Agroecology is a novel approach to agriculture that combines ecological principles with social and economic elements to build sustainable and resilient food systems. It is gaining worldwide recognition and support as a promising alternative to traditional agriculture, with many farmers, groups, and legislators lobbying for its adoption to meet the concerns of sustainable food production and environmental stewardship.
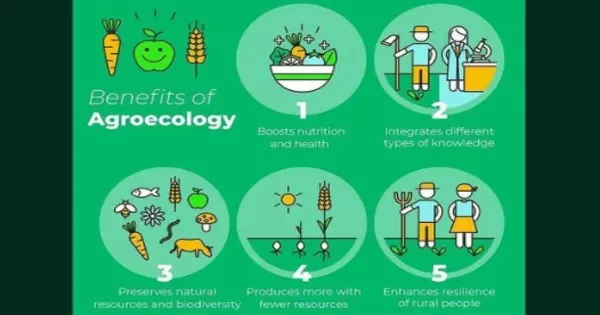
Agroecological techniques emphasize diverse farming systems, including the production of a diverse range of crops and livestock. This diversification improves food security by lowering vulnerability to crop failures, pests, and illnesses. Furthermore, agroecology encourages nutritious and healthful food production, which contributes to better diets and community health.
Farmers can benefit financially from agroecological methods, especially in the long run. Agroecology can improve farm profitability and resilience by lowering input costs, increasing soil fertility, and diversifying revenue sources, benefiting both farmers and the greater agricultural industry. Its goal is to imitate natural ecosystems, resulting in a more balanced ecological system with less negative environmental impacts.
Advantages of agroecology include:
- Environmental Sustainability: Agroecological practices minimize negative impacts on the environment, such as soil erosion, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Resilience: By promoting biodiversity and ecological balance, agroecological systems are often more resilient to pests, diseases, and extreme weather events.
- Food Security: Agroecology can contribute to improved food security by enhancing small-scale farmers’ productivity, diversifying crops, and promoting local food systems.
- Health Benefits: Reducing the use of synthetic inputs in agroecology can lead to healthier and safer food for consumers, as well as improved working conditions for farmers.
- Rural Development: Agroecology promotes the growth of local economies and rural communities by encouraging self-sufficiency, reducing reliance on external inputs, and creating social cohesion.
- Biodiversity conservation: Agroecological approaches promote the preservation and enhancement of biodiversity on farms. Agroecology helps to conserve plant and animal species by combining different crops, agroforestry, and establishing habitat for beneficial insects and wildlife.
The benefits of agroecology may differ depending on local conditions, farm size, and the practices used. Overall, agroecology appears to be a promising path toward more sustainable and resilient agricultural systems that address environmental, social, and economic concerns. It provides a holistic and multifaceted approach to agriculture that tackles both environmental and social concerns, paving the way for future sustainable and resilient food systems.