The term agency bond is the debt issued by a government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) or a federal agency, also referred to as agency debt. Usually, though, they are less liquid than treasuries and do not have the same total federal guarantee. It is a protection provided by a government-sponsored corporation or by a department of the federal government other than the U.S. Treasury. The key distinction between a GSE and a federal agency is that a GSE’s commitments are not ensured by the administration, though a bureaucratic office’s obligation is upheld up by an administration ensure.
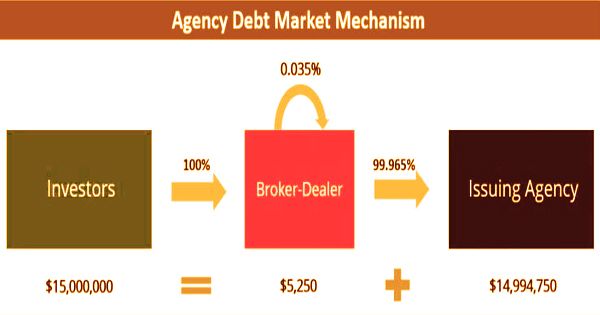
Agency debt market mechanism
Compared to the treasury, agency bonds offer higher interest rates, although a relative lack of liquidity can render them unfit for some investors. It comes in a large range of structures, maturities, and rates of coupons; most allow payments of semi-annual interest. Usually, agency bonds are sold by broker-dealers. Consequently, some agency bonds are callable, some have fixed coupon rates, some have gliding coupon rates, and some have surprising interest installment dates. Every office barters bonds as indicated by its own needs and schedule, however numerous organizations issue bonds month to month. Below are the important characteristics of agency bonds:
- Low risk: Agency bonds are regarded to be very stable and usually have good credit scores.
- Higher return: Compared to treasuries, which are deemed risk-free, they have higher returns.
- Highly liquid: They are actively traded and hence, are highly liquid.
There are two types of agency bonds, including federal government agency bonds and government-sponsored enterprise (GSE) bonds.
Federal Government Agency Bonds: That includes the Federal Housing Authority (FHPA), the Small Business Authority (SBA), and the National Government Mortgage Association (GNMA or Ginnie Mae). Similar to treasuries, bonds issued by federal government entities are usually backed by the federal government. While keeping this agency bond, an investor gets monthly interest payments. At its development date, the full assumed worth of the organization bond is gotten back to the bondholder. Government organization securities offer a somewhat higher financing cost than Treasury bonds since they are less fluid.
Government-Sponsored Enterprise (GSE) Bonds: Organizations such as the Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae), Federal Home Loan Mortgage (Freddie Mac), Federal Farm Credit Banks Financing Company, and the Federal Home Loan Bank are provided with a GSE (Government-Sponsored Enterprise). GSE is a quasi-governmental organization that has been established to increase the availability of credit and reduce the cost of financing targeted sectors of the economy. They are privately owned businesses that fill a public need, and hence might be upheld by the legislature and subject to government oversight.
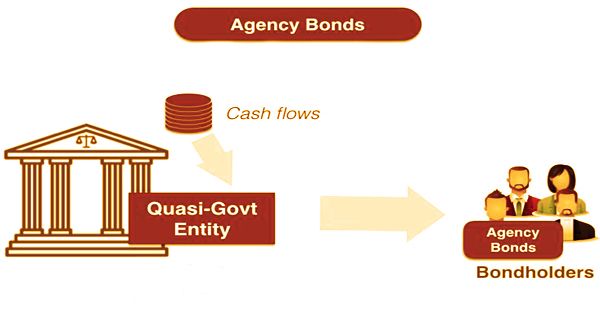
Example of Agency Bonds
Agency bonds are issued over a variety of maturities, from less than one year to 30-year bonds. Below are some common bond structures that include agency debt:
- Short-term notes
- Medium-term notes
- Callable bonds
- Fixed coupon bonds
Floaters, which come with a variable coupon charge, and zero-coupon discount bonds (sometimes called “discos” are two additional bond structures that can be found in the agency market. When all is said in done, the organization security market is fluid; nonetheless, the more “organized” office security is, the littler the market will in general be for the security. Clearly, this can make liquidity issues for the speculator. Some organization securities have fixed coupon rates while others have coasting rates.
Agency bonds, when acquired at a discount, can, when sold or redeemed, subject investors to capital gains taxes. Capital gains or losses are charged at the same rates as securities when selling agency bonds. It should be remembered that agency bonds are a key component of the capacity of a GSE to provide its intended public service. Premium earned on GSE obligation isn’t charge excluded, while enthusiasm on government organization obligation is charge absolved. It is a significant detail as assessment may apply a huge impact on an organization’s ventures.
Information Sources: