IVF: In Vitro Fertilization
In Vitro Fertilization or IVF is a complex series of procedures used to treat fertility or genetic problems and assist with the conception of a child.
IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used for infertility treatment and gestational surrogacy, in which a fertilized egg is implanted into a surrogate’s uterus, and the resulting child is genetically unrelated to the surrogate. Some countries banned or otherwise regulate the availability of IVF treatment, giving rise to fertility tourism. Restrictions on availability of IVF include costs and age to carry a healthy pregnancy to term. IVF is mostly attempted if less invasive or expensive options have failed or are unlikely to work. IVF is a choice for couples who are not able to conceive without assistance.
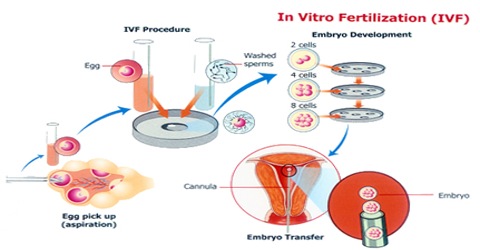
Process of IVF
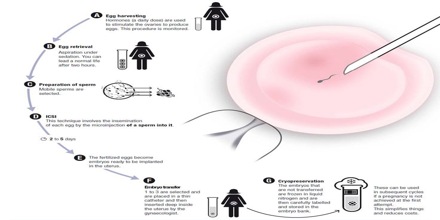
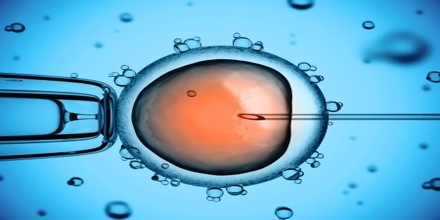
The process of IVF starts a few weeks before ovulation. Many women are given a drug to control ovulation so that eggs can be more readily collected, according to WebMD. The doctor will also monitor the eggs’ development over the next few weeks. Once they are mature, they are harvested with a small needle. Patients undergoing this procedure are usually sedated and given pain medicine when they wake up. Soon after, sperm is collected, either by a donor specified by the woman or from a sperm bank. The eggs and sperm are then placed in a glass dish so that the sperm can fertilize the eggs. After two to five days, the healthiest eggs are selected and set aside. Between one and three eggs are then implanted into the uterus through the use of a catheter inserted in the cervix. The remainder can be frozen for future attempts. Success rates for women under the age of 34 are between 30 and 40 percent, with rates dropping after age 35. Older women who choose to use IVF often use donor eggs, which increases their chances of becoming pregnant despite their own age.
Medical uses of IVF
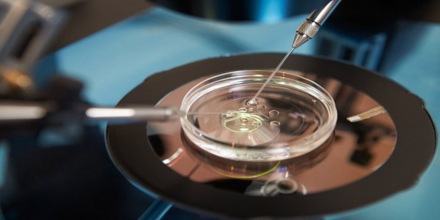
IVF may be used to overcome female infertility where it is due to problems with the fallopian tubes, making fertilisation in vivo difficult. It can also assist in male infertility, in those cases where there is a defect in sperm quality; in such situations intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be used, where a sperm cell is injected directly into the egg cell. This is used when sperm has difficulty penetrating the egg, and in these cases the partner’s or a donor’s sperm may be used. ICSI is also used when sperm numbers are very low. When indicated, the use of ICSI has been found to increase the success rates of IVF. IVF is also considered suitable in cases where any of its expansions is of interest, that is, a procedure that is usually not necessary for the IVF procedure itself, but would be virtually impossible or technically difficult to perform without concomitantly performing methods of IVF. Such expansions include preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) to rule out presence of genetic disorders, as well as egg donation or surrogacy where the woman providing the egg isn’t the same who will carry the pregnancy to term.
Advantages and Disadvantages of In Vitro Fertilization
Advantages
IVF helps patients who would be otherwise unable to conceive. The ultimate advantage of IVF is achieving a successful pregnancy and a healthy baby. IVF can make this a reality for people who would be unable to have a baby otherwise:
Blocked tubes: For women with blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, IVF provides the best opportunity of having a child using their own eggs.
Older patients/ patients with a low ovarian reserve: IVF can be used to maximise the chance of older patients conceiving. At CREATE, we have great expertise with older women and those with low ovarian reserve. We use Natural and Mild IVF to focus on quality of eggs, rather than quantity.
Male infertility: Couples with a male infertility problem will have a much higher chance of conceiving with IVF than conceiving naturally. We have a number of laboratory techniques to facilitate this including intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). We also liaise with an experienced urologist, Mr Vinod Nargund.
Unexplained infertility: 1 in 6 couples will suffer infertility problems and sometimes these remain undiagnosed after investigation. These patients may benefit from intervention.
PCOS: Polycystic ovary syndrome is common condition in which there is a hormone imbalance leading to irregular menstrual cycles. IVF has proved very successful in patients with PCOS, who will not respond appropriately to fertility medication in isolation.
Endometriosis: Patients with endometriosis, where parts of the womb lining grow outside the womb, may like to try IVF, as it has proved successful in this group.
Premature ovarian failure: Women with premature ovarian failure or menopause can have IVF treatment using donor eggs, which typically has high success rates.
Disadvantages
An IVF cycle may be unsuccessful. The success of IVF is not guaranteed, and patients often have to undergo more than one cycle of treatment before they are successful. Currently just over 25% of all IVF cycles result in a live birth. This naturally varies woman to woman, and a fertility specialist will be able to give a more accurate and personalised likelihood of success. It is important to be realistic but positive about the chances of success.
There may be associated side effects. As a medical treatment, IVF comes with a small chance of developing side effects, the most severe of these being severe ovarian hyper-stimulation syndrome (OHSS). Fortunately, the use of fewer or no drugs in natural and mild IVF cycles means that the already small likelihood of developing unwanted side effects is dramatically decreased or eliminated. CREATE Fertility takes the possibility of side effects very seriously, and as a result of our carefully constructed treatment protocols has never had a patient admitted to hospital with severe OHSS.
Multiple pregnancy. In IVF treatments, there is often more than one embryo put back into the uterus, and this leads to a higher likelihood of multiple pregnancy; around 20-30% of IVF pregnancies are multiple pregnancies. Multiple pregnancies do carry associated health risks to mother and baby: there is an increased chance of premature labour, miscarriage, need for caesarean, stillbirth and infant health problems with multiple pregnancies. It is important for all fertility clinics to have robust single embryo transfer policies, to avoid the risks of multiple pregnancy. At CREATE, we have a low multiple birth rate and focus on the reduction of multiple births.