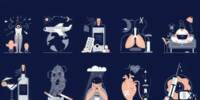
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects more than just the joints. The condition can harm a variety of body systems in some people, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that occurs when your immune system mistakenly attacks your own body’s tissues. Unlike osteoarthritis, which causes wear and tear on your joints, rheumatoid arthritis affects the lining of your joints, causing painful swelling that can eventually lead to bone erosion and joint deformity.
The high level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the rheumatoid arthritis (RA) microenvironment, combined with the disease’s persistent inflammatory nature, can cause damage to joints, bones, and the synovium. Strategies that combine effective RA microenvironment regulation with imaging-based monitoring could lead to advancements in RA diagnosis and treatment.
Researcher found that the M@P-siRNAsT/I suppressed TNF-α/IL-6 expression and overcame the hypoxic nature of the RA microenvironment, thus alleviating RA-induced joint damage in a mouse model.
A research team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology and the University of Texas at Austin has proposed a new strategy for treating rheumatoid arthritis with precision.
The researchers integrated small interfering RNAs (siRNAsT/I) and Prussian blue nanoparticles (PBNPs) to silence the expression of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α/IL-6 and scavenge the ROS associated with the RA microenvironment.
The study was published in PNAS.
To enhance the in vitro and in vivo biological stability, biocompatibility, and targeting capability of the siRNAsT/I and PBNPs, the researchers prepared macrophage membrane vesicles (MMVs) to construct biomimetic nanoparticles, M@P-siRNAsT/I.
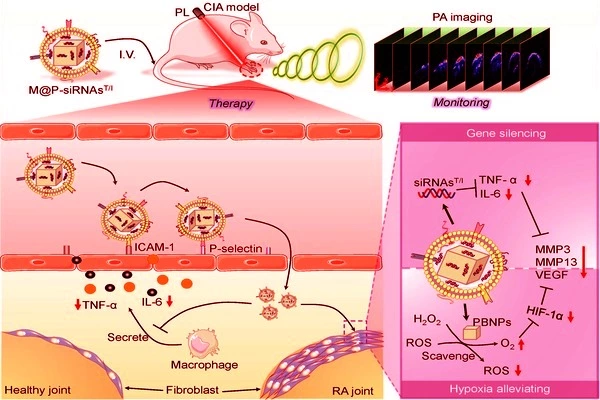
They found that the M@P-siRNAsT/I suppressed TNF-α/IL-6 expression and overcame the hypoxic nature of the RA microenvironment, thus alleviating RA-induced joint damage in a mouse model.
Moreover, near-infrared photoacoustic imaging (PAI) allowed the targeting behavior of the M@P-siRNAsT/I to be followed in real time, thus permitting an evaluation of their therapeutic efficacy without the need for invasive procedures. These findings show that macrophage-biomimetic M@P-siRNAsT/I and their analogs assisted by PAI can provide a new strategy for RA diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring.
Rheumatoid arthritis has numerous physical and social consequences, as well as the potential to reduce one’s quality of life. It can result in pain, disability, and death. Heart disease that develops prematurely. People who have RA are also more likely to develop other chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes.