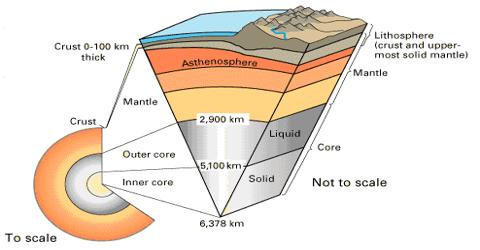
The Internal Structure of the Earth is layered in spherical shells, like an onion. These layers can be defined by either theirchemical or their rheological properties. Earth has an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous mantle, a liquid outer core that is much less viscous than the mantle, and a solid inner core. Scientific understanding of Earth’s internal structure is based on observations of topography and bathymetry, observations of rock in outcrop, samples brought to the surface from greater depths by volcanic activity, measurements of the gravity field of Earth, and experiments with crystalline solids at pressures and temperatures characteristic of Earth’s deep interior.
Earth’s Internal Structure