Introduction :
In this Assignment, first try to give an idea about Financial Management, structure & its area of activities. Then I select a company named Reneta Ltd. is a listed public limited company in Dhaka Stock Exchange (DSE) for my work. After that I focus on company’s profile & analysis the annual report 2005 of Reneta ltd. In this assignment I am mainly focus on five major financial analysis (The financial results of the Company for the year 2005 & Compare with 2004 &2003, Balance Sheet as at 31 December 2005, Profit and Loss Account, Statement of changes in equity for the year ended 31 December 2005 & Cash flow statement for the year ended 31 December 2005). After this analysis I suggest some thing that I believe help the organization for improving there productivity.
|
Financial Management: Can be defined as the process of acquiring and using funds to accomplish a financial objective. The name of Financial Management is Managerial finance or corporate finance.
Role of finance in a typical Business Organization:
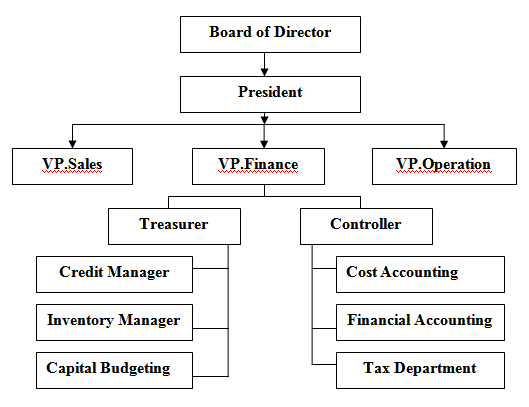
Activities of Financial management in Business Organization:
The role of a corporation’s management is to increase the value of the firm to its shareholders while observing applicable laws and responsibilities. Corporate finance deals with the strategic financial issues associated with achieving this goal, such as how the corporation should raise and manage its capital, what investments the firm should make, what portion of profits should be returned to shareholders in the form of dividends, and whether it makes sense to merge with or acquire another firm.
1) Preparation of Balance Sheet Approach to Valuation:
A simple way of valuing the equity of a company is simply to take its balance sheet and subtract liabilities from assets to arrive at the equity value. However, this book value has little resemblance to the real value of the company. First, the assets are recorded at historical costs, which may be much greater than or much less their present market values. Second, assets such as patents, trademarks, loyal customers, and talented managers do not appear on the balance sheet but may have a significant impact on the firm’s ability to generate future profits
2) Measurement of Cash vs. Profits:
Another way to value the firm is to consider the future flow of cash. Since cash today is worth more than the same amount of cash tomorrow, a valuation model based on cash flow can discount the value of cash received in future years, thus providing a more accurate picture of the true impact of financial decisions
3) Measurement of Cash Cycle:
The duration of the cash cycle is the time between the date the inventory (or raw materials) is paid for and the date the cash is collected from the sale of the inventory. A company’s cash cycle is important because it affects the need for financing. The cash cycle is calculated as:
Days in inventory + Days in receivables – Days in payables
4) Calculating Revenue, Expenses, and Inventory:
A firm’s income is calculated by subtracting its expenses from its revenue. However, not all costs are considered expenses; accounting standards and tax laws prohibit the expensing of costs incurred in the production of inventory. Rather, these costs must be allocated to inventory accounts and appear as assets on the balance sheet. Once the finished goods are drawn from inventory and sold, these costs are reported on the income statement as the cost of goods sold (COGS). If one wishes to know how much product the firm actually produced, the cost of goods produced in an accounting period is determined by adding the change in inventory to the COGS.
5) Assessment of Financial Ratios:
A firm’s performance can be evaluated using various financial ratios. Ratios are used to measure leverage, margins, turnover rates, return on assets, return on equity, and liquidity. Additional insight can be gained by comparing ratios among firms in the industry.
6) Decision making Bank Loans:
Bank loans can be classified according to their durations. There are short-term loans (one year or less), long-term loans (also known as term loans), and revolving loans that allow one to borrow up to a specified credit level at any time over the duration of the loan. Some revolving loans automatically renew at maturity; these loans are said to be “evergreen.”
7) Find the Sources and Uses of Cash:
There are two sources of cash: reducing assets or increasing liabilities or equity. Similarly, a company uses cash either by increasing assets or decreasing liabilities or equity.
8) Ensure Sustainable Growth:
A company’s sustainable growth rate is calculated by multiplying the ROE by the earnings retention rate.
9) Measurement of Firm Value, Equity Value, and Debt Value
10) Assessment of organizational Capital Structure
11) Organizational Risk Management
- Business risk
- Financial risk
- Total corporate risk
12) Assessment of Cost of Capital
13) Free Cash Flows
14) Decision Making in Cash Flows to Debt and Equity
15) Decision Making in Hurdle Price
16) Debt Assessment
17) Investment Decision
18) Optimal Capital Structure
19) Share exchange
20) Mergers and Acquisitions
Methodology:
For this assignment I went to Dhaka stock exchange to buy the financial report. And also personally visit the Renata Ltd Head office to collect necessary information.
Objectives:
First of all it should be mention that making an assignment is always challenging. For completing assignment on “The practices of Financial Management in Business Organization” needs time and hard work. I found lots of work for individual area but. But not too much work in full Financial Management practices. After working on this assignment I get lots of information about Financial Management practices which I believe some thing were unaware in past. Here is the summary of our objectives-
- It helps me to get the basic knowledge about Financing in organization.
- As a student of Business Studies I get lots of information about organizational practices.
- Practical knowledge in financial management.
- It helps me to find the how total financial activities are going on in the organization.
Limitation of the Work:
While I working on this assignment I had face some problem. Problems are-
- Problem in getting information about total Financial Management structure.
- Lack of primary data made this work little bit dry.
- Not enough journal & magazines.
- Lack of primary data
- Sometimes non-cooperative people.
- Lack of time is another big problem while I working on this assignment.
Company Profile :
|
Historical High-Lights:
Renata Limited is one of leading Pharmaceutical company in Bangladesh. Founded in 1972 as a subsidiary of Pfizer Inc. Ownership transferred from Pfizer Inc. to local institutions and the general public in 1993. Company name subsequently changed from Pfizer Laboratories (Bangladesh) Limited to Renata Limited.
Type of Company : Listed Public Limited (Dhaka Stock Exchange)
Turnover: US $21.0 Million
Retained Earnings: US $5.0 Million
Net Asset Value: US $11.0 Million
Main Business:
Manufacture and Marketing of Human Pharmaceuticals.
Manufacture and Marketing of Animal Therapeutics of Nutrition products (No. 1 in Market in terms of Sales.)
Renata 120,000 Square Feet (11,150 m2) Plant is located in Dhaka on 12 Acres of Land.
Quality Recognition: ISO9001 (DNV)
No. of Employees: 1267
Trade Mark Acquisition:
- Trademarks for three Hoechst Marion Roussel (HMR) products perpetually assigned to Renata. These products are
- Bactamox (Amoxicillin Tablet and Dry Syrup)
- Alsporin (Cephalexin Tablet and Dry Syrup)
- Pyralgin (Paracetamol Tablet and Suspension)
- This acquisition was made following a three-year relationship with HMR. From 1997-2000, Renata manufactured 19 Penicillin and Cephalosporin formulations on behalf of HMR.
Export : Human Pharmaceuticals to Myanmar, Nepal and SriLanka
Distributors and Affiliations:
- Distributor for Chiron Vaccines (Rabipur)
- Distributor for BASF (Animal Nutrition Products)
- Distributor Evans Vanodine (disinfectant)
- Distributor for Schering-Plough Animal Health (Vaccines)
- Distributor for Pfizer, India (Animal Health)
- Distributor for Zinpro, USA (Metal Amino Acid Complexes)
- Distributor for Biomin Laboratories, Singapore (Mycotoxin Binders and Nutraceuticals)
Licensing Arrangement :
Providing technical assistance to Deurali Janata Pharmaceuticals Private Limited (Nepal)
Contract Manufacturing :Contract manufacturing Oral Dehydration Salt formulation
Investment :
100% Shareholding in Renata Agro Industries Limited (One of largest poultry breeding and hatching operation in Bangladesh).
Financial Analysis
For the year
2005
In my personal finding, collect the annual report of 2005 & searching website of Renata Ltd, the financial department of Renata Ltd doing all over the activities of Preparation of Balance Sheet Approach to Valuation, Measurement of Cash vs. Profits, Measurement of Cash Cycle, Calculating Revenue, Expenses, and Inventory, Assessment of Financial Ratios, Decision making Bank Loans, Find the Sources and Uses of Cash, Ensure Sustainable Growth, Measurement of Firm Value, Equity Value, and Debt Value, Assessment of organizational Capital Structure, Organizational Risk Management, Decision Making in Cash Flows to Debt and Equity etc. Renata ltd is a Public Limited (Dhaka Stock Exchange) company, So Financial Management play an important role in proper distribution for each share holder.
In following I discuss some financial Statement of year 2005 of Renata Ltd
| FINANCIAL RESULTS : | |||
The financial results of the Company for the year 2005 & Compare with 2004 &2003 | |||
2005 | 2004 | 2003 | |
Taka | Taka | Taka | |
| Profit before tax | 279,387,690 | 208,308,833 | 150,434,885 |
| Less: Provision for tax | 86,819,430 | 62,820,892 | 44,873,677 |
| Net Profit after tax | 192,568,260 | 145,487,941 | 105,561,208 |
| Add: Un-appropriated profit brought forward | 313,458,030 | 216,734,815 | 152,689,300 |
| Profit available for appropriation | 506,026,290 | 362,222,756 | 258,250,508 |
| APPROPRATION RECOMMENDED: | |||
| Tax holiday reserve | 2,197,657 | 6,924,906 | 6,649,168 |
| Dividend proposed: | |||
| a) Cash dividend @ Taka 50/- per Share | 33,471,850 | 27,893,200 | 23,244,350 |
| b) Stock dividend (Bonus Share) in the ratio of | |||
| one bonus share for every five (1:5) Shares held | 13,388,740 | 11,157,280 | 9,297,740 |
46,860,590 | 39,050,480 | 32,542,090 | |
| Dividend distribution tax @ 10% of cash dividend | – | 2,769,320 | 2,324,435 |
| Balance Un-appropriated profit carried forward | 456,968,043 | 313,478,050 | 216,734,815 |
506,026,290 | 362,222,756 | 258,250,505 | |
Assessment of Balance Sheet as at 31 December 2005
Renata Limited | |||||
Balance Sheet as at 31 December 2005 | |||||
2005 | 2004 | ||||
| Sources of fund | Notes | Taka | Taka | ||
| Shareholders’ equity: | |||||
| Share capital | 4 | 66,943,700 | 55,786,400 | ||
| Proposed bonus shares | 13,388,700 | 11,157,300 | |||
| Revaluation surplus | 5 | 156,482,355 | 156,774,863 | ||
| Tax holiday reserve | 46,862,514 | 44,664,857 | |||
| Unappropriated profit | 6 | 456,968,084 | 313,458,030 | ||
740,645,353 | 581,841,450 | ||||
| Deferred liability – staff gratuity | 7 | 60,324,000 | 52,822,000 | ||
| Deferred tax liability | 8 | 55,975,450 | 57,663,916 | ||
856,944,803 | 692,327,366 | ||||
| Applications of fund | |||||
| Property, plant and equipment: | 9 | ||||
| At cost/revaluation | 619,228,840 | 597,325,841 | |||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | 219,989,057 | 194,770,823 | |||
399,239,783 | 402,555,018 | ||||
| Capital work in-progress | 10 | 139,891,546 | 10,683,181 | ||
| Investment at cost | 11 | 63,070,376 | 63,070,376 | ||
| Current assets: | |||||
| Stocks and stores | 12 | 388,384,007 | 361,664,208 | ||
| Debtors | 13 | 162,224,078 | 112,899,272 | ||
| Advances, deposits and prepayments | 14 | 32,294,635 | 28,141,978 | ||
| Cash and bank balances | 15 | 89,452,557 | 70,710,981 | ||
672,355,277 | 573,416,439 | ||||
| Less: Current liabilities: | |||||
| Creditors of goods | 16,645,268 | 3,653,923 | |||
| Accrued expenses | 65,951,508 | 39,594,897 | |||
| Other finance | 16 | 27,154,025 | 19,658,040 | ||
| Short term bank loans | 17 | 192,425,445 | 206,014,979 | ||
| Provision for taxation | 18 | 80,483,330 | 56,807,350 | ||
| Unclaimed dividend | 1,480,753 | 985,939 | |||
| Proposed cash dividend | 33,471,850 | 27,893,200 | |||
| Dividend distribution tax | – | 2,789,320 | |||
417,612,179 | 357,397,648 | ||||
| Net current assets | 254,743,098 | 216,018,791 | |||
856,944,803 | 692,327,366 | ||||
Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31 December 2005:
Renata Limited | ||||||
Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31 December 2005 | ||||||
2005 |
| 2004 | ||||
| Non-tax | ||||||
| holiday | Tax holiday | |||||
Notes | Unit 1 & 2 | Unit 3 | Total | Total | ||
| Schedule-A | ||||||
Taka | Taka | Taka | Taka | |||
| Turnover | 19 | 1,535,985,743 | 72,570,096 | 1,608,555,839 | 1,351,797,184 | |
| Cost of goods sold | 20 | -772,535,952 | -56,661,484 | -829,197,436 | -697,413,608 | |
| Gross profit | 763,449,791 | 15,908,612 | 779,358,403 | 654,383,576 | ||
| Other income | 21 | 16,957,354 | – | 16,957,354 | 7,676,622 | |
780,407,145 | 15,908,612 | 796,315,757 | 662,060,198 | |||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||
| Administrative, selling | ||||||
| and distribution expenses | 22 | -478,827,482 | -529,600 | -479,357,082 | -417,069,271 | |
| Operating profit | 301,579,663 | 15,379,012 | 316,958,675 | 244,990,927 | ||
| Non-operating expenses (net) | 23 | -22,826,562 | -1,090,000 | -23,916,562 | -26,266,652 | |
278,753,101 | 14,289,012 | 293,042,113 | 218,724,275 | |||
| Contribution to WPPF | -12,973,993 | -680,430 | -13,654,423 | -10,415,442 | ||
| Profit before tax | 265,779,108 | 13,608,582 | 279,387,690 | 208,308,833 | ||
| Tax expenses: | ||||||
| Current tax | 18 | -85,567,896 | -2,596,622 | -88,164,518 | -59,322,757 | |
| Deferred tax | 1,345,089 | – | 1,345,089 | -3,498,135 | ||
-84,222,807 | -2,596,622 | -86,819,429 | -62,820,892 | |||
| Profit after tax | 181,556,301 | 11,011,960 | 192,568,261 | 145,487,941 | ||
| Unappropriated profit brought forward | 313,458,030 | 216,734,815 | ||||
| Profit available for appropriation | 506,026,291 | 362,222,756 | ||||
| Appropriation: | ||||||
| Tax holiday reserve | -2,197,657 | -6,924,906 | ||||
| Proposed bonus shares (1 share for 5 shares held) | -13,388,700 | -11,157,300 | ||||
| Proposed cash dividend (Tk 50 per share) | -33,471,850 | -27,893,200 | ||||
| Dividend distribution tax | – | -2,789,320 | ||||
-49,058,207 | -48,764,726 | |||||
| Unappropriated profit carried forward | 456,968,084 | 313,458,030 | ||||
| Basic earnings per share (par value Tk 100) – Note 24 | 287.66 | 260.79 | ||||
Statement of changes in equity for the year ended 31 December 2005
Renata Limited | ||||||
Statement of changes in equity for the year ended 31 December 2005 | ||||||
Share | Proposed | Revaluation | Tax holiday | Unappropriated | ||
capital | bonus shares | surplus | reserve | Profit | Total | |
Taka | Taka | Taka | Taka | Taka | Taka | |
| Balance at 31 December 2003 | 46,488,700 | 9,297,740 | 157,410,748 | 37,739,951 | 216,734,815 | 467,671,954 |
| Bonus shares issued | 9,297,700 | -9,297,700 | – | – | – | |
| Depreciation adjustment on revaluation surplus | – | – | -635,885 | – | – | -635,885 |
| Deferred tax on RS | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Net profit after tax for the year | – | – | – | – | 145,487,941 | 145,487,941 |
| Tax holiday reserve | – | – | – | 6,924,906 | -6,924,906 | |
| Proposed bonus shares | – | 11,157,300 | – | – | -11,157,300 | |
| Proposed cash dividend | – | -40 | – | – | -27,893,200 | -27,893,240 |
| Dividend distribution tax | – | – | – | – | -2,789,320 | -2,789,320 |
| Balance at 31 December 2004 | 55,786,400 | 11,157,300 | 156,774,863 | 44,664,857 | 313,458,030 | 581,841,450 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Bonus shares | 11,157,300 | -11,157,300 | – | – | – | |
| Deferred tax onRS | 343,377 | 343,377 | ||||
| Depreciation adjustment on revaluation surplus | – | – | -635,885 | – | – | -635,885 |
| Net profit after tax for the year | – | – | – | – | 192,568,261 | 192,568,261 |
| Tax holiday reserve | – | – | – | 2,197,657 | -2,197,657 | |
| Proposed bonus shares | – | 13,388,700 | – | – | -13,388,700 | |
| Proposed cash dividend | – | – | – | – | -33,471,850 | -33,471,850 |
| Balance at 31 December 2005 | 66,943,700 | 13,388,700 | 156,482,355 | 46,862,514 | 456,968,084 | 740,645,353 |
Assessment of Cash flow statement for the year ended 31 December 2005
Renata Limited | |||||
Cash flow statement for the year ended 31 December 2005 | |||||
2005 | 2004 | ||||
Taka | Taka | ||||
A. | Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||
| Collection from customers and other income | 1,836,005,683 | 1,563,365,046 | |||
| Payment of VAT | -243,974,768 | -207,944,797 | |||
| Payment to suppliers and employees | -1,292,169,955 | -1,189,842,753 | |||
| Cash generated from operation | 299,860,960 | 165,577,496 | |||
| Financing cost | -23,916,562 | -26,417,268 | |||
| Payment of tax | -64,488,538 | -48,129,584 | |||
| Net cash from operating activities | 211,455,860 | 91,030,644 | |||
B | Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||
| Purchase of property, plant and equipment | -151,986,364 | -89,370,581 | |||
| Investment in shares | – | -2,499,900 | |||
| Sale proceeds of property, plant and equipment | 260,000 | 269,375 | |||
| Net cash used in investing activities | -151,726,364 | -91,601,106 | |||
C. | Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||
| Medium term loan repaid | – | -10,000,000 | |||
| Dividend paid | -27,398,386 | -23,081,044 | |||
| Net cash from financing activities | -27,398,386 | -33,081,044 | |||
D | Net cash outflows for the year (A+B+C) | 32,331,110 | -33,651,506 | ||
E | Opening cash and cash equivalents | -135,303,998 | -101,652,492 | ||
F | Closing cash and cash equivalents (D+E) | -102,972,888 | -135,303,998 | ||
Beside This Renata Ltd Management Practices following financial measurement & activities
- Property, plant and equipment.
- Capital work in-progress
- Investment at cost
- Stocks and stores
- Debtors
- Trade debtors
- Advances, deposits and prepayments
- Cash and bank balances
- Workers’ profit participation fund
- Short term bank loans
- Provision for taxation
- Turnover
- Cost of goods sold
- Cost of goods manufactured
- Cost of raw materials consumed
- Purchases, issues and stocks of raw materials
- Summarized quantity of purchases, issues and stocks of raw materials
- Administrative, selling and distribution expenses & other expenses
- Basic earnings per share (EPS)
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Payments to directors and officers
- Capacity utilization – single shift basis
- Outstanding letters of credit
- Cash flows from operating activities:
- Cash flows from investing activities:
- Cash flows from financing activities:
Recommendation:
While I researching in this assignment, there are some lacking. I feel that Reneta Ltd can improve them a lot. So I have some suggestion & this are-
- Improving the infrastructure financial management.
- Need more publications & proper explanation.
- Improving the facility & trained professional.
- Improving productivity the training facility should be increasing.
- For costs minimize financial management suggest product bench marking & product value chain system.
- Need to be developing according to the global needs.
- Raw materials of the Reneta products are comparatively very high. So it needs new supplier.
- Financial department need to give attention in EPS.
- Decision making should be properly for new launch (Product & Technology).
- Accounting system should be full computerized.
Conclusion:
After going through all the financial analysis of the company I think the company is in a good position. Although some analyses are falling gradually yet if the company pays a little attention to the related matters which can improve, they will do much better in later.
Finally, I would like to say that financial management is one of the core departments in the business organization point of view. A good business organization needs strong financial management department for achieving there mission & objective.