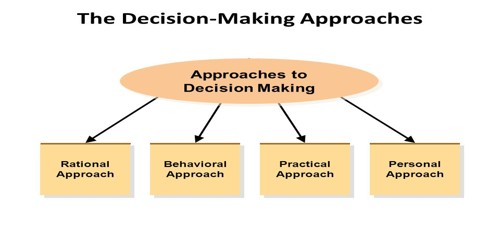
Behavioral Approach to Decision Making
Behavioral approach is also known as descriptive approach and administrative model. This theory is proposed by Herbert A Simon, a well known economist, in which he attempts to explain how decisions are made in real life situations. A manager has to make decisions under different conditions and situations. While taking a decision how a manager perceives the things, how does he react and how does he try to resolve, all this is human behavior.
Managers have limited and simplified view of problems because they do not have full information about the problems, do not possess knowledge of all possible alternative solutions, do not have the ability to process environmental and technological information and do not have sufficient time and resources to conduct an exhaustive search for alternative solutions to the problems. Therefore, this model is based on two concepts: bounded rationality and satisfying.
Task-Oriented Behavior
A professional using a task-oriented approach to business management focuses on planning, coordinating and assigning employee tasks. This type of manager focuses on employee behavior in terms of assignments and what’s best for the business.
Employee-Oriented Approach
An employee-oriented approach to business management places emphasis on the interpersonal relationships of workers. A manager using this behavioral method doesn’t place great emphasis on production where it increases employee anxiety and damages the ability of employees to establish strong bonds. This type of manager wants employees to have positive working relationships and strives to create a welcoming office environment.
Path-Goal Theory
Path-goal leadership theory is a situational style of behavioral management in which the work environment and the characteristics of employees influence which behavioral approach to management is most effective. Path-goal leadership has four leadership types: directive, supportive, participative and achievement-oriented. Determining which behavioral approach to use requires a manager to consider employee skills, experience, nature of the assignment, dynamic of the work group and the office environment.
Need Theories of Management
Motivating employees can be difficult if a manager doesn’t recognize the needs of her workforce. Incorporating need theories — first pioneered by psychologist Abraham Maslow — into a manager’s behavior approach can help her improve her motivational strategies. Maslow’s need theories have five distinct types of need arranged by hierarchy: psychological, safety, belonging/love, esteem and self-actualization. These theories also assume that humans can never completely satisfy needs and that the need for satisfaction motivates behavior.
In real life situation decision-making is sub-rational, fragmented and pragmatic activity. According to Herberton Simol, the norm of’ satisfying’ represents and describes actual decision-making behaviour of the manager and involves choosing a course of action that is satisfactory or good enough under the circumstances.
Information Source: