Agricultural value chain finance
Agricultural value chain finance is concerned with the flows of funds to and within a value chain to meet the needs of chain actors for finance, to secure sales, to buy inputs or produce, or to improve efficiency. The concept of Value Chain Finance is broad, and the term is used to describe varying aspects of the approach and its supporting tools. For example – most financing providers tend to focus on one particular element of the value chain, e.g. farmers or milk processors. Because of the strong interdependencies within the value chain, all actors require access to financing, to guarantee overall growth.
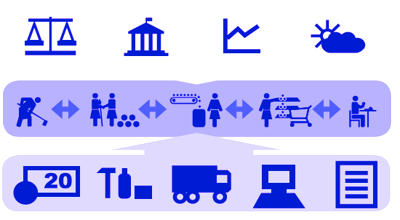
Fig. Common agricultural value chain flow
Agricultural value chain finance offers an opportunity to reduce cost and risk in the financing, and reach out to smallholder farmers. Value chain finance offers an opportunity to expand the financing opportunities for agriculture, improve efficiency and repayments in the financing, and consolidate value chain linkages among participants in the chain. Examining the potential for value chain finance involves a holistic approach to analyze the chain, those working in it, and their inter-linkages. These linkages allow financing to flow through the chain. For example, inputs can be provided to farmers and the cost can be repaid directly when the product is delivered, without the need for farmers taking a loan from a bank or similar institution. This is common under contract farming arrangements. Understanding value chain finance can improve the overall effectiveness of those providing and requiring agricultural financing.

Value chain finance in agriculture must be seen in the light of the larger context, not only of the value chains proper but also the business environment of each country as this impacts value chains and the financial systems. Types of value chain finance include product financing through trader and input supplier credit or credit supplied by a marketing company or a lead firm. Financing agriculture continues to be perceived as having high costs of operation, high risks, and low returns on investment. Other trade finance instruments include receivables financing where the bank advances funds against an assignment of future receivables from the buyer and factoring in which a business sells its accounts receivable at a discount. Develop rural social services such as health and child care, improve access to water and fuel, and upgrade infrastructure including market areas reserved and equipped for women with children, to reduce women’s burdens and improve their lives. Also falling under value chain finance are asset collateralization, such as on the basis of warehouse receipts, and risk mitigation, such as forward contracting, futures, and insurance.