Trading of shares between two counterparties conducted outside formal exchanges and without the oversight of an exchange regulator is over-the-counter (OTC) or off-exchange trading. The word over-the-counter (OTC) can be used instead of on one centralized exchange in reference to stocks that are exchanged by a dealer network. These protections don’t meet the prerequisites to have a posting on standard market trade. OTC exchanging is done in over-the-counter business sectors (a decentralized spot with no physical area), through vendor organizations. In an OTC exchange, the cost isn’t really freely uncovered.
The OTC also applies to other financial instruments, such as derivatives (traded through a dealer network) or debt securities. Trade transactions occur via the listing facilities of the Over the Counter Bulletin Board (OTCBB) or the Pink Sheets. Over-the-counter trading, unlike trading on structured markets, does not require only standardized products to be exchanged (e.g. a clearly specified set of quantities and product quality). The OTCBB is an electronic citation and exchanging administration that encourages higher liquidity and better data sharing. Likewise, costs are not generally distributed to people in general. OTC agreements are reciprocal, and each gathering could confront credit hazard concerns with respect to its counterparty.

Over-The-Counter (OTC)
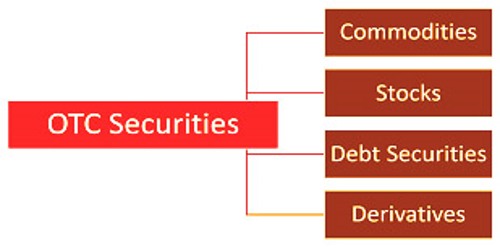
OTC and exchange trading takes place in the form of commodities, financial instruments (including stocks), and derivatives of those items. A broad variety of financial instruments and goods are composed of OTC securities. Over-the-counter traded financial instruments include stocks, debt securities, and derivatives. Stocks that trade through OTC are usually smaller companies that are unable to satisfy the formal exchange listing requirements. Nonetheless, in some cases, even enormous organizations’ stocks are exchanged over-the-counter. Stocks that exchange on trades are considered recorded stocks while stocks that exchange through OTC are called unlisted stocks. In OTC, market contracts are two-sided (for example the agreement is just between two gatherings), and each gathering could have acknowledged hazard worries for regard to the next gathering.
A stock exchange encourages liquidity, offers transparency, protects market price, and alleviates credit risk during a trade with respect to party default. The price doesn’t have to be released publicly in an over-the-counter transaction. OTC securities are exchanged by broker-dealers who use the OTCBB to negotiate directly with each other through computer networks and by phone. Derivatives form a significant part of over-the-counter trading, which is particularly important for the use of derivatives to hedge risks. The absence of restrictions on the quantity and nature of the exchanged goods makes it possible for the parties involved in the exchange to adjust the contract conditions of the agreement to the risk exposure.
OTC Securities
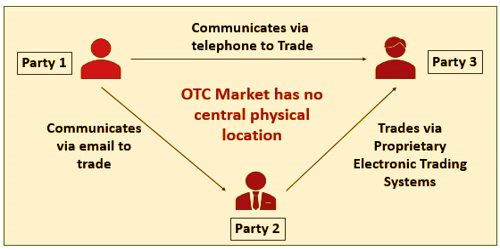
Banks spare the expense of the trade posting charges by coordinating purchases and sells from customers inside or from another financier firm. Other money related instruments, for example, subsidiaries likewise exchange through the vendor organization. Like trade exchanging, the over-the-counter exchange happens with budgetary instruments, subsidiaries, and items nonetheless, items that are exchanged on trade must be directed and normalized. Over-the-counter trading of stocks is carried out in the United States across networks of market makers. The OTC Markets Association and the Financial Industry Regulation Authority (FINRA) oversee these two well-known networks. These networks provide participating business dealers with quotation services. The purchases are carried out online or by telephone by dealers.
For hedging risk, over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives are particularly important in that they can be used to build a’ perfect hedge.’ When looking at OTC vs. exchange trading, there are also prominent variations to note. The primary distinction between the transaction channels is that each party is privy to the offers of all the counterparties on an exchange, which is not always the case on dealer networks. The OTC Markets Group works the absolute most notable organizations, for example, the Best Market (OTCQX), the Venture Market (OTCQB), and the Pink Open Market. While over-the-counter business sectors stay a basic component of worldwide money, OTC subsidiaries have outstanding hugeness. The more noteworthy adaptability gave to showcase members empowers them to alter subsidiary agreements to all the more likely suit their danger introduction.
Over-the-counter (OTC) Market
OTC trading also increases overall financial market liquidity, as companies that are unable to trade on formal exchanges gain access to capital through over-the-counter markets. Investors can find the stocks of companies that are small and expanding through the OTC marketplaces. These companies may also file reports to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulators, depending on the listing site. OTC trading, however, is subject to various threats. The probability of default of the other party before the completion or termination of a contract is one of the most critical of the counterparty risk.
A trade market and an OTC market are the two essential methods of figuring budgetary business sectors. Vendors act as market producers in OTC business sectors by providing the cost estimates at which they’ll purchase and sell money or security. In addition, the absence of straightforwardness and more fragile liquidity comparative with the conventional trades can trigger awful occasions during a money related emergency. The versatility of the nature of derivative contracts will make the situation worse. The more complex nature of the securities makes assessing their fair value more difficult. The risk of speculation and unpredictable events can also harm the market’s stability.
Information Sources: