Marketing vs. Promotion
Marketing concept vs. Promotion concept
Marketing concept: A total system of business activities designed to plan, price, promote, and distribute, want satisfying products to target markets to achieve organizational objectives.
Promotion concept: One of the four elements of marketing mix, it increases company sales by communication product information to potential customer.
The marketing mix:
Product: A set of tangible and intangible attributes, including packaging, color, price, quality and brand, plus the seller’s services and reputation-a product may be a good, service, place, person, or idea.
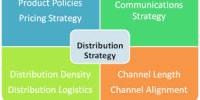
Place or Distribution: Distribution refers to the channel structure used to transfer products from an organization to its customers.
Price: The value or worth of a product.
Promotion: One of the four elements of marketing mix, it increases company sales by communication product information to potential customer.
Planning:
Public Relation: Marketing relation with public through direct communication advertising and behavior, when they come to the shop
The promotion mix
Advertising: Advertising differs from the other marketing communication elements in several ways. although advertising has a greater ability to reach a larger number of people simultaneously than do the other elements, it has less ability to prompt an immediate change in consumer behavior, and though not always explicit.
Personal selling: Personal selling is face-to-face contact between the marketer and a prospective customer. Personal selling is most important for companies that sell products requiring explanation, demonstration, and service, such as high technology products Homes and travel.
Sales promotion: Sales promotion aims to generate immediate sales for a limited period of time. Sales promotions can support advertising campaigns. Advertising and sales promotion can work together to create a synergy in which each makes other more effective.
Direct marketing: Companies that distribute their products directly, without the use of a reseller, engage in direct marketing. Rather than stores or salespeople, direct marketing relies on advertising media to inform and stimulate customer purchase. Online marketing is the newest direct channel.
E-commerce: E-commerce means selling goods and services through electronic means, usually over the internet.
Publicity: The non personal communication of information is not paid for by an individual or organization.
Types of communication used in promotion
Non personal communication – Advertising and publicity:
One way communication: one way communication is a communication which is done from one side by one person. There is no feedback in this communication.
Media’s orientation: media orientations work closely with creative and account executives. It is important for the creative to know which media will be used, because the choices have such a large impact on how advertisements are designed.
Mass level: mass level is the level of mass media where are several types of media among them the best media will be selected
Cost effectiveness: cost effectiveness is a process by which cost will be minimized by choosing that media where target people can be caught.
Used in both pull and push strategies: Pull Strategy is a strategy that directs marketing efforts at the consumer and tempts to pull the products through the channels and
Push Strategy is a strategy that directs marketing efforts at resellers, where success depends on the ability of these intermediaries to market the product, which they often do with advertising.
Other non personal communication: suitable for less technology oriented products like FMCG, less expensive products, exciting and known products.
Personal communication- personal selling methods used in promotion;
Two way communication: the communication between the two persons as well as feedback can be found at the same time that is called two way communications.
Personnel orientation: personnel orientation means to provide the training of the employee or personnel by which they will be able to reach the information to the customers. Even they will provide detail information about the product by displaying indifferent fair.
One to one level: The communication through which information is acknowledged by one person to other person.
Result orientation: Result orientation refers to that orientation where the personnel show the result and fruitfulness to the customers a benefited person who used and benefited by using the product.
Less coverage: Less coverage means a company advertised the product through differing media but they felt to cover the large number of people, they become wasted coverage.
Expensive method: Expensive method means if the company wants to ad through a particular media or channel they need to pay much more money which is less coverage than feedback.
Used in both pull and push Strategy: Pull Strategy is a strategy that directs marketing efforts at the consumer and tempts to pull the products through the channels. And
Push Strategy is a strategy that directs marketing efforts at resellers, where success depends on the ability of these intermediaries to market the product, which they often do with advertising.
Others personal communication techniques,
Suitable for technology oriented products, new products, Demo experience required for usage.
Types of sales promotion
Consumer products
Products produced for and purchased by, households or end consumers for their personal use.
- Consumer-oriented:
- Trade oriented:
Industrial products
Product sold primarily for use in producing other products.
Integrating the Elements of the promotion mix
The product life cycle
| Market Situation | Promotion Strategy |
| Customers are not aware of the product features, nor do they understand how it will benefit them. | Introduction stage: Inform and educate potential customers that the product exists, how it might be used, and what wants satisfying benefits it provides. |
| Customers are aware of products benefits, the products selling well, and middlemen want to handle it | Growth stage: stimulate selective demand as competition grows. Increase emphasis on advertising. Middlemen share more of the total promotional effort. |
| Competition intensifies and sales level off. | Maturity stage: Advertising is used more to persuade a rather than only to provide information. |
| Sales and profits are declining new and better products and coming into the market. | Declining stage: All promotional efforts are cut back substantially. The cues becomes reminding and remaining customer. |
Product Characteristics:
Complexity: when a company starts to produce the product then they face various types of barriers and problems which abstract to manufacture the product.
Cost: Cost is a main fact of producing product. Sometimes if requires high cost sometimes low cost. Two types of cost – variable cost, fixed cost.
The target audience: The final player in the advertising world is the target audience. All strategy starts with the customer the target audience has a direct bearing on the overall advertising strategy, especially the creative strategy and the media strategy. The task of learning about the target audience is laborious and may take thousands of hours and millions of dollars to accomplish.
Consumer vs. Business:
Consumer: consumer is the final person who consumes the product.
Business: Business means when a person invests money in legal ways and purpose of earning money and providing service to the people.
Pull Vs. Push
Pull strategy:
Pull Strategy is a strategy that directs marketing efforts at the consumer and tempts to pull the products through the channels.
Push Strategy:
Push Strategy is a strategy that directs marketing efforts at resellers, where success depends on the ability of these intermediaries to market the product, which they often do with advertising.
Pull vs. Push strategy and their combination
For IUBAT MBA program Promotional objectives
Sales Target: The purpose or the target prospect or customer calls for MBA program providing
Market share Targets: The main objectives of giving advertisement to promote IUBAT MBA program is to enlarge the market share.
Communication Targets: There are several types of communication ways of promoting MBA program; among them any one can be chosen for communication target to capture the customer, communication target should be designed in such a way which is memorable and to get the attention of people.
Awareness: At the awareness stage the seller’s task is to let the buyers know the product or brand exists. The person who are interested doing MBA program, go to that person and aware different things, which and create goodwill about IUBAT MBA.
Information: Information goes beyond awareness to learning about a product features and providing all type of information about IUBAT MBA program.
Brand Preference: Creating preference involves distinguishing among brands such that market prefers you’re.
Share of voice: To develop the right tone of voice, copyrighters write to a typical user.
Share of mind: Share of mind refers to entails the actual decision or commitment to admission.
Share of heart: share of heart means we will provide such information that will say the word of heart of the target audience.
Target Audience: The students who completed their Bachelor degree or the people who are working in different organization do not complete their MBA degree.
Objective: To promote the MBA program, to influence the target customer to get admitted in IUBAT
Degree of change: There should be a trend to change the format, word, theme on the basis of time and situation of the market.
Time frame: IUBAT can advertise on the basis of period of semester, or they can advertise through out the whole year continuously.
Advertising Media
Television: Choosing appropriate television advertising outlets is not easy because there are so many options. Companies must carefully select those programs and channels most likely to reach their target audience.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High reach | Greater clutter |
| High frequency potential | Low recall due to clutter |
| Low cost per contact | Channel surfing during commercials |
| High intrusion values | Short amount of copy |
| Quality creative opportunities | High cost pre ad |
Radio: Radio may not be considered as glamorous as television. This makes it more difficult to attract talented creative to prepare ads.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Recall promoted | Short exposure time |
| Narrower target markets | Low attention |
| Ad music can match stations programming | Few chances to reach national audience |
| High segment potential | Target duplication when several stations use the same format |
| Flexibility in making new ads | overload |
Outdoor: Billboards along major roads are the most common from of outdoor advertising. Billboards, however, are only one from of outdoor advertising. Transit advertising is mainly an urban advertising form that uses vehicles such as buses and taxis to carry messages can circulate through the community.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Able to select key geographic areas | Short exposure time |
| Accessible for local ads | Brief messages |
| Low cost per impression | Little segmentation possible |
| Broad reach | Cluttered travel routes |
Magazines: The glamour of television has overshadowed magazines for a long time. For many advertisers, magazines have always been a second choice.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| High market segmentation | Declining readership |
| Target audience interest by magazine | High level to clutter |
| Direct response techniques | Long lead time to ad showing |
| High color quality | Little flexibility |
| Long life | High cost |
Newspaper: Newspapers represent the largest medium in respect to total advertising billing. It has been this way for several decades, despite the growth in competing media, especially television.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Priority of local ads | Poor buying procedures |
| High Flexibility | Short life span |
| High credibility | Major clutter |
| Strong audience interest | Poor quality reproduction |
| Longer copy message possible | Interest classified competition |
Direct Mail: Another major advertising medium is direct mail. Many companies send ads directly to target markets of customers through mailing lists or blanket for more general products.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Normally lands in the hands of the person | Expensive |
| Significant amount of family purchasing decisions | Clutter |
| Direct response programs | The Nuisance factor |
Internet: Internet marketing is the creative opportunities available and the short lead time.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Creative possibilities | Clutter on each side |
| Short lead time to send ad | Difficult producers to place ads and buy time |
| Simplicity of segmentation | Only for computer owners |
| High audience interest on each web site | Low intrusion value |
| Easier to measure responses directly | Short life span |
Criteria for selecting media
Cost: The cost of each medium should be considered in relation to the amount of funds available to pay for it and its reach or circulation.
Compatibility with media habits of target audience: The audience reached by the medium should match the geographic area in which the product is distributed. Furthermore, the selected medium should reach the desired types of prospects with a minimum of wasted coverage. Wasted coverage occurs when an ad reaches people who are not prospects for the product many media even national and other large market media can be targeted at small, specialized market segment.
Compatibility with products: The product attributes or benefits without any claim of superiority.
Compatibility with message: Ads designed to invoke feelings and emotions and match them with the product, service, or company.
Types of Advertising
Product advertisements: Advertising that focuses on a particular product or brand. Product advertising in subdivided into direct action – seeks a quick response. Indirect action – is designed to stimulate decant over a longer period of time.
Institutional advertisements: Advertising that presents about the advertiser’s business or tries and create a favorable impression build goodwill about the organization.
Pioneering: Primary demand of advertising of the introductory stage is product life cycle that is intended to inform the target market.
Reminder: Aim to stimulate repeat purchase that they made the right choice expensive.
Advocacy advertising: Advocacy advertising is a type of corporate advertising that involves creating advertisements and purchasing space to deliver a specific, targeted message.
Competitive Advertising: another section in the key decisions part of the advertising plan is to analyze the product in comparison to competing products.
Advertising Appeals
Rational appeals: Rational appeals are normally based the hierarchy of effects model. The goal of the rational appeal is to provide the information needed to help the market decision.
Emotional appeals: Emotional appeals are based on three ideas. First, consumer ignores most advertisement. Second, rational appeals go unnoticed the consumer in the market for a particular product at the time it is advertising. Third, and most important, emotional advertising can capture a viewers attention and help develop an attachment between consumer and brand.
Scarcity appeals: Another appeal that is occasionally used is scarcity. When there is a limited supply of the product, the value of the product increases. Scarcity appeals urge consumers to buy a particular product because of a limitation.
Emotional Appeals
Joy: Joy is an extremely important component in advertising. Joy helps to get attention of listeners and is linked to emotion.
Love: A company should advertise in a way that will reflect love with each other and interconnect with motion.
Sex: As advertisers look for ways to break through the advertising clutter, they use sexual appeals with increasing regularity
Fear: Advertising use fear to sell a variety of products. Life insurance companies focus on the consequences of not having life insurance if a person dies.
Humor: Using exaggeration, slapstick comedy, or humorous stories, advertisers attempt to draw the audience into the message.
Execution Styles
Slice of life: Typical format is to depict “real people” experiencing a dilemma or crisis, interrupt this story with some information the brand, the return to the story about show how the brand resoles the problem. The advertiser hopes the audience will relate to the story and associate the brand with the happy ending.
Lifestyle: Lifestyle is the pattern of living that reflects how people allocate their time, energy, and money. Lifestyle analysis is the examining the ways people allocate their time, energy; and money.
Personality symbol: A symbol is used to depict the benefits of the product in a concrete fashion. It is Common for services where visualization of a good is not possible.
Musical: Music can be intrusive thereby gaining the attention of someone who previously was not listening to or watching a program
Humor: Using exaggeration, slapstick comedy, or humorous stories, advertisers attempt to draw the audience into the message.
Endorsements: As authority figure or celebrity presents the product. The advertiser hopes the credibility or attractiveness of the spokesperson will spill over the product.
Media Terminology
Reach: Reach is the percentage of the target population exposed at least once to the advertiser’s message during a specific time frame. This means the reach is not based on actual data but is calculated from the laws of chance.
Rating: rating is a process of measuring of what percentage a company achieved through the advertising.
Frequency: Equally as important as the percentage of people exposed (reach) is the number of times they are exposed. This rate of exposure is called Frequency. While the reach estimate is based on only a single exposure, frequency estimates the number of times the exposure is expected to happen.
Cost per Thousand: The process of measuring the target audience size against the cost of that audience is called efficiency or more popularly, cost per thousand (CPM). Cost Per Thousand is the best to use CPM analysis to compare vehicle within one medium. It is also important to base it only on the portion of the audience that has the target characteristics, such as women between the ages of 25 to 34. to calculate the CPM we need two figures like cost of the unit and the estimated target audience.
Gross Rating Points (GPRS): the sum of the total exposure potential of a series of media vehicles expressed as a percentage of the audience population.
Impact: The qualitative value of a message exposure through a given medium.
Wasted coverage: Wasted coverage occurs when an ad reaches people who are not prospects for the product many media even national and other large market media can be targeted at small, specialized market segment.
Sales Promotion
Consumer products: Products produced for and purchased by, households or end consumers for their personal use.
Industrial products: Product sold primarily for use in producing other products.
Consumer Products:
Consumer- oriented-
Coupons: Coupons is legal certificates that is offered by manufacturers and retailers that grant specified savings on selected product when presented for redemption at the point of purchase.
Premiums: Premium is a tangible reward received for performing a particular act, such as purchasing a product or visiting the point-of-purchase.
Samples: offers a trial amount of a product.
Sweepstakes: Sweepstakes refer to the contests that require only the participant supply his or her name to participate in a random drawing.
Rebates: Rebate is a sales promotion the customer to recover part of the product’s cost from the manufacturer in the form of cash.
Trade- oriented-
Point of purchase: It displays designed by the manufacturer and distributed to retailers to promote a particular brand or line of products.
Advertising allowances: The manufacturer pays the wholesaler or retailer a certain amount of money to advertise the manufacture’s product.
Display allowances: A direct payment of cash or goods is given to the retailer if the retailer agrees to set up the point of sales display.
Merchandise assistance: It Means the displays, signs, and positioning of the brand in that particular store. Creative and attention getting displays in the store serve to do much more than stock the product. They can greatly add to a sense of excitement about the product and lead to much greater involvement by the consumer in that product.
Quantity discounts: A deduction from a seller’s list price that is offered to buy when a large quantity of the product is purchased.
Industrial products-
Trade shows: In business-to- business marketing, total expenditures on trade shows ranks third, with only advertising and sales promotions receiving greater funding.