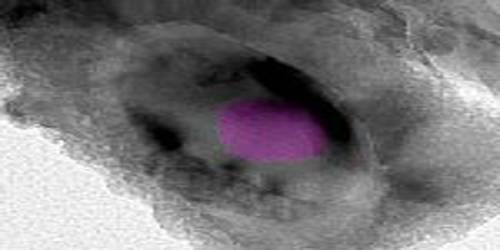
Brownleeite is a silicide mineral with chemical formula MnSi. It was discovered by researchers of the Johnson Space Center in Houston while analyzing the Pi Puppid particle shower of the comet 26P/Grigg-Skjellerup. The only other known natural manganese silicide is mavlyanovite, Mn5Si3.
General Information
- Category: Native element class, Fersilicite group
- Formula: MnSi
- Crystal system: Isometric
- Crystal class: Tetartoidal (23)
- Crystal habit: Cubic grain in microscopic dust particle (< 2.5 μm)
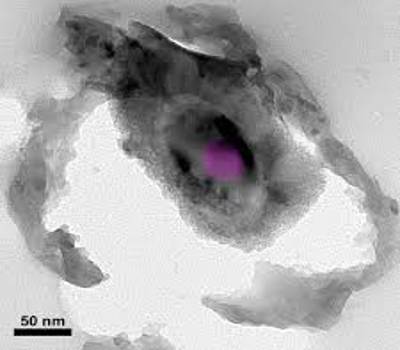
The particles were collected from the stratosphere over the south-western US in April 2003 using an ER-2 high-altitude research aircraft of the NASA. The team of researchers from USA, Germany, and Japan was led by NASA scientist Keiko Nakamura-Messenger.
To determine the mineral’s origin and examine other dust materials, a new transmission electron microscope was installed in 2005 at Johnson Space Center.
The mineral name was approved by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA Number 2008-011). The NASA scientists named the mineral after Donald E. Brownlee, professor of astronomy at the University of Washington, Seattle.
Information Source: