive to the needs of society.
• To develop overall personality of each employee in its multidimensional aspect.
• To enhance employee’s capabilities to perform the present job.
• To equip the employees with precision and clarity in transaction of business.
• To inculcate the sense of team spirit, team work and inter-team collaboration.
Human Resource Management: Functions
In order to achieve the above objectives, Human Resource Management of Airtel undertakes the following activities:
1. Human resource or manpower planning.
2. Recruitment, selection and placement of personnel.
3. Training and development of employees.
4. Appraisal of performance of employees.
5. Taking corrective steps such as transfer from one job to another.
6. Remuneration of employees.
7. Social security and welfare of employees.
8. Setting general and specific management policy for organizational relationship.
9. Collective bargaining, contract negotiation and grievance handling.
10. Staffing the organization.
11. Aiding in the self-development of employees at all levels.
12. Developing and maintaining motivation for workers by providing incentives.
13. Reviewing and auditing manpower management in the organization
14. Potential Appraisal and Feedback Counseling.
15. Role Analysis for job occupants.
16. Job Rotation.
17. Quality Circle, Organization development and Quality of Working Life.
Human Resource Management: Major Influencing Factors
After merger and acquisition HRM of Airtel influenced by following factors, which will work as various issues affecting its strategy:
• Size of the workforce.
• Rising employees’ expectations
• Drastic changes in the technology as well as Life-style changes.
• Composition of workforce. New skills required.
• Environmental challenges.
• Lean and mean organizations.
• Impact of new economic policy. Political ideology of the Govern¬ment.
• Downsizing and rightsizing of the organizations.
• Culture prevailing in the organization etc.
We have conducted the literature search connected to the topic to support and direct the research. This search was mainly conducting on the University databases, Journal databases, Library Journals, websites and Textbooks.
The Human Resource outsourcing Survey Report released in June 2004 found that Human Resource function that are entirely background checking, employee assistance/counseling and Flexible Spending include administration. The outsourced functions include management of health care benefit, pension benefit administration and payroll. Despite these increment in Human Resource outsourcing activities to date the empirical articles on outsourcing Human Resource function focus on the impact of organizational characteristics (Klaas, 2003), the role, the transaction costs (Gainey et al, 2003; Klaas, 2003; Klaas et al, 1999), the relationship between Human Resource departments, size and outsourcing activity (Pommerenke et al, 1996) and the rational and consequence of Human Resource outsourcing, and the time of outsourcing (Greer et al, 1999). The question concerning the appropriate time to outsource HUMAN RESOURCE practices based on the internal and external forces driving the firm to consider outsourcing however is not directly addressed, although Klaas, McClendon & Gainey (1999) come close in their analysis of moderate variables in the relationship between amount of HUMAN RESOURCE outsourcing and perceived benefits from outsourcing. A separate article by Klaas, McClendon & Gainey (2001) also discussed on few organizational characteristics that lead firms to outsource the Human Resource activities but does not consider Human Resource performance as a dependent variable. As such it is necessary to address the question of when to outsource the Human Resource function by looking into the theoretical issue of outsourcing in the literature representing disciplines other that Human Resource to from a basis for Human Resource outsourcing. However a brief discussion of definitions and Human Resource activities is presented first.
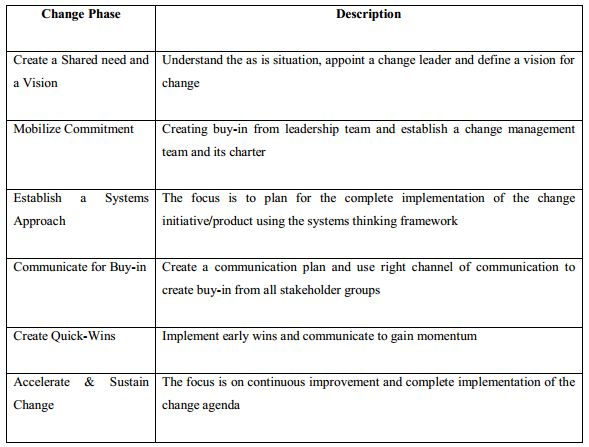
Change of Human Resource Practice between Warid Telecom and Airtel Bangladesh Limited after merger and acquisition
Airtel bought 70% of the market share of Warid Limited of Bangladesh and Airtel started operating in December 20, 2010. The model that Airtel used to change things in Warid is:
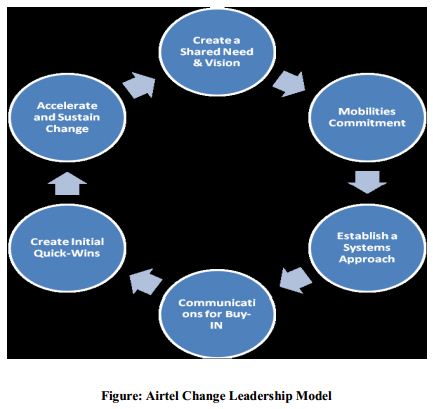
The description of this model is given in the following table:
HR Practices in Warid
1. Recruitment and Selection:
Recruitment and Selection process started with the position activation till the finalization of the candidate and issuance of offer letter. The steps of are:
• Associate Requisition/Position Activation:
• The vacancy identified by the line manger would be validated through the Requisition form initiated along with the job description.
• Human Resource Department evaluated whether the vacancy should have been filled and what employment nature (contractual, full time or part time) would be best suited for filling up the vacancy.
• Any vacancy that needed to be budgeted would have to be approved by the CEO.
• Sources of Recruitment: The sources of recruitment were:
• Associates working with Warid Bangladesh Limited or Group Companies
• CV Database
• Walk-in Interviews
• Job advertisements
• Employee referrals
Screening:
• Eligible candidates were initially short listed by the line manager within 07 days after receiving CVs.
• Interview Evaluation Form was used to evaluate the skills, competencies and interpersonal traits of the candidates
• Identification of suitable candidates for final interview would be made based upon
recommendations of Divisional Head/Line Manger within 02 days after the interview
Selection:
• Panel comprising of one BEC member, CEO and GM HUMAN RESOURCE & A would finalize hiring of General Manager, Deputy GM and Senior Manager.
• Panel comprising of CEO, GM HR&A and Divisional Head would interview and select candidates shortlisted by HUMAN RESOURCE for the positions of Manager. Hiring on any position below Manager was finalized by GM HUMAN RESOURCE&A and the concerned Divisional Head.
Reference/Salary Check:
• Verbal reference checks are mandatory before the hiring of the short-listed candidate.
• Last two salary slips of any prospective candidate if currently/previously employed are compulsory.
Offer Letter:
• The offer had to be initially negotiated by the respective Human Resource Manager and finalized by the GM HR&A in consultation with functional management where required, depending on the seniority of the role.
• Offer letter after necessary negotiations by GM HR&A or Head of Human Resource would have to be issued within 02 days after final selection that will remain valid for three working days from the date of issue
• Medical Examination: Medical examination for the selected candidate was undertaken before joining of the candidate.
2. Training and Development:
• Need Based Trainings
• Performance and skill inventory are practically used for identifying the training needs in the organizations
• Summary of skills and abilities of an associate were given in the skills inventory and a comparison was created of what skills an employee possessed and what he required to possess.
• Both Performance Appraisal and skills inventory were used to help identify training needs.
• Return on Investment for the Company (ROI):
• Purpose of investment on trainings was to enhance the skill level and productivity of the employee.
• Training bond was signed GM HR&A and the concerned trainee.
3. Performance Management System
• Performance appraisal is an important tool of Performance management system.
• Formal assessment of the employees was done twice a year.
• Done to review performance of his/her team members.
• Ensure communication between supervisor and employees
• Identify employee training needs
• Evaluate and reward the performance under Pay for Performance concept.
4. Compensation and Benefits
• Cellular Phone Policy:
• To maintain accessibility across the company, all the associates of Warid were provided with postpaid connection.
• The official connection was issued by Divisional Head for the series of numbers allocated to the respective division.
• Nearly located Warid Care used to issue the numbers.
• Cellular Phone limits:
Leave Policy:
There were four types of leaves that the associates received. These were:
1. Annual Leave: Annual leave were entitled for 20 working days
2. Sick Leave: For 14 days.
3. Casual Leave: For 10 days
4. Maternity Leave: Female employees were given 16 weeks maternity leave.
Group Life Insurance Policy:
All associates of the company were eligible for Group Life Insurance Policy.
Following Life Insurance Coverage was provided through this policy:
General Manager: Tk 10 Million
DGM: Tk 7.5 Million
Senior Manager: Tk. 5 Million
Manager: Tk. 3 Million
Assistant Manager: Tk. 1.5 Million
Sr. Exec/Exec/Sr. Officer/Officer/MT: Tk 0.5 Million.
5. Employee Separation:
• Separation during probation period: During the probation period employment were closed by either side, with or without assigning any reason by providing at least one weeks‟ notice.
• Final settlement process: During the notice period the associate would return all company belongings to divisional head. An exit interview would be conducted by General Manager HR&A.
• Gratuity policy: The purpose of gratuity was to attract and retain employees and motivate them to pursue a long term career with Warid.
• Repay/Adjustment of Loan/Withdrawals
• Recoveries of the loan or advance were made from the monthly salary of the employee in 12 equal monthly installments.
• Interests on such loan were charged at the prevailing FDR date.
• Termination of membership of the trust: Membership of the trust was automatically terminated or expired on the date of retirement or living the company by any member.
HUMAN RESOURCE Practices in Airtel Bangladesh Limited:
1. Talent Acquisition:
The purpose of Talent Acquisition is Recruitment and Selection. The entire recruitment and selection procedure is done by Talent acquisition. The steps of recruitment and selection of ABL is similar to Warid except for the fact that there was very limited amount of recruitment via reference which is lot more in Airtel Bangladesh Limited. Airtel takes help from Placement offices of different universities which Warid didn’t do. So now employee references are more valid and talented fresh graduates are employed directly, so more employment opportunities are being created. ABL takes help from consultancy firms like:
1. Monowar Associates
2. Grow n Excel
3. Human Resource Kites
4. Absolute Solution
5. E-Zone Human Resource Management
These consultancy firms are specialized in sourcing and the source of getting CVs become more. Internal Job Posting (IJP) has been started with Airtel, which was not there in Warid. As a result employees who want to change their job or responsibilities can apply easily.
2. Training Management:
Along with the trainings given during Warid time, three new training has been introduced. These are:
1. Functional Training
2. Leadership Training
3. Competency based Training.
3. Performance Management System (PMS):
The current Performance Cycle is April-March, a review is done in October in Human Resource function, whereas in Sales and Marketing function four reviews are done because their job is more critical and they demand more motivation to stay on the job. All the functions do their performance in April on the basis of some KRAs and give them to Human Resource on May. Human Resource finishes them by May 31st and gives them to all the departments on June 1st. KRAs were not so structured during Warid time but Airtel structured things for better understanding and performance. Usually the feedback is done in 2 steps.
These are:
1. 3 months initial performance feedback.
2. Year end performance feedback.
The KRA of Human Resource are somewhat like Cost minimization of the organization, whereas the KRA of Sales is revenue earning, and revenue targeting.
4. Employee Engagement:
Employee engagement involves fun activities at office on different occasions like Pohela Baishakh, Mother’s Day, International Mother Language Day, Valentine’s Day, Pohela Falgun etc. Except these there are also engagement activities at work to motivate employees like when somebody does something good they get “Well done” or “Thank you” tag on their cubicle.
5. Compensation:
The compensation structure has not changed from Warid time except for there is nothing called Gross Salary anymore, salary is given in TCTC (Total cost to company) format, which is the international format followed in the world now. The gratuity period of ABL is 1 year and probation period is 3 months which is the lowest in industry.
Recommendation:
1. Work pressure of the employees should be reduced by hiring more people and distributing work among them.
2. Airtel depends a lot on Bdjobs.com for getting CVs for Territory Manager, Key Account Manager, Manager Compliance; most of the time good CVs are not found there so then Human Resource takes people from reference which is time consuming, as a result Human Resource cannot meet the demand of different departments in supplying employees as they require.
3. More training can be introduced to improve skills of the employees.
4. Airtel does not verify the original educational documents of the employees, which it should.
5. As Airtel is an Indian company so they put a lot of Indian values at work and decoration of the Human Resource floor of the building which can be renovated.
Conclusion:
Recent research and literature demonstrate in the topic of Human resource management, and studies show that the changes of HR practice directly related to positive organizational and business outcomes.
This study examined the overall changes of HR practice from Warid to Airtel Bangladesh Limited. The days of Warid were vastly different than Airtel days, and I have found the latter positive. Where Warid was more rigid Airtel is much flexible in nature.
The research would suggest that in an agency such as the study site, where the workers are significantly engaged, production outcomes would be high and customer service would be exceptional. Just because of the changes everything has become more realistic & more fun. Employee engagement, compensation, performance management system, training & management everything changed in Airtel Bangladesh Limited after merging.
Though every company has some good and bad sides. But Airtel is trying to reduce its bad side and trying to become number one telecom company.