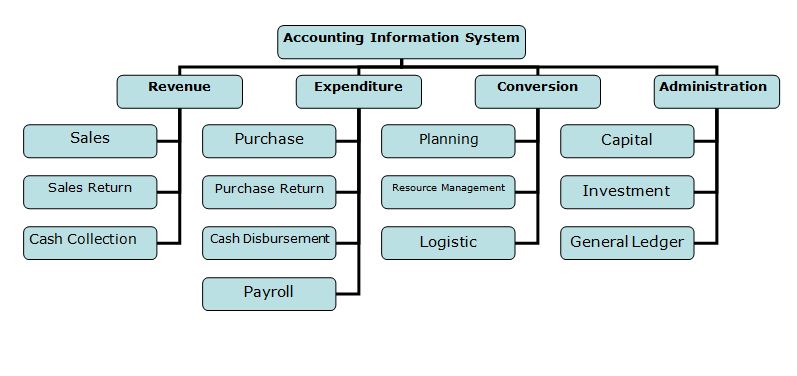
Accounting information system (AIS):
AIS Is a system of collection, storage and processing of financial and accounting data that is used by decision makers. An accounting information system is generally a computer-based method for tracking accounting activity in conjunction with information technology resources. The resulting statistical reports can be used internally by management or externally by other interested parties including investors, creditors and tax authorities. It includes education in the latest database management techniques and system modeling approaches, and provides the Internet implementation experience necessary to practice systems development in today’s technological environment.
1. Revenue:
Revenue process includes
- Sales
- Sales Return
- Cash Collection
a) Sales process
Purchase order ——-> Price Verification ——-> Sales order ——-> Credit Limit ——-> Inventory & sales preparation ——-> Prepare shipment documents ——-> Update accounts receivables ——-> Update General Ledger
Purchase order
A purchase order (PO) is a commercial document issued by a buyer to a seller, indicating types, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services. Bangladeshi mans wear brand Cats eye company ltd submits a purchase order of 500 pcs of shirt to Micro Fiber Company Limited.
Price Verification:
Micro fiber company ltd (seller) submit a price quotation of Tk 650 per pcs to Cats eye (buyer). Buyer verifies the price and confirm the final price at Tk 600 per pcs.
Sales order
A sales order records the customer’s originating purchase order which is an external document. The customer’s PO is the originating documents which trigger the creation of the sales order. In a manufacturing environment, a sales order can be converted into a work order.
Credit Limit
As a regular customer, The Cats eye company ltd gets a credit facility of Tk 7,00,000 from Micro Fiber company ltd. After receive the PO, the company immediately verify the buyers credit limit for future operations.
Inventory & sales preparation
After checking the credit limit, the seller checks the availability of the product in warehouse. If the product is available and matches with the buyer’s sample, then the seller prepares the goods for shipment as per the buyer’s requirement.
Prepare shipment documents
Seller sends the goods to the buyer after preparing the invoice and packing list. After that seller update the sales record accordingly.
Update accounts receivables & General Ledger
Seller updates the accounts receivable as per the sales record and prepare monthly statement and general ledger accounts.
b) Sales return process
Receive goods from customer ——-> Warehouse & Inventory ——-> Update sales record ——-> Update account receivable ——-> Update General Ledger
Receive goods from customer
Buyer (Cats eye company ltd) returns 50pcs of defective goods (shirt) to the seller (Micro Fiber Company Ltd). The billing departments of seller match the return goods with the original sales invoice while receive.
Warehouse & Inventory
Warehouse checks the condition of the returned goods. If it is in repairable condition then repair it and send to the buyer or update the inventory and COGS. If it is not in repairable condition, it consider as scrap.
Update sales record
After receiving the sales return, seller update the sales return record and prepare a credit memo and send it to customer.
Update account receivable
After the sales return, seller updates the account receivable accounts, cash record and general ledger.
C) Cash collection process
Cash receive from customer ——-> Update account receivable
Cash receive
Seller receives cash/cheque payment from buyer and prepare a cash receipt journal while it match with the original sales invoice.
Update account receivable
After receiving the cash payment, seller updates the accounts receivable accounts and general ledger.
2. Expenditure:
Expenditure process includes
- Purchase
- Purchase Return
- Cash Disbursement
- Payroll
- Purchase:
What is purchase?
Purchase defined as “the acquisition of needed goods and services at the optimum cost from competent, reliable sources in a timely manner.”. Though there are several organizations that attempt to set standards in the purchasing process and the process can vary between organizations to organization.
The Golden Rule of Purchasing:
Purchasing must acquire needed goods and services:
- Of the right quality
- In the right quantity
- At the right price
- At the right time
Purchase process
Where information technology is not heavily ingrained – Traditional Purchasing processes tend to be characterized by high levels of bureaucracy, encumbered with manual authorization (often requiring multiple signatures independent of the order value.), slow communications and a focus on unit price rather than long term commodity arrangements.
Purchase requisition & Authorized purchase requisition
A purchase requisition provides authorization for the Procurement Department to initiate a purchasing transaction. The requisition form is available from the Procurement Department, and contains a complete list of information that is required to complete a purchasing transaction.
Vendor selection
The vendor selection process can be a very complicated
Purchase order
A completed purchase requisition will be reviewed and approved in the Procurement Department according to the organization’s policy for requisition approval. Once the requisition has been approved, it will be used to create a Purchase Order (PO).
Receive goods
Vendor prepares to supply the goods and service to the buyer after receives the PO. Buyer prepare a receiving record after receive the goods.
Update inventory record
Buyer receive invoice from seller (supplier) and update the inventory records.
Update accounts payable
Buyer updates the accounts payable after the new purchase record.
Sales return & update accounts payable (if need)
Buyer updates the accounts payable if any purchase return occur.
Update General Ledger
Buyer updates the general ledger as per the purchase records.
- Purchase return process
A purchase return occurs when a buyer returns merchandise that it has purchased from a supplier.
Rejected goods from customer ——-> Authorization to return goods ——-> Document Match ——-> Prepare debit memo & send to vendor ——-> Receive credit/ cash from vendor & update account payable ——-> Update inventory record ——-> Update General Ledger
Rejected goods return from customer
Goods can be return to vendor for various reasons with a authorization of return.
Return goods with a debit memo
Return goods after match with the purchase invoice and send a debit memo to the vendor.
Update account payable, inventory record & general ledger
Update account payable and inventory record after receiving refund or credit memo from vendor against return.
- Cash Disbursement process
Cash disbursement means the payment of money against purchase.
Identify the invoice of due payments ——-> Prepare for payments ——-> Cheque sign after document check ——-> Payment to vendor ——-> Update cash record ——-> Update accounts payable record ——-> Update General Ledger
Identify the due invoices
Identify the vendors invoices which payment is still due and prepare for payment.
Payment to vendor and update the cash record
Payment of the vendor against the due payments after cheque signs and updates the cash records.
Update account payable and general ledger
Account payable and general ledger accounts will upgrade after payment to vendor.
- Payroll process
The payroll is the amount of money that a company pays its employees at any given time. Sometimes every two weeks, or sometimes once every month
Time sheet submit by the employee ——-> Working hour correction and approve the time sheet ——-> Prepare payroll register ——-> Prepare payroll Voucher ——-> Transfer fund to payroll bank account ——-> Update general ledger
Time sheet submission & checking
Employee submits there time sheet where there working time was recorded. Authority will approve that after checking/correction the working hours.
Prepare payroll register & voucher
The payroll register will prepare as per the corrected working hours.
Payroll voucher and transfer fund in payroll bank
Payroll voucher will create as per the payroll register. The fund will transfer to the payroll bank and update general ledger.
3. Conversion:
Conversion process includes
- Planning
- Resource Management
- Logistics
- Planning
Business planning is a process that involves the creation of a mission or goal for a company. The process of business planning can be very broad, encompassing each aspect of the operation.
- Resource Management
The process of using a company’s resources in the most efficient way possible is considered as resource management. These resources can tangible resources such as goods and equipment, financial resources, and labor resources such as employees. Resource management can include ideas such as making sure one has enough physical resources for one’s business.
- Logistics
Logistics is defined as a business planning framework for the management of material, service, information and capital flows.
4. Administration:
Administration process includes
- Capital
- Investment
- General Ledger
- Capital:
Capital is the money that is going to be invested in a business. Some of the money will come out of from personal investment. Some of the money may come from another source of financing, such as a bank or a small business center loan. That’s the capital for starting a business. Knowing how much capital needs to start a business will be a deciding factor on the type of business might be start.
Here we consider tk 50 lac as our capital, where tk 25 lac from personal investment and tk 25 lac from bank loan.
- Investment:
Investment encompasses a wide variety of funding options. While funding for capital investment is generally in the form of common or preferred equity issuance, it may also be through straight or convertible debt. Funds invested in a firm or enterprise for the purposes of furthering its business objectives. Capital investment may also refer to a firm’s acquisition of capital assets or fixed assets such as manufacturing plants and machinery that is expected to be productive over many years.
- General Ledger:
The general ledger is a collection of the group of accounts that supports the value items shown in the major financial statements. It is built up by posting transactions recorded in the sales daybook, purchases daybook, cash book and general journals daybook. The general ledger can be supported by one or more subsidiary ledgers that provide details for accounts in the general ledger. For instance, an accounts receivable subsidiary ledger would contain a separate account for each credit customer, tracking that customer’s balance separately. This subsidiary ledger would then be totaled and compared with its controlling account (in this case, Accounts Receivable) to ensure accuracy as part of the process of preparing a trial balance.